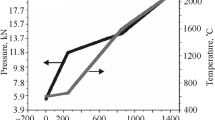
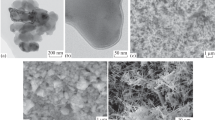
Abstract
Spark plasma sintering (SPS) is a newly developed technique that enables poorly sinterable aluminum nitride (AlN) powder to be fully densified. It is addressed that pure AlN sintered by SPS has relatively low thermal conductivity. In this work, SPS of AlN ceramic was carried out with Y2O3, Sm2O3 and Li2O as sintering aids. Effects of additives on AlN densification, microstructure and properties were investigated. Addition of sintering aids accelerated the densification, lowered AlN sintering temperature and was advantageous to improve properties of AlN ceramic. Thermal conductivity and strength were found to be greatly improved with the present of Sm2O3 as sintering additive, with a thermal conductivity value about 131 Wm−1K−1 and bending strength about 330 MPa for the 2 wt% Sm2O3-doped AlN sample SPS at 1,780 °C for 5 min. XRD measurement revealed that additives had no obvious effect on the AlN lattice parameters. Observation by SEM showed that AlN ceramics prepared by SPS method manifested quite homogeneous microstructure. However, AlN grain sizes and shapes, location of secondary phases varied with the additives. The thermal conductivity of AlN ceramics was mainly affected by the additives through their effects on the growth of AlN grain and the location of liquid phases.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhou HP, Yao YC, Wu Y (1998) J Chin Ceram Soc 26(4):517
Risbud SH, Shan CH (1995) Mater Sci Eng A204:146
Groza JR, Zavaliangos A (2000) Mater Sci Eng A287:171
Omori M (2000) Mater Sci Eng A287:183
Zhang DM (2002) In: Study on mechanism of pulse electric current sintering of ceramic materials. Dissertation For Doctor’s Degree, Wuhan University of Technology
Qiao L, Zhou HP, Li CW (2003) Mater Sci Eng B99:102
Khor KA, Cheng KH, Yu LG et al (2003) Mater Sci Eng A347:300
Khor KA, Yu LG, Murakoshi Y (2005) J Euro Ceram Soc 25:1057
Jarrige J, Lecompte JP, Mullot J et al (1997) J Euro Ceram Soc 17:1891
Tu YD, Hundere AM, Hoier R et al (2002) J Euro Ceram Soc 22:247
Terao R, Tatami J, Meguro T et al (2002) J Euro Ceram Soc 22:1051
Du S, Liu Z, Li LT et al (1995) Mater Lett 25:105
Qiao L, Zhou HP, Chen KX et al (2003) J Euro Ceram Soc 23:1517
Slack GA (1973) J Phys Chem Solids 34:321
Harris JH, Yongman RA, Teller RG (1990) J Mater Res 5(8):1763
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (50232020).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, M.J., Zhang, L.M., Shen, Q. et al. Microstructure and properties of spark plasma sintered AlN ceramics. J Mater Sci 41, 7934–7938 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-006-0862-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-006-0862-5