Abstract
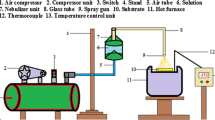
The effect of Sn concentration on zinc oxide (ZnO) film properties has been investigated by depositing films with various Sn concentrations in the solution (Sn/Sn + Zn ratio from 0 to 50 at%) at a substrate temperature of 350°C by ultrasonic spray pyrolysis (USP) technique. The deposited films were characterized for their electrical, structural, morphological and elemental properties using current-voltage and conductivity-temperature measurements, X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy and energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy. Electrical investigations showed that the resistivity of ZnO films decreases for lower Sn concentration (at 10%) and then increases for higher Sn concentration (at 30–50%). Also, depending on the increasing Sn concentration, energies of donor-like traps for ZnO films decreased and activation energy of donors for ZnO films increased. The XRD patterns showed that the as-deposited films have polycrystalline structure and the crystalline nature of the films was deteriorated with increasing Sn concentration and a shift to amorphous structure was seen. The effect of Sn concentration was to increase the surface roughening and change considerably the morphologies of ZnO films. The most homogenous surface was seen in ZnO films. EDS results showed that all elements in the starting solutions were in the solid films and Zn element is more dominant than Sn on the surfaces. After all investigations, it was determined that Sn incorporation dramatically modifies the properties of ZnO films. ZnO and ZnO:Sn (10 at%) films have a low resistivity and high transparency in the visible range and may be used as window material and antireflecting coating in solar cells while the other films may be used in gas sensors where high conductivity is unnecessary.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. ORTEGA, G. SANTANA and A. MORALES-ACEVEDO, Superficies y Vacio 9, 294.
W. T. SEEBER, M. O. ABOU-HELAL, S. BARTH, D. BEIL, T. HÖCHE, H. H. AFIFY and S. E. DEMIAN, Materi. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2 (1999) 45.
P. NUNES, E. FORTUNATO and R. MARTINS, Thin solid Films 383 (2001) 277.
B. JOSEPH, K. G. GOPCHANDRAN, P. V. THOMAS, P. KOSHY and V. K. VAIDYAN, Mater. Chem. Phys. 58 (1999) 71.
F. PARAGUAY D., W. ESTRADA L., D. R. ACOSTA N., E. ANDRADE and M. MIKI-YOSHIDA, Thin Solid Films 350 (1999) 192.
F. M. AMANULLAH, K. J. PRATAP and V. HARI BABU, Mater. Sci. Engng. B 52 (1998) 93.
G. K. BHAUMIK, A. K. NATH and S. BASU, ibid. 52 (1998) 25.
K. B. SUNDARAM and A. KHAN, Thin Solid Films 295 (1997) 87.
YUNG-JEN LIN and CHING-JIUNN WU,Surf. Coat. Techn. 88 (1996) 239.
B. J. LOKHANDE and M. D. UPLANE, Appl. Surf. Sci. 167 (2000) 243.
D. R. ACOSTA, E. P. ZIRONI, E. MONTOYA and W. ESTRADA, Thin Solid Films 288 (1996) 1.
T. SCHULER and M. A. AEGERTER, ibid. 351 (1999) 125.
K. T. RAMAKRISHNA REDDY, H. GOPALASWAMY, P. J. REDDY and R. W. MILES, J. Cryst. Growth 210 (2000) 516.
S. SHANTHI, C. SUBRAMANIAN and P. RAMASAMY, Mater. Sci. Engng. B 57 (1999) 127.
B. Thangaraju, Thin Solid Films 402 (2002) 71.
A. K. IVANOV-SCHITZ, A. V. NISTUK and N. G. CHABAN, Solid State Ion. 139 (2001) 153.
I. TANIGUCHI, D. SONG and M. WAKIHARA, J. Power Sourc. 109 (2002) 333.
F. ATAY, S. KOSE, V. BILGIN and I. AKYUZ, Mater. Lett. 57 (2003) 3461.
F. ATAY, S. KOSE, V. BILGIN and I. AKYUZ, Balkan Phys. Lett. 10(2) (2002) 70.
V. BILGIN, PhD Thesis, Osmangazi University, Turkey, 2003, p. 165.
F. ATAY, V. BILGIN, I. AKYUZ and S. KOSE, Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 6 (2003) 197.
M. A. LAMPERT and P. MARK, “Current Injection in Solids.” (Academic Press, USA, 1970) p. 347.
K. C. KAO and W. HWANG, “Electrical Transport in Solids, International Series in the Science of the Solid State” (Pergamon Press, 1979) p. 663.
J. MA, F. JI, H. L. MA and S. Y. LI, Solar Energy Materials Solar Cells, 60 (2000) 341.
Y. IGASAKI and H. KANMA, Appl. Surf. Sci. 169/170 (2001) 508.
H. KIM, A. PIQUE, J. S. HORWITZ, H. MURATA, Z. H. KAFAFI, C. M. GILMORE and D. B. CHRISEY, Thin Solid Films 377–378 (2000) 798.
T. K. SUBRAMANYAM, B. SRINIVASULU NAIDU and S. UTHANNA, Optical Mater. 13 (1999) 239.
A. S. RIAD, S. A. MAHMOUD and A. A. IBRAHIM, Physica. B 296 (2001) 319.
B. D. CULLITY, “The Elements of X-Ray Diffraction” 2nd ed. (Addison-Wesley, Reading, MA, 1978).
C. BARRETTA and T. B. MASSALASKI, “Structure of Metals” (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1966) p. 205.
S. A. NASSER, H. H. AFIFY, S. A. EL-HAKIM and M. K. ZAYED, Thin Solid Films 315 (1998) 327.
H. H. HUANG and M. H. HON, J. Cryst. Growth 222 (2001) 540.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bilgin, V., Kose, S., Atay, F. et al. The effect of Sn concentration on some physical properties of zinc oxide films prepared by ultrasonic spray pyrolysis. J Mater Sci 40, 1909–1915 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-005-1210-x
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-005-1210-x