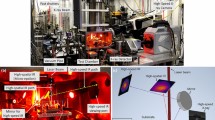
Abstract
Melt pool characteristics reflect the formation mechanisms and potential issues of flaws. Long-term, high-precision, and real-time detection of melt pool characteristics is one of the major challenges in the industrial application of additive manufacturing technology. This work proposes, for the first time, the melt pool characteristics detection platform based on multi-information fusion in the plasma arc welding (PAW) process, which fully utilizes real-time photodiode signals and high-precision, information-rich melt pool temperature fields. By optimizing the detection area and wavelength selection of the platform, particularly through the unique photodiode signal acquisition system capable of detecting the high-sensitivity area of the melt pool, we effectively mitigate the influences of intense arc light and welding wire obstruction on the temperature signals and photodiode signals. Through applying machine learning, the trained model integrates photodiode signals with temperature signals from the high-sensitivity area, thereby achieving real-time acquisition of high-precision average temperature. By combining the fused signals collected from the platform and the scanning results from micro-computed tomography (CT), we evaluate and verify the influence of flaws and droplets on the melt pool characteristics, realizing the determination of flaw occurrence based on the abnormal variations of average temperature. The experimental results demonstrated that the platform fully utilized the advantages of long-term and real-time acquisition of the photodiode signal and the high-precision and information-rich of the melt pool temperature field, achieving long-term, high-precision, and real-time detection of melt pool characteristics.




























Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
Aendenroomer, A. J. R., & Den, O. G. (1998). Weld pool oscillation as a tool for penetration sensing during pulsed GTA welding. Welding Journal, 77, 181-s.
Berumen, S., Bechmann, F., Lindner, S., et al. (2010). Quality control of laser-and powder bed-based Additive Manufacturing (AM) technologies. Physics Procedia, 5, 617–622. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phpro.2010.08.089
Boone, N., Zhu, C., Smith, C., et al. (2018). Thermal near infrared monitoring system for electron beam melting with emissivity tracking. Additive Manufacturing, 22, 601–605. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2018.06.004
Caprio, L., Demir, A. G., & Previtali, B. (2020). Observing molten pool surface oscillations during keyhole processing in laser powder bed fusion as a novel method to estimate the penetration depth. Additive Manufacturing, 36, 101470. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2020.101470
Clijsters, S., Craeghs, T., Buls, S., et al. (2014). In situ quality control of the selective laser melting process using a high-speed, real-time melt pool monitoring system. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 75(5), 1089–1101. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0924-0136(01)00522-2
de Winton, H. C., Cegla, F., & Hooper, P. A., et al. (2021). A method for objectively evaluating the defect detection performance of in-situ monitoring systems. Additive Manufacturing, 48, 102431. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2021.102431
Dunbar, A. J., & Nassar, A. R. (2018). Assessment of optical emission analysis for in-process monitoring of powder bed fusion additive manufacturing. Virtual and Physical Prototyping, 13(1), 14–19. https://doi.org/10.1080/17452759.2017.1392683
Everton, S. K., Hirsch, M., Stravroulakis, P., et al. (2016). Review of in-situ process monitoring and in-situ metrology for metal additive manufacturing. Materials & Design, 95, 431–445. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2016.01.099
Feng, W., Mao, Z., Yang, Y., et al. (2022). Online defect detection method and system based on similarity of the temperature field in the melt pool. Additive Manufacturing, 54, 102760. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2022.102760
Gökhan, D. A., De Giorgi, C., & Previtali, B. (2018). Design and implementation of a multisensor coaxial monitoring system with correction strategies for selective laser melting of a maraging steel. Journal of Manufacturing Science and Engineering, 140(4), 041003. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4038568
Hao, C., Liu, Z., Xie, H., et al. (2020). Real-time measurement method of melt pool temperature in the directed energy deposition process. Applied Thermal Engineering, 177, 115475. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2020.115475
