Abstract
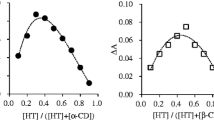
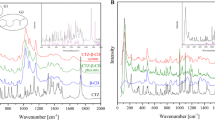
BHA (butylated hydroxyanisole) was complexed with α- and β-cyclodextrins with the objective of characterizing the thermal stability. From phase solubility diagrams, the association constants for the complexes of α-CD:BHA and β-CD:BHA were found as 49.3 and 585 L mol−1, respectively. To increase the thermal stability of BHA, its molecular encapsulation in α-CD and β-CD, was tested using molar ratios of 1:1 and 1:2 (BHA:CD) and the complex preparation techniques of kneading and physical mixture. The products of complexation were characterized by differential scanning calorimetry and thermogravimetry, indicating the formation of a BHA:β-CD complex and showing that the release of the complexed BHA occurs in the temperature range of 280–350 °C, well above the temperature at which BHA sublimates. Dissolution tests have shown that the BHA: β-CD complex produced by kneading has high efficiency of dissolution and partition coefficient experiments demonstrated that the presence of β-CD leads to higher concentration of BHA in the organic phase.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
National Toxicology Program, Eleventh Report on Carcinogens.: Butylated hydroxyanisole (BHA) CAS no. 25013-16-5. http://ntp.niehs.nih.gov/ntp/roc/eleventh/profiles/s027bha.pdf (2009). Accessed 27 Feb 2009
Williams, G.M., Iatropoulos, M.J., Whysner, J.: Safety assessment of butylated hydroxyanisole and butylated hydroxytoluene as antioxidant food additives. Food Chem. Toxicol. 37(9–10), 1027–1038 (1999)
Ramalho, V., Jorge, N.: Antioxidantes utilizados em óleos, gorduras e alimentos gordurosos. Quim. Nova 29(4), 755–760 (2006)
Szejtli, J., Szente, L.: Cyclodextrins as food ingredients. Food Sci. Technol. 15, 137–142 (2004)
Vora, J., Boroujerdi, M.: Enhanced aqueous solubility of phenolic antioxidants using modified β-cyclodextrins. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 21, 495–502 (1995)
Higuchi, T., Connors, K.A.: Phase Solubility Techniques (Advances in Analytical Chemistry and Instrumentation), pp. 117–212. Wiley Interscience, New York (1965)
Khan, K.A., Rhodes, C.T.: The concept of dissolution efficiency. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. Wallingford 27, 48–49 (1975)
Bekers, O., Uijtendaal, E.V., Beijnen, J.H., Bult, A., Underberg, W.J.M.: Cyclodextrins in the pharmaceutical field. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 17, 1503–1549 (1991)
Zia, V., Rajewski, R.A., Stella, V.J.: Effect of cyclodextrin charge on complexation of neutral and charged substrates: comparison of sulfobutyl ether-β-cyclodextrin to hydroxypropyl β-cyclodextrin. Pharm. Res. 18(5), 667–673 (2001)
Archontaki, H., Vertzoni, M., Athanassiou-Malaki, M.: Study on the inclusion complexes of bromazepam with β and β-hydroxypropyl-cyclodextrins. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 28, 761–769 (2002)
Yilmaz, V.T., Karadag, A., Içbudak, H.: Thermal decomposition of β-cyclodextrin inclusion complexes of ferrocene and their derivatives. Thermochim. Acta 261, 107–118 (1995)
Rama, A.C.R., Veiga, F., Figueiredo, I.V., Souza, A., Caramona, M.: Complexos de inclusão de indometacina com hidroxipropil-β-ciclodextrina. Estudos de dissolução e coeficiente de partição. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 42(1), 59–68 (2006)
Frijlink, H.W., Schoonen, A.J.M., Lerk, C.F.: The effects of cyclodextrins on drug absorption I: in vitro observations. Int. J. Pharm. Amst. 49, 91–102 (1989)
Nakajima, T., Sunagawa, M., Hirohashi, T.: Studies of cyclodextrin inclusion complexes. II. Application of the partition coefficient method. Chem. Pharm. Bull. Tokyo 32(2), 401–408 (1984)
Uekama, K., Uemura, Y., Irie, T., Otagiri, M.: Analysis of interfacial transfer and absorption behaviour of drugs following dissolution from β-cyclodextrin complexes. Chem. Pharm. Bull. Tokyo 31(10), 3637–3643 (1983)
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to the supporting institutions: CAPES (Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior) and UEM (Universidade Estadual de Maringá).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barão, C.E., Zanin, G.M. & de Moraes, F.F. Molecular inclusion of butylated hydroxyanisole (BHA) into alpha and beta cyclodextrins. J Incl Phenom Macrocycl Chem 71, 179–187 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-011-9925-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-011-9925-6