Abstract
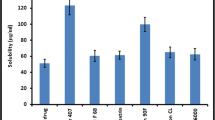
In the present investigation, cyclodextrin complexation process was explored for development of tablet formulation of WHO approved fixed dose combination of lopinavir and ritonavir with reduced tablet size, shorter disintegration time and higher bio-availability in comparison to reference product. In preliminary studies, we found that lopinavir solubility and dissolution rate is poor into the dissolution medium recommended by FDA, whereas ritonavir solubilized fairly into dissolution medium with adequate dissolution rate. Solid-state cyclodextrin complexation technology was used for enhancement of dissolution rate of lopinavir into dissolution medium. Various cyclodextrins were screened by comparison on basis of enhancement of dissolution rate of lopinavir (LPV) and the order was found as gamma cyclodextrin (γ-CD) > hydroxypropyl beta-cyclodextrin (HP-β-CD) > methyl beta-cyclodextrin (M-β-CD) > beta-cyclodextrin (β-CD), with Q120 values (i.e. percentage of dissolved drug at 120 min.) were 10.1 for the pure LPV and 56.3, 51.3, 30.3 and 10.3 for LPV/γ-CD, LPV/HP-β-CD, LPV/M-β-CD and LPV/β-CD, respectively. Anomalous results were found between stability constant, dissolution rate and saturation solubility. It was found that cyclodextrin having higher stability constant value with LPV, provides higher saturated solubility of LPV in aqueous media but at slow dissolution rate and vice versa. The γ-CD was selected for complexation with lopinavir in the stoichiometric ratio 1:1.5 M of LPV to γ-CD. Various processes such as kneading method, milling technique, sonication, freeze drying and autoclaving were tried, from which kneading method was found to give best dissolution results. The corresponding solid complexes were characterized by differential scanning calorimetric, X-ray powder diffraction and scanning electron microscopy studies. Based on various studies, the complexation phenomenon between LPV and γ-CD was found to follow non-inclusion behavior. Pharmacokinetic studies were carried out in Sprague-Dawley rats using cross over design with a 3 day wash out period. The bioavailability of lopinavir was found to be enhanced significantly using cyclodextrin complex tablet formulation.
Graphical Abstract















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Roberts, N.A., Martin, J.A., Kinchington, D., Broadhurst, A.V., Craig, J.C., Duncan, I.B., Galpin, S.A., Handa, B.K., Kay, J., Krohn, A., Lambert, R.W., Merrett, J.H., Mills, J.S., Parkes, K.E.B., Redshaw, S., Ritchie, A.J., Taylor, D.L., Thomas, G.J., Machin, P.J.: Rational design of peptide-based HIV proteinase inhibitors. Science 248, 358–361 (1990)
Richman, D.D.: HIV chemotherapy. Nature 410, 995–1001 (2001)
Boffito, M., Dickinson, L., Hill, A., Back, D., Moyle, G., Nelson, M., Higgs, C., Fletcher, C., Mandalia, S., Gazzard, B., Pozniak, A.: Pharmacokinetics of once-daily saquinavir/ritonavir in HIV-infected subjects: comparison with the standard twice-daily regimen. Antivir. Ther. 9, 423–429 (2004)
Ribera, E., Lopez, R.M., Diaz, M., Pou, L., Ruiz, L., Falco, V., Crespo, M., Azuaje, C., Ruiz, I., Ocana, I., Clotet, B., Pahissa, A.: Steady-state pharmacokinetics of a double-boosting regimen of saquinavir soft gel plus lopinavir plus minidose ritonavir in human immunodeficiency virus-infected adults. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 48, 4256–4262 (2004)
Lang, M., Roesel, J.L.: HIV-1 protease inhibitors: development, status, and potential role in the treatment of AIDS. Arch. Pharm. 326, 921–924 (1993)
Robins, T., Plattner, J.: HIV protease inhibitors: their anti-HIV activity and potential role in treatment. J. AIDS 6, 162–170 (1993)
Zeldin, R.K., Petruschke, R.A.: Pharmacological and therapeutic properties of ritonavir-boosted protease inhibitor therapy in HIV-infected patients. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 53, 4–9 (2004)
Zhu, T., Chiu, Y., Doan, T., Klein, C., Chang, M., Brun, S., Hanna, G., Awni, W.: New tablet formulation of Lopinavir/Ritonavir is bioequivalent to the capsule at a dose of 800/200 mg. 45th Interscience Conference on Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy. Poster H-1894 (2005)
