Abstract
The electrophoretic depositional (EPD) behavior of yttria-stabilized zirconia (YSZ) powder with 8 mol% Y2O3, which is a common material for oxygen sensors as a solid electrolyte, was investigated on stainless steel and carbon based substrates. Ethanol + HNO3 based suspensions were used for the EPD experiments, and three different YSZ powders, one commercially available powder and two own-made coprecipitated powders, were deposited. The latter powders were calcined at 900 and 1200 °C, respectively. The concentration of the suspension was 3 g/300 cm3 and a small amount of HNO3 solution was added as a dispersant. A DC electric field of 100–200 V/15 mm was applied between parallel electrodes. On stainless steel electrodes it was found that the own-made coprecipitated powder calcined at 1200 °C, showing the best deposition properties, whereas the commercial YSZ powder showed the best depositional properties on carbon electrodes. These characteristic depositional behaviors are discussed with regard to the adhesive force between the particles and the different electrodes, and some powder properties, e.g., particle size distribution and packing behavior.
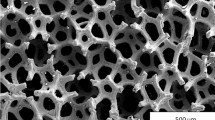
A thick, continuous, free-standing YSZ film with a thickness of around 10 μm was successfully obtained after firing the deposit on the carbon electrode in flowing air.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hayashi S, Nakagawa Z (2004) J Ceram Soc Japan, Suppl 112:S1135
Suzuki S, Yamada T, Hayakawa N, Oshima T (2005) Bull Ceram Soc Japan 40:742 (in Japanese)
Hayashi S, Aoki T, Nakagawa Z (2005) J Ceram Soc Japan 113:513
Zhitomirsky I, Petric A (2004) J Mater Sci 39:825
Negishi H, Yamaji K, Sakai N, Horita T, Yanagishita H, Yokokawa H (2004) J Mater Sci 39:833
Tadanaga K, Takahashi K, Tatsumisago M, Matsuda A (2006) Key Eng Mater 314:159
Fariñas JC, Moreno R, Requena J, Moya JS (1989) Mater Sci Eng A 109:97
Acknowledgments
Authors are grateful to Dr. Fumiaki Yokoyama of Toyo Tanso Co., Ltd. Japan for supplying specially machined carbon electrodes, to Dr. Yasushi Sugawara of Akita Prefectural Industrial Technology Center for using a SEM (S-4500), and to Dr. Hideki Murakami of Faculty of Engineering and Resource Science, Akita University for using a BET equipment.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hayashi, S., Sato, C. & Nakagawa, Ze. Effect of different electrode materials on electrophoretic depositional behavior of yttria-stabilized zirconia powder. J Mater Sci 41, 8068–8073 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-006-0620-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-006-0620-8