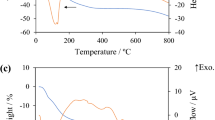
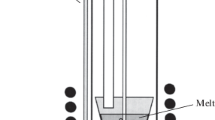
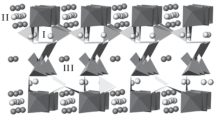
Abstract
Submicrometer dispersions of rod-like alkali metal titanates were prepared by the flux method, from the reaction of TiOSO4 or TiO2 precursors in molten alkali metal nitrates, doped with carbonates or hydroxides. Mono-, di-, tetra-, and hexatitanates are formed as a function of the precursor nature and the melt composition. As a rule, in these syntheses poorly crystalline or amorphous solids are obtained, showing the structure of polytitanates on the nanoscopic level. Lamellar potassium hexatitanate can be exchanged by action of a diluted acid, leading to protonic form, free from the alkali metal but retaining initial morphology. Reactivity of TiOSO4 and TiO2 in molten alkali metal nitrates and their mixtures with the corresponding carbonates was studied by mass spectrometry of the gases evolved during heating of the reaction mixtures. For both pure and doped nitrates it changes in the expected row Li>Na>K, following the melts oxobasicity sequence.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
B. TREMILLON, La Chimie en Solvants non Aqueux, Presses Universitaires de France, Paris, 1971.
P. AFANASIEV and C. GEANTET, Coord. Chem. Rev. 178–180 (1998) 1725.
M. DESCEMOND, C. BRODHAG, F. THEVENOT, B. DURAND, M. JEBROUNI and M. ROUBIN, J. Mater. Sci. 28 (1993) 2283.
Y. DU and D. INMAN, J. Mater. Chem. 5 (1995) 1927.
P. AFANASIEV, C. GEANTET, M. LACROIX and M. BREYSSE, J. Catal. 162 (1996) 143.
P. AFANASIEV, Chem. Mater. 11 (1999) 1999.
M. TIRUMAL, P. JANE and A. K. GANGULI, Mater. Chem. Phys. 70 (2001) 7.
P. AFANASIEV, Synthesis of Microcrystalline LiNbO3 in Molten Nitrate, Mater. Lett. 34 (1998) 253.
A. ABOUJALIL, J.-P. DELUOME, F. CHASSAGNEUX, J.-P. SCHARFF and B. DURAND, J. Mater. Chem. 8 (1998) 160.
J.-P. DELOUME, J.-P. SCHARFF, P. MAROTE, B. DURAND and A. ABOU-JALIL, J. Mater. Chem. 9 (1999) 107.
A. V. GOROKHOVSKY, J. I. ESCALANTE-GARCIA, T. SANCHES-MONJARAS and G. VARGAS-GUTIERREZ.
M. H. WENG, T. J. LIANG and C. L. HUANG, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 22 (2002) 1693.
S. J. KIM, M. H. CHO, D.-S. LIM and H. JANG, Wear 251 (2001) 1484.
A. R. ARMSTRONG, G. ARMSTRONG, G. CANALES and P. G. BRUCE, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 43 (2004) 2286.
B. L. WANG, Q. CHEN, R. H. WANG and L.-M. PENG, Chem. Phys. Lett. 376 (2003) 726.
G. H. DU, Q. CHEN, P. D. HAN, Y. YU and L.-M. PENG, Phys. Rev. B 67 (2003) 035323.
P. AFANASIEV, D. H. KERRIDGE, J. Alloys Comp. 322 (2001) 97.
X. WANG, L. GAO, F. ZHOU, Z. ZHANG, M. JI, C. TANG, T. SHEN and H. ZHENG, J. Cryst Growth 265 (2004) 220.
P. AFANASIEV, J. Alloys Comp. 340(1–2) (2002) 74
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Afanasiev, P. Molten salt syntheses of alkali metal titanates. J Mater Sci 41, 1187–1195 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-005-3656-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-005-3656-2