Abstract
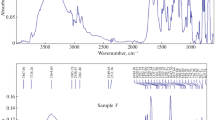
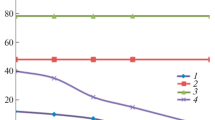
The effect of the macrocycle size on the gel-to-sol evolution of cyclodextrin-based hydrogel is here investigated by using Fourier transform infrared absorption in attenuated total reflectance geometry (FTIR-ATR). Different types of nanosponges obtained by polymerization of α- and β-cyclodextrin (CDNS) with an activated derivative of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid have been progressively hydrated in order to follow the evolution of these systems from a gel state to a liquid suspension. The in deep analysis of the high-frequency vibrational dynamics of the hydrogel during its gel-sol evolution revealed that the microscopic origin of this phenomenon is strictly connected to different hydrogen bond environments in which water molecules confined in the pores of nanosponges can arrange. By following a well consolidated approach, the OH stretching band of water, clearly observed in the high-frequency range of the vibrational spectra of nanosponges hydrogel, has been decomposed into sub-bands assigned to different arrangements of water molecules at various degrees of cooperativity. A comparison of the diagrams obtained for homologous CDNS prepared from α- and β-CD shows how the size of cyclodextrin macrocycle allows to efficiently modulate the gelation points at constant cyclodextrin/crosslinker molar ratio n.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hoare, T.R., Kohane, D.S.: Hydrogels in drug delivery: progress and challenges. Polymer 49, 1993–2007 (2008)
Lin, C.C., Metters, A.T.: Hydrogels in controlled release formulations: network design and mathematical modeling. Adv. Drug Delivery Rev. 58, 1379–1408 (2006)
Slaughter, B.V., Khurshid, S.S., Fisher, O.Z., Khademhosseini, A., Peppas, N.A.: Hydrogels in regenerative medicine. Adv. Mater. 21, 3307–3329 (2009)
Baumann, M.D., Kang, C.E., Stanwick, J.C., Wang, Y.F., Kim, H., Lapitsky, Y., Shoichet, M.S.: An injectable drug delivery platform for sustained combination therapy. J. Controlled Release 138, 205–213 (2009)
Kim, Y.T., Caldwell, J.M., Bellamkonda, R.V.: Nanoparticle-mediated local delivery of methylprednisolone after spinal cord injury. Biomaterials 30, 2582–2590 (2009)
Baumann, M.D., Kang, C.E., Tator, C.H., Shoichet, M.S.: Intrathecal delivery of a polymeric nanocomposite hydrogel after spinal cord injury. Biomaterials 31, 7631–7639 (2010)
Santoro, M., Marchetti, P., Rossi, F., Perale, G., Castiglione, F., Mele, A., Masi, M.: Smart approach to evaluate drug diffusivity in injectable agar-Carbomer hydrogels for drug delivery. J. Phys. Chem. B 115, 2503–2510 (2011)
Rossi, F., Casalini, T., Santoro, M., Mele, A., Perale, G.: Methylprednisolone release from agar-Carbomer-based hydrogel: a promising tool for local drug delivery. Chem. Pap. 65, 903–908 (2011)
Gagnon, M.A., Lafleur, M.: Self-diffusion and mutual diffusion of small molecules in high-set curdlan hydrogels studied by 31P NMR. J. Phys. Chem. B 113, 9084–9091 (2009)
Brandl, F., Kastner, F., Gschwind, R.M., Blunk, T., Tessmar, J., Gopferich, A.: Hydrogel-based drug delivery systems: comparison of drug diffusivity and release kinetics. J. Controlled Release 142, 221–228 (2010)
Lin, C.C., Boyer, P.D., Aimetti, A.A., Anseth, K.S.: Regulating MCP-1 diffusion in affinity hydrogels for enhancing immuno-isolation. J. Control Release 142, 384–391 (2010)
Biondi, M., Ungaro, F., Quaglia, F., Netti, P.A.: Controlled drug delivery in tissue engineering. Adv. Drug Delivery Rev. 60, 229–242 (2008)
Peppas, N.A., Hilt, J.Z., Khademhosseini, A., Langer, R.: Hydrogels in biology and medicine: from molecular principles to bionanotechnology. Adv. Mater. 18, 1345–1360 (2006)
Elisseeff, J., McIntosh, W., Anseth, K., Riley, S., Ragan, P., Langer, R.: Photoencapsulation of chondrocytes in poly(ethylene oxide)-based semi-interpenetrating networks. Biomed. Mater. Res. 51, 164–171 (2000)
Rossi, F., Perale, G., Masi, M.: Biological buffered saline solution as solvent in agar-Carbomer hydrogel synthesis. Chem. Pap. 64, 573–578 (2010)
Mele, A., Castiglione, F., Malpezzi, L., Ganazzoli, F., Raffaini, G., Trotta, F., Rossi, B., Fontana, A.: HR MAS NMR, powder XRD and Raman spectroscopy study of inclusion phenomena in & β-CD nanosponges. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 69, 403–409 (2011)
