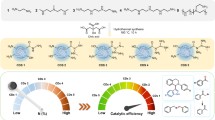
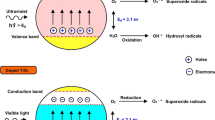
Abstract
This work aims to study the production of hydrogen peroxide gas (H2O2) through photocatalysis. It consists of two main parts. In the first part, we explore the optimal conditions for synthesizing H2O2 gas from humidity using a gas system photoreactor. Through experimentation, we discovered that the fabricated photoreactor, equipped with three series of coated photocatalyst-supporting plates, can synthesize H2O2 gas up to 3 ppmv. The photoreactor incorporates key components, including a photocatalyst material, UV light source, ventilation fan, and air filter. The identified optimal conditions included a relative humidity of 60‒65% RH and an air flow rate of 12.0 m/s. The TiO2/1%SiO2 photocatalyst, composed of SiO2 particles smaller than 63 μm, yielded the most favorable results. The second part focused on studying the role of SiO2 in TiO2/SiO2. We observed that modifying the TiO2 morphology with SiO2 created a pore structure on the surface. This structural modification leads to the formation of Ti‒O‒Si bonds, which facilitate electron and hole trapping on the photocatalyst surface. Furthermore, the presence of hydroxyl groups on the surface enhanced the attraction of reactant molecules. XRD results reveal a mixed-phase structure of TiO2 (anatase‒rutile)/SiO2 amorphous, contributing to improved electron and hole pathways within the photocatalyst.
Graphical abstract











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baik, K.Y., Jo, H., Ki, S.H., Kwon, G.C., Cho, G.: Synergistic effect of hydrogen peroxide and cold atmospheric pressure plasma-jet for microbial disinfection. Appl. Sci. 13, 3324 (2023). https://doi.org/10.3390/app13053324
Finnegan, M., Linley, E., Denyer, S.P., McDonnell, G., Simons, C., Maillard, J.Y.: Mode of action of hydrogen peroxide and other oxidizing agents: differences between liquid and gas forms. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 65, 2108–2115 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/dkq308
McDonell, G.: The use of hydrogen peroxide for disinfection and sterilization applications. Chem. Funct. Groups (2014). https://doi.org/10.1002/9780470682531.pat0885
Hou, H., Zeng, X., Zhang, X.: Production of hydrogen peroxide through photocatalytic processes: a critical review of recent. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 59, 17356–17376 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201911609
Burek, B.O., Bahnemann, D.W., Bloh, J.Z.: Modeling and optimization of the photocatalytic reduction of molecular oxygen to hydrogen peroxide over titanium dioxide. ACS Catal. 9, 25–37 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.8b03638
Wang, L., Cao, S., Guo, K., Wu, Z., Ma, Z., Piao, L.: Simultaneous hydrogen and peroxide production by photocatalytic water splitting. Chin. J. Catal. 40, 470–475 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1872-2067(19)63274-2
Sukkasem, T., Nuchitprasittichai, A., Janphuang, P., Junpirom, S.: TiO2/SiO2 coated 310S stainless steel for hydrogen peroxide generation via photocatalytic reaction. Curr. Appli Sci. Tech. 22, 3 (2022). https://doi.org/10.55003/cast.2022.03.22.001
Wang, L., Zhang, J., Zhang, Y., Yu, H., Qu, Y., Yu, J.: Inorganic metal-oxide photocatalyst for H2O2 production. Small 18, 2104561 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.202104561
He, B., Luo, C., Wang, Z., Zhang, L., Yu, J.: Synergistic enhancement of solar H2O2 and HCOOH production over TiO2 by dual co-catalyst loading in a tri-phase system. Appl. Cat B: Envi 323, 122200 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2022.122200
Nabih, S., Shalan, A.E., Serea, E.S.A., Goda, M.A., Sanad, M.F.: Photocatalytic performance of TiO2@SiO2 nanocomposites for the treatment of different organic dyes. J. Mat. Sci. Mater. Electron. 30, 9623–9633 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-01296-y
Bellardita, M., Addamo, M., Paola, A.D., Marci, G., Palmisano, L., Cassar, L., Borsa, M.: Photocatalytic activity of TiO2/SiO2 systems. J. Hazard. Mater. 174, 707–713 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.09.108
Klondon, R.: Removal of air pollutants by photocatalytic process using TiO2/SiO2 coated Dan Kwian pottery. SUTIR 48–49. (2013). http://sutir.sut.ac.th:8080/jspui/handle/123456789/4751
Joseph, C.G., Taufiq-Yap, Y.H., Musta, B., Sarjadi, M.S., Elilarasi, L.: Application of plasmonic metal nanoparticles in TiO2–SiO2 composite as an efficient solar-activated photocatalyst: a review paper. Front. Chem. 8, 568063 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2020.568063
Panayotov, D., Yates, J.T.: Bifunctional hydrogen bonding of 2-chloroethyl ethyl sulfide on TiO2–SiO2 powders. J. Phys. Chem. B 107, 38 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1021/jp0304273
Balachandran, K., Venckatesh, R., Sivaraj, R., Rajiv, P.: TiO2 nanoparticles versus TiO2–SiO2 nanocomposites: a comparative study of photo catalysis on acid red 88. Spectrochim. Acta Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 128, 468–474 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2014.02.127
