Abstract
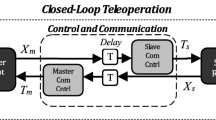
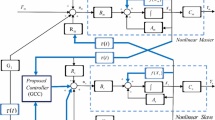
This paper investigates simple and robust transparency-attainable control architectures for bilateral teleoperation. The strength of two-channel control architectures and time-delay control are exploited. First, two types of transparency-attainable two-channel control architecture are derived. In spite of the simplicity of using two communication channels, these architectures have problems in terms of implementation; they are not simple enough and not robust to uncertainties, such as errors in modeling the plant and force sensor noise. To solve the problems, time-delay control laws for two-channel control architecture are proposed. The model-independent, nonlinear, and robust characteristics of time-delay control mitigate the problems related to complexity and robustness. Finally, the proposed control laws are applied to experiments using a 2-DOF master–slave system. The experimental results confirm the validity of the theoretical approaches.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lawrence, D.A.: Stability and transparency in bilateral teleoperation. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 9(5), 624–637 (1993). doi:10.1109/70.258054
Hokayem, P.F., Spong, M.W.: Bilateral teleoperation: an historical survey. Automatica 42(12), 2035–2057 (2006)
Hashtrudi-Zaad, K., Salcudean, S.E.: Analysis of control architectures for teleoperation systems with impedance/admittance master and slave manipulators. Int. J. Rob. Res. 20(6), 419–445 (2001). doi:10.1177/02783640122067471
Yokokohji, Y., Yoshikawa, T.: Bilateral control of master–slave manipulators for ideal kinesthetic coupling-formulation and experiment. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 10(5), 605–620 (1994). doi:10.1109/70.326566
Hashtrudi-Zaad, K., Salcudean, S.E.: Transparency in time-delayed systems and the effect of local force feedback for transparent teleoperation. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 18(1), 108–114 (2002). doi:10.1109/70.988981
Reboulet, C., Plihon, Y., Briere, Y.: Interest of the dual hybrid control scheme for teloperation with time delays. In: Experimental Robotics IV, the 4th Int. Symposium on Experimental Robotics, pp. 498–506. Springer, New York (1995)
Salcudean, S.E., Hashtrudi-Zaad, K., Tafazoli, S., DiMaio, S.P., Reboulet, C.: Bilateral matched-impedance teleoperation with application to excavator control. IEEE Control Syst. Mag. 19(6), 29–37 (1999). doi:10.1109/37.806913
Fite, K.B., Speich, J.E., Goldfarb, M.: Transparency and stability robustness in two-channel bilateral telemanipulation. ASME J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control 123, 400–407 (2001). doi:10.1115/1.1387018
Fite, K.B., Shao, L., Goldfarb, M.: Loop-shaping for transparency and stability robustness in bilateral telemanipulation. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 20(3), 620–624 (2004). doi:10.1109/TRA.2004.825474
Anderson, R.J., Spong, M.W.: Bilateral control of teleoperators with time delay. IEEE Trans. Automat. Contr. 34(5), 494–501 (1989)
Imaida, T., Yokokohji, Y., Doi, T., Oda, M., Yoshikawa, T.: Ground–space bilateral teleoperation of ETS-VII Robot Arm by direct bilateral coupling under 7-s time delay condition. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 20(3), 499–511 (2004). doi:10.1109/TRA.2004.825271
Baier, H., Schmidt, G.: Transparency and stability of bilateral kinesthetic teleoperation with time-delayed communication. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 40, 1–22 (2004). doi:10.1023/B:JINT.0000034338.53641.d0
Hsia, T.C., Lasky, T.A., Guo, Z.: Robust independent joint controller design for industrial robot manipulators. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 38(1), 21–25 (1991). doi:10.1109/41.103479
Chang, P.H., Park, B.S., Park, K.C.: An experimental study on improving hybrid position/force control of a robot using time delay control. Mechatronics 6(8), 915–931 (1996). doi:10.1016/S0957-4158(96)00028-1
Brooks, T.L.: Telerobotic response requirements. In: IEEE Int. Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics, pp. 113–120 (1990)
Kron, A., Schmidt, G.: Stability and performance analysis of kinesthetic control architectures for bimanual telepresence systems. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 46, 1–26 (2006). doi:10.1007/s10846-006-9032-x
Stanczyk, B., Peer, A., Buss, M.: Development of a high-performance haptic telemanipulation system with dissimilar kinematics. Adv. Robot. 20(46), 1303–1320 (2006). doi:10.1163/156855306778792461
Hirche, S., Hinterseer, P., Steinbach, E., Buss, M.: Transparent data reduction in networked telepresence and teleaction systems. Part I: communication without time delay. Presence 16(5), 523–531 (2007). doi:10.1162/pres.16.5.523
Ferre, M., Barrio, J., Melchiorri, C., Bogado, J.M., Castedo, P.L., Ibarra, J.M.: Experimental results on bilateral control using an industrial telemanipulator. In: Ferre, M., et al. (eds.) Advances in Telerobotics. STAR, vol. 31, pp. 177–190. Springer, Heidelberg (2007)
Hannaford, B.: A design framework for teleoperators with kinesthetic feedback. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 5(4), 426–434 (1989). doi:10.1109/70.88057
Aliaga, I., Rubio, A., Sanchez, E.: Experimental quantitative comparison of different control architectures for master–slave teleoperation. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 12(1), 2–11 (2004). doi:10.1109/TCST.2003.819586
Craig, J.J.: Introduction to Robotics: Analysis and Control, 2nd edn. Addison-Wesley, Reading (1989)
Jin, M., Kang, S.H., Chang, P.H.: Robust compliant motion control of robot with nonlinear friction using time delay estimation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 55(1), 258–269 (2008). doi:10.1109/TIE.2007.906132
Jung, J.H., Chang, P.H., Kwon, O.-S.: A new stability analysis of time delay control for input/output linearizable plants. In: American Control Conference, pp. 4972–4979 (2004)
Savitzky, A., Golay, M.J.E.: Smoothing and differentiation of data by simplified least squares procedures. Anal. Chem. 36, 1627–1639 (1964). doi:10.1021/ac60214a047
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, J., Park, HS. & Chang, P.H. Simple and Robust Attainment of Transparency Based on Two-Channel Control Architectures Using Time-Delay Control. J Intell Robot Syst 58, 309–337 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10846-009-9376-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10846-009-9376-0