Abstract
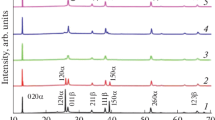
Molybdenum trioxide (MoO3) was evaporated from a tungsten resistive source in presence of hydrogen as carrier gas at pressures from 100 Pa to 600 Pa. Crystalline samples of molybdenum oxide were obtained at source temperatures below 950 °C. However, at source temperatures above 1000 °C, nanoporous structures were obtained, with porosity in the range of 10–85 nm. As shown by X-ray diffraction as well as selected area electron diffraction (SAED), the nanoporous material was amorphous. Under transmission electron microscopy (TEM) examination, and due to the electron beam, progressive formation of crystalline clusters was observed, as revealed by sequential changes of SAED and dark field images and corroborated in the high resolution TEM images (HRTEM). The growth of crystalline clusters at the nanometer scale occurs without destruction of the nanoporous structures.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kresge CT, Leonowicz ME, Roth WJ, Vartuli JC, Beck JS (1992) Nature (London) 359:710
Hussain Z (2001) J Mater Res 16:2695
Ferroni M, Guidi V, Martinelli G, Sacerdotti M, Nelli P, Sberveglieri G (1998) Sens Actuators B 48:285
Zeng HC (1998) Inorg Chem 37:1967
Wang S, Zhang Y, Wang W, Li G, Ma X, Li X, Zhang Z, Qian Y (2006) J Cryst Growth 290:96
Wang D, Su D, Schlögl R (2003) Cryst Res Technol 38(2):153 DOI 10.1002/crat. 200310018
Zach MP, Ng KH, Penner RM (2000) Science 290:2120
Margulis L, Salitra G, Tenne R, Talianker M (1993) Nature (London) 365:113
Hersfinkel M, Gheber LA, Volterra B, Hutchison JL, Margulis L, Tenne R (1994) J Am Chem Soc 116:1914
Feldman Y, Wasserman E, Srolouvitz DJ, Tenne R (1995) Science 267:222
Hagrman PJ, Hagrman D, Zubieta J (1999) Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 38:2638
Granqvist C, Buhrman R (1976) J Appl Phy 47(5):2200
Turker M (2004) Mater Sci Eng A 367:74
Acknowledgements
This work has been partially funded by the Chilean government under contract FONDECYT 1040954 and MECESUP contract UCH0205. D. E. D-D acknowledges a CONICYT fellowship. We acknowledge enlightening discussions with Dr. M. Pilleux.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Diaz-Droguett, D.E., Fuenzalida, V.M., Diaz-Espinoza, M.S. et al. Electron beam effects on amorphous molybdenum oxide nanostructures grown by condensation in hydrogen. J Mater Sci 43, 591–596 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-007-1602-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-007-1602-1