Hojjatzadeh, S. M. H., Parab, N. D., Yan, W., et al. (2019). Pore elimination mechanisms during 3D printing of metals. Nature Communications, 10(1), 3088. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-10973-9
Jayasinghe, S., Paoletti, P., Sutcliffe, C., et al. (2022). Automatic quality assessments of laser powder bed fusion builds from photodiode sensor measurements. Progress in Additive Manufacturing. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40964-021-00219-w
Khairallah, S. A., Martin, A. A., Lee, J. R. I., et al. (2020). Controlling interdependent meso-nanosecond dynamics and defect generation in metal 3D printing. Science, 368(6491), 660–665. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aay7830
Khanzadeh, M., Chowdhury, S., Tschopp, M. A., et al. (2019). In-situ monitoring of melt pool images for porosity prediction in directed energy deposition processes. IISE Transactions, 51(5), 437–455. https://doi.org/10.1080/24725854.2017.1417656
Kirka M. M., Fernandez-Zelaia P., Lee Y., et al. (2020). Mechanical performance of a non-weldable ni-base superalloy: Inconel 738 fabricated by electron beam melting. In: Superalloys 2020: Proceedings of the 14th international symposium on superalloys. Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-51834-9_105
Kriczky, D. A., Irwin, J., Reutzel, E. W., et al. (2015). 3D spatial reconstruction of thermal characteristics in directed energy deposition through optical thermal imaging. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 221, 172–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2015.02.021
Kruth, J. P., Duflou, J., Mercelis, P., et al. (2007). On-line monitoring and process control in selective laser melting and laser cutting//Proceedings of the 5th Lane Conference. Laser Assisted Net Shape Engineering, 1, 23–37.
Lapointe, S., Guss, G., Reese, Z., et al. (2022). Photodiode-based machine learning for optimization of laser powder bed fusion parameters in complex geometries. Additive Manufacturing, 53, 102687. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2022.102687
Liu, W. W., Tang, Z. J., Liu, X. Y., et al. (2017a). A review on in-situ monitoring and adaptive control technology for laser cladding remanufacturing. Procedia Cirp, 61, 235–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2016.11.217
Liu, X. F., Jia, C. B., Wu, C. S., et al. (2017b). Measurement of the keyhole entrance and topside weld pool geometries in keyhole plasma arc welding with dual CCD cameras. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 248, 39–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2017.05.012
Liu, X. F., Wu, C. S., Jia, C. B., et al. (2017c). Visual sensing of the weld pool geometry from the topside view in keyhole plasma arc welding. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 26, 74–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2017.01.011
Liu, Z., Wu, C., Cui, S., et al. (2017d). Correlation of keyhole exit deviation distance and weld pool thermo-state in plasma arc welding process. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 104, 310–317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2016.08.069
Liu, Z., Wu, C. S., & Gao, J. (2013). Vision-based observation of keyhole geometry in plasma arc welding. International Journal of Thermal Sciences, 63, 38–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2012.07.006
Ma, H., Mao, Z., Feng, W., et al. (2022). Online in-situ monitoring of melt pool characteristic based on a single high-speed camera in laser powder bed fusion process. Applied Thermal Engineering, 211, 118515. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2022.118515
Mao, Z., Feng, W., Ma, H., et al. (2023). Continuous online flaws detection with photodiode signal and melt pool temperature based on deep learning in laser powder bed fusion. Optics & Laser Technology, 158, 108877. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2022.108877
Ren, Z., Gao, L., Clark, S. J., et al. (2023). Machine learning–aided real-time detection of keyhole pore generation in laser powder bed fusion. Science, 379(6627), 89–94. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.add4667
Rezaeifar, H., & Elbestawi, M. A. (2021). On-line melt pool temperature control in L-PBF additive manufacturing. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 112, 2789–2804. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-020-06441-0
Saad, E., Wang, H., & Kovacevic, R. (2006). Classification of molten pool modes in variable polarity plasma arc welding based on acoustic signature. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 174(1–3), 127–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2005.03.020