Fukushima, K., Terasaka, S., Haraya, K., Kodera, S., Seki, Y., Wada, A., Ito, Y., Shibata, N., Sugioka, N., Takada, K.: Pharmaceutical approach to HIV protease inhibitor atazanavir for bioavailability enhancement based on solid dispersion system. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 30, 733–738 (2007)
Kupferschmidt, H.H., Fattinger, K.E., Ha, H.R., Follath, F., Krahenbuhl, S.: Grapefruit juice enhances the bioavailability of the HIV protease inhibitor saquinavir in man. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 45, 355–359 (1998)
Griffin, B.T., Driscoll, C.M.: A comparison of intestinal lymphatic transport and systemic bioavailability of saquinavir from three lipid-based formulations in the anaesthetized rat model. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 58, 917–925 (2006)
Betageri, G.V., Deshmukh, D.V., Gupta, R.B.: Oral sustained-release bioadhesive tablet formulation of didanosine. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 27, 129–136 (2001)
De Jaeghere, F., Allemann, E., Kubel, F., Galli, B., Cozens, R., Doelker, E., Gurny, R.: Oral bioavailability of a poorly water soluble HIV-1 protease inhibitor incorporated into pH-sensitive particles: effect of the particle size and nutritional state. J. Control. Release 68, 291–298 (2000)
Eerdenbrugh, B.V., Froyen, L., Martens, J.A., Blaton, N., Augustijns, P., Brewster, M., Mooter, G.V.: Characterization of physico-chemical properties and pharmaceutical performance of sucrose co-freeze-dried solid nanoparticulate powders of the anti-HIV agent loviride prepared by media milling. Int. J. Pharm. 338, 198–206 (2007)
Torne, J.S., Vavia, P.R.: Inclusion complexation of anti-HIV drug with β-cyclodextrin. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 56, 253–259 (2006)
Loftsson, T., Jarho, P., Masson, M., Jarvinen, T.: Cyclodextrins in drug delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2, 335–351 (2005)
Higuchi, T., Connors, K.A.: Phase-solubility techniques. Adv. Anal. Chem. Instr. 4, 117–212 (1965)
Loftsson, T., Hreinsdottir, D., Masson, M.: Evaluation of cyclodextrin solubilization of drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 302, 18–28 (2005)
Guo, J., Ping, Q., Jiang, G., Dong, J., Qi, S., Feng, L., Li, Z., Li, C.: Transport of leuprolide across rat intestine, rabbit intestine and Caco-2 cell monolayer. Int. J. Pharm. 278, 415–422 (2008)
Jadhav, G.S., Vavia, P.R., Nandedkar, T.D.: Danazol-β-cyclodextrin binary system: a potential application in emergency contraception by the oral route. AAPSPharmSciTech. 8, Article 35 (2007)
Bilensoy, E., Rouf, M.A., Vural, I., Şen, M., Hıncal, A.A.: Mucoadhesive, thermosensitive, prolonged-release vaginal gel for clotrimazole: β-cyclodextrin complex. AAPS PharmSciTech. 7 (2006)
Boffito, M., Else, L., Back, D., Taylor, J., Khoo, S., Sousa, M., Pozniak, A., Gazzard, B., Moyle, G.: Pharmacokinetics of atazanavir/ritonavir once daily and lopinavir/ritonavir twice and once daily over 72 h following drug cessation. Antivir. Ther. 13, 901–907 (2008)
Bai, Y., Xu, G.Y., Xin, X., Sun, H.Y., Zhang, H.X., Hao, A.Y., Yang, X.D., Yao, L.: Interaction between cetyltrimethylammonium bromide and β-cyclodextrin: surface tension and interfacial dilational viscoelasticity studies. Colloid. Polym. Sci. 286, 1475–1484 (2008)
Onclin, S., Mulder, A., Huskens, J., Ravoo, B.J., Reinhoudt, D.N.: Molecular printboards: # monolayers of β-cyclodextrins on silicon oxide surfaces. Langmuir 20, 5460–5466 (2004)
Acknowledgments
Gaurav Goyal would like to acknowledge financial assistance in the form of a postgraduate research scholarship from the University Grants Commission, India funded by the Major Research Project under Xth Plan and AICTE to provide sponsorship towards development of instrumentation facilities under NAFETIC scheme.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goyal, G., Vavia, P.R. Complexation approach for fixed dose tablet formulation of lopinavir and ritonavir: an anomalous relationship between stability constant, dissolution rate and saturation solubility. J Incl Phenom Macrocycl Chem 73, 75–85 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-011-0022-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-011-0022-7