Kibombo, H.S., Peng, R., Rasalingam, S., Koodali, R.T.: Versatility of heterogeneous photocatalysis: synthetic methodologies epitomizing the role of silica support in TiO2 based mixed oxides. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2, 1737–1766 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1039/C2CY20247F
Okada, K., Yamamoto, N., Kameshima, Y., Yasumori, A., Kenneth, J.D.M.: Effect of silica additive on the anatase-to-rutile phase transition. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 84, 1591–1596 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1151-2916.2001.tb00882.x
Ji, H., Du, P., Zhao, D., Li, S., Sun, F., Duin, E.C., Liu, W.: 2D/1D graphitic carbon nitride/titanate nanotubes heterostructure for efficient photocatalysis of sulfamethazine under solar light: catalytic hot spots at the rutile–anatase–titanate interfaces. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 263, 118357 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.118357
Hurum, D.C., Agrios, A.G., Gray, K.A.: Explaining the enhanced photocatalytic activity of degussa P25 mixed-phase TiO2 using EPR. J. Phys. Chem. B 107, 4545–4549 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1021/jp0273934
Liu, X., Ji, H., Li, S., Liu, W.: Graphene modified anatase/titanate nanosheets with enhanced photocatalytic activity for efficient degradation of sulfamethazine under simulated solar light. Chemosphere. 233, 198–206 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.05.229
Ji, H., Liu, W., Sun, F., Huang, T., Chen, L., Liu, Y., Qi, J., Xie, C., Zhao, D.: Experimental evidences and theoretical calculations on phenanthrene degradation in a solar-light-driven photocatalysis system using silica aerogel supported TiO2 nanoparticles: insights into reactive sites and energy evolution. Chem. Eng. J. 419, 129605 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.129605
Panarelli, E.G., Livraghi, S., Maurelli, S., Polliotto, V., Chiesa, M., Giamello, E.: Role of surface water molecules in stabilizing trapped hole centres in titanium dioxide (anatase) as monitored by electron paramagnetic resonance. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A: Chem. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2016.02.015
Schneider, J., Matsuoka, M., Takeuchi, M., Zhang, J., Horiuchi, Y., Anpo, M., Bahnemann, D.W.: Understanding TiO2 photocatalysis: mechanisms and materials. Chem. Rev. 114, 9919–9986 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1021/cr5001892
Masolo, E., Senes, N., Pellicer, E., Baró, M.D., Enzo, S., Pilo, M.I., Mulas, G., Garroni, S.: Evaluation of the anatase/rutile phase composition influence on the photocatalytic performances of mesoporous TiO2 powders. Int. J. Hydro Ener. 40(42), 14483–14491 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2015.05.180
Xu, F., Xiao, W., Cheng, B., Yu, J.: Direct Z-scheme anatase/rutile bi-phase nanocomposite TiO2 nanofiber photocatalyst with enhanced photocatalytic H2-production activity. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 39(28), 15394–15402 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2014.07.166
Luo, Z., Poyraz, A.S., Kuo, C.H., Miao, R., Meng, Y., Chen, S.Y., Jiang, T., Wenos, C., Suib, S.L.: Crystalline mixed phase (anatase/rutile) mesoporous titanium dioxides for visible light photocatalytic activity. Chem. Mater. 27(1), 6–17 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1021/cm5035112
Yaemsunthorn, K., Kobielusz, M., Macyk, W.: TiO2 with tunable anatase-to-rutile nanoparticles ratios: how does the photoactivity depend on the phase composition and the nature of photocatalytic reaction? ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 4(1), 633–643 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsanm.0c02932
Li, Y., Zhang, Y., Zhang, C., Deng, L., Li, S., Zhuang, C.: Self-healing of oxygen vacancies and phase transition-induced built-in electric field regulate H2 and H2O2 production. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 655, 12–22 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2023.10.090
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by Technopolis, Suranaree University of Technology. The authors also gratefully acknowledge the support provided by the Synchrotron Light Research Institute (SLRI) and the Center of Excellence in Biomechanics Medicine.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
TS; writing—original draft, visualization, conceptualization, data curation, formal analysis, methodology. NP; experimental section, formal analysis. PK; experimental section, formal analysis. SP; experimental section, formal analysis. AN; writing—review and editing. SJ; writing—review and editing, project administration. PJ; resources, methodology.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sukkasem, T., Nuchitprasittichai, A., Junpirom, S. et al. Role of SiO2 in TiO2/SiO2 photocatalyst for hydrogen peroxide gas generation from air humidity via photocatalysis. J Incl Phenom Macrocycl Chem (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-023-01211-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-023-01211-3