Castiglione, F., Crupi, V., Majolino, D., Mele, A., Rossi, B., Trotta, F., Venuti, V.: Inside new materials: an experimental numerical approach for the structural elucidation of nanoporous cross-linked polymers. J. Phys. Chem. B 116, 13133–13140 (2012)
Rossi, B., Caponi, S., Castiglione, F., Corezzi, S., Fontana, A., Giarola, M., Mariotto, G., Mele, A., Petrillo, C., Trotta, F., Viliani, G.: Networking properties of cross-linked polymeric systems probed by inelastic light scattering experiments. J. Phys. Chem. B 116, 5323–5327 (2012)
Castiglione, F., Crupi, V., Majolino, D., Mele, A., Panzeri, W., Rossi, B., Trotta, F., Venuti, V.: Vibrational dynamics and hydrogen bond properties of beta-CD nanosponges: an FTIR-ATR, Raman and solid-state NMR spectroscopic study. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 75, 247–254 (2013)
Castiglione, F., Crupi, V., Majolino, D., Mele, A., Rossi, B., Trotta, F., Venuti, V.: Effect of cross-linking properties on the vibrational dynamics of cyclodextrin-based polymers: an experimental-numerical study. J. Phys. Chem. B 116, 7952–7958 (2012)
Crupi, V., Fontana, A., Giarola, M., Majolino, D., Mariotto, G., Mele, A., Melone, L., Punta, C., Rossi, B., Trotta, F., Venuti, V.: Connection between the vibrational dynamics and the cross-linking properties in cyclodextrins-based polymers. J. Raman Spectrosc. 44, 1457–1462 (2013)
Castiglione, F., Crupi, V., Majolino, D., Mele, A., Rossi, B., Trotta, F., Venuti, V.: Vibrational spectroscopy investigation of swelling phenomena in cyclodextrin nanosponges. J. Raman Spectrosc. 44, 1463–1469 (2013)
Crupi, V., Majolino, D., Mele, A., Rossi, B., Trotta, F., Venuti, V.: Modelling the interplay between covalent and physical interactions in cyclodextrin-based hydrogel: effect of water confinement. Soft Matter 9, 6457–6464 (2013)
Crupi, V., Majolino, D., Mele, A., Melone, L., Punta, C., Rossi, B., Toraldo, F., Trotta, F., Venuti, V.: Direct evidence of gel-sol evolution in cyclodextrin-based hydrogel as revealed by FTIR-ATR spectroscopy. Soft Matter (2014). doi:10.1039/C3SM52354C
Trotta, F. Tumiatti, W. 2003 Cross-linked polymers based on cyclodextrin for removing polluting agents; Patent WO 03/085002
Trotta, F., Tumiatti, W., Cavalli, R., Zerbinati, O., Roggero, C.M., Vallero, R. 2006 Ultrasound-assisted synthesis of cyclodextrin-based nanosponges; Patent number WO 06/002814
Trotta, F., Tumiatti, W., Cavalli, R., Roggero, C., Mognetti, B., Berta, G. 2009 Cyclodextrin-based nanosponges as a vehicle for antitumoral drugs; Patent number WO 09/003656 A1
Crupi, V., Longo, F., Majolino, D., Venuti, V.: Vibrational properties of water molecules adsorbed in different zeolitic frameworks. J. Phys. Condens. Matt. 18, 3563–3580 (2006)
Crupi, V., Majolino, D., Migliardo, P., Venuti, V.: Diffusive relaxations and vibrational properties of water and H-bonded systems in confined state by neutrons and light scattering: state of the art. J. Phys. Chem. B 104, 11000–11012 (2000)
Crupi, V., Majolino, D., Migliardo, P., Venuti, V.: Wanderlingh: a FT-IR absorption analysis of vibrational properties of water encaged in NaA zeolites: evidence of a “structure maker” role of zeolitic surface. Eur. Phys. J. E 12, S55–S58 (2003)
Crupi, V., Interdonato, S., Longo, F., Majolino, D., Migliardo, P., Venuti, V.: New insight on the hydrogen bonding structures of nanoconfined water: a Raman study. J. Raman Spectrosc. 39, 244–249 (2008)
Crupi, V., Longo, F., Majolino, D., Venuti, V.: Raman spectroscopy: probing dynamics of water molecules confined in nanoporous silica glasses. Eur. Phys. J. Special Topics 141, 61–64 (2007)
Crupi, V., Majolino, D., Migliardo, P., Venuti, V.: Inter- and intramolecular hydrogen bond in liquid polymers: a Foureir transform infrared response. Mol. Phys. 98, 1589–1594 (2000)
Crupi, V., Longo, F., Majolino, D., Venuti, V.: T dependence of vibrational dynamics of water in ion-exchanged zeolites A: a detailed Fourier transform infrared attenuated total reflection study. J. Chem. Phys. 123, 154702 (2005)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Castiglione, F., Crupi, V., Majolino, D. et al. Gel-sol evolution of cyclodextrin-based nanosponges: role of the macrocycle size. J Incl Phenom Macrocycl Chem 80, 77–83 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-014-0391-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-014-0391-9