Spears, T. G., & Gold, S. A. (2016). In-process sensing in selective laser melting (SLM) additive manufacturing. Integrating Materials and Manufacturing Innovation, 5(1), 16–40. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40192-016-0045-4
Sun, Y., Gu, D., Dai, D., et al. (2020). Thermal behavior and microstructure evolution mechanism of W-20% Fe alloy fabricated by laser metal deposition. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 183, 105772. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2020.105772
Taherkhani, K., Sheydaeian, E., Eischer, C., et al. (2021). Development of a defect-detection platform using photodiode signals collected from the melt pool of laser powder-bed fusion. Additive Manufacturing, 46, 102152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2021.102152
Veiga, F., Suarez, A., Aldalur, E., et al. (2022). Wire arc additive manufacturing of invar parts: Bead geometry and melt pool monitoring. Measurement, 189, 110452. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2021.110452
Wang, H., & Kovacevic, R. (2002). On-line monitoring of the keyhole welding pool in variable polarity plasma arc welding. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part B: Journal of Engineering Manufacture, 216(9), 1265–1276. https://doi.org/10.1243/095440502760291817
Wang, Y., & Chen, Q. (2002). On-line quality monitoring in plasma-arc welding. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 120(1–3), 270–274. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0924-0136(01)01190-6
Wu, B., Pan, Z., Ding, D., et al. (2018). A review of the wire arc additive manufacturing of metals: Properties, defects and quality improvement. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 35, 127–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2018.08.001
Wu, D., Hu, M., Huang, Y., et al. (2021). In situ monitoring and penetration prediction of plasma arc welding based on welder intelligence-enhanced deep random forest fusion. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 66, 153–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2021.04.007
Wu, D., Huang, Y., Zhang, P., et al. (2020). Visual-acoustic penetration recognition in variable polarity plasma arc welding process using hybrid deep learning approach. IEEE Access, 8, 120417–120428. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3005822
Xia, C., Pan, Z., Li, Y., et al. (2022). Vision-based melt pool monitoring for wire-arc additive manufacturing using deep learning method. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 120(1–2), 551–562. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-022-08811-2
Xiao, Y. H., & Den, O. G. (1990). A study of GTA weld pool oscillation. Welding Journal, 69(8), 289.
Xiao, Y. H., & Den, O. G. (1993). Weld pool oscillation during GTA welding of mild steel. Welding Journal-New York-, 72, 428-s.
Zhang, G., Wu, C. S., & Liu, Z. (2014). Experimental observation of both keyhole and its surrounding thermal field in plasma arc welding. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 70, 439–448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2013.11.036
Zhang, P., Zhou, X., Ma, H., et al. (2021). Anomaly detection in laser metal deposition with photodiode-based melt pool monitoring system. Optics & Laser Technology, 144, 107454. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2021.107454
Zhang, Y., Mi, J., Li, H., et al. (2022). In situ monitoring plasma arc additive manufacturing process with a fully convolutional network. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 120(3–4), 2247–2257. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-022-08929-3
Zhao, C. X., Van Steijn, V., Richardson, I. M., et al. (2009). Experimental characterization of GTA weld pool surface flow using PIV. In: Trends in welding research 2008: proc. 8th int. conf (pp. 201–210).
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 11972084), the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant No. 2017YFB1103900), the National Science and Technology Major Project (Grant No. 2017-VI-0003-0073), the Beijing Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. 1192014), and the BIT Research and Innovation Promoting Project (Grant No. 2023YCXZ001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mao, Z., Feng, W., Han, X. et al. Development of a melt pool characteristics detection platform based on multi-information fusion of temperature fields and photodiode signals in plasma arc welding. J Intell Manuf (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-024-02342-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-024-02342-1