Abstract
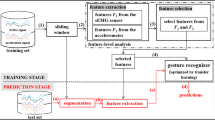
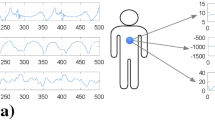
Collaborative robots are an integral component of the intelligent manufacturing field. The recognition of hand motions based on surface electromyography signals is even more significant for advancing the research of collaborative robots. However, supervised learning based hand motions recognition methods require an enormous quantity of data as support and must meet the condition of independent and identical distribution. In real-world scenarios, gender classifications, collecting conditions, and even individual-to-individual variances may influence the data, posing a challenge for the recognition of hand motions from new participants. Consequently, we propose a domain adaptive framework based on subspace and second-order statistical distribution alignment (SSDA) to overcome the issue of non-independently and identically distributed data shift. We combine the second-order statistical distribution alignment and subspace alignment. SSDA diminishes the geometric and statistical distribution discrepancies between the training and test sets in hand motions recognition. SSDA enhances the average accuracy of hand motions recognition by 26.66%, 14.43%, and 25.76% in three cross-domain scenarios (cross-gender, cross-circumstance, and cross-individual), respectively, compared with the baseline method of direct classification. Experimental results indicate that the proposed method is effective in solving the problem of distribution shift between target data (test set) and priori data (training set) in hand motions recognition. Simultaneously, it improves the recognition accuracy of classifier for different distributed data, thereby providing a new idea for achieving efficient human–robot collaboration.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abreu, J. G., Teixeira, J. M., Figueiredo, L. S., & Teichrieb, V. (2016). Evaluating sign language recognition using the Myo armband. In 2016 XVIII symposium on virtual and augmented reality (SVR) (pp. 64–70). https://doi.org/10.1109/SVR.2016.21
Ahmed, A. A., & Aly, S. (2014). Appearance-based Arabic Sign Language recognition using Hidden Markov Models. In 2014 international conference on engineering and technology (ICET) (pp. 1–6). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICEngTechnol.2014.7016804
Ahmed, M. A., Zaidan, B. B., Zaidan, A. A., Salih, M. M., & bin Lakulu, M. M. (2018). A review on systems-based sensory gloves for sign language recognition state of the art between 2007 and 2017. Sensors, 18(7), 2208. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18072208
Ahsan, Md. R., Ibrahimy, M. I., & Khalifa, O. O. (2011). Electromygraphy (EMG) signal based hand gesture recognition using artificial neural network (ANN). In 2011 4th international conference on mechatronics (ICOM) (pp. 1–6). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICOM.2011.5937135
Atzori, M., Gijsberts, A., Castellini, C., Caputo, B., Hager, A.-G.M., Elsig, S., Giatsidis, G., Bassetto, F., & Müller, H. (2014). Electromyography data for non-invasive naturally-controlled robotic hand prostheses. Scientific Data, 1(1), 140053. https://doi.org/10.1038/sdata.2014.53
Bitzer, S., & van der Smagt, P. (2006). Learning EMG control of a robotic hand: towards active prostheses. In Proceedings 2006 IEEE international conference on robotics and automation, 2006. ICRA 2006 (pp. 2819–2823). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/ROBOT.2006.1642128
Botros, F. S., Phinyomark, A., & Scheme, E. J. (2022). Electromyography-based gesture recognition: Is it time to change focus from the forearm to the wrist? IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 18(1), 174–184. https://doi.org/10.1109/TII.2020.3041618
Cheok, M. J., Omar, Z., & Jaward, M. H. (2019). A review of hand gesture and sign language recognition techniques. International Journal of Machine Learning and Cybernetics, 10(1), 131–153. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-017-0705-5
Cook, D., Feuz, K. D., & Krishnan, N. C. (2013). Transfer learning for activity recognition: A survey. Knowledge and Information Systems, 36(3), 537–556. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10115-013-0665-3
Cote-Allard, U., Fall, C. L., Drouin, A., Campeau-Lecours, A., Gosselin, C., Glette, K., Laviolette, F., & Gosselin, B. (2019). Deep learning for electromyographic hand gesture signal classification using transfer learning. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, 27(4), 760–771. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNSRE.2019.2896269
Donahue, J., Jia, Y., Vinyals, O., Hoffman, J., Zhang, N., Tzeng, E., & Darrell, T. (2014). DeCAF: A deep convolutional activation feature for generic visual recognition. In International conference on machine learning (pp. 647–655). PMLR. Retrieved April 5, 2022, from https://proceedings.mlr.press/v32/donahue14.html
Faccio, M., Granata, I., Menini, A., Milanese, M., Rossato, C., Bottin, M., Minto, R., Pluchino, P., Gamberini, L., Boschetti, G., & Rosati, G. (2022). Human factors in cobot era: A review of modern production systems features. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-022-01953-w
Fernando, B., Habrard, A., Sebban, M., & Tuytelaars, T. (2013). Unsupervised visual domain adaptation using subspace alignment. In 2013 IEEE international conference on computer vision (pp. 2960–2967). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2013.368
Goehring, D., Hoffman, J., Rodner, E., Saenko, K., & Darrell, T. (2014). Interactive adaptation of real-time object detectors. In 2014 IEEE international conference on robotics and automation (ICRA) (pp. 1282–1289). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICRA.2014.6907018
Gong, B., Shi, Y., Sha, F., & Grauman, K. (2012). Geodesic flow kernel for unsupervised domain adaptation. In 2012 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (pp. 2066–2073). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2012.6247911
Grau, A., Indri, M., Lo Bello, L., & Sauter, T. (2021). Robots in industry: The past, present, and future of a growing collaboration with humans. IEEE Industrial Electronics Magazine, 15(1), 50–61. https://doi.org/10.1109/MIE.2020.3008136
Hariharan, B., Malik, J., & Ramanan, D. (2012). Discriminative decorrelation for clustering and classification. In A. Fitzgibbon, S. Lazebnik, P. Perona, Y. Sato, & C. Schmid (Eds.), Computer vision—ECCV 2012 (Vol. 7575, pp. 459–472). Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-33765-9_33
He, J., & Jiang, N. (2020). Biometric from surface electromyogram (sEMG): Feasibility of user verification and identification based on gesture recognition. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 8, 58. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2020.00058
Ibrahim, N. B., Selim, M. M., & Zayed, H. H. (2018). An automatic Arabic sign language recognition system (ArSLRS). Journal of King Saud University - Computer and Information Sciences, 30(4), 470–477. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksuci.2017.09.007
Jiang, S., Kang, P., Song, X., Lo, B., & Shull, P. (2022). Emerging wearable interfaces and algorithms for hand gesture recognition: A survey. IEEE Reviews in Biomedical Engineering, 15, 85–102. https://doi.org/10.1109/RBME.2021.3078190
Kermany, D. S., Goldbaum, M., Cai, W., Valentim, C. C. S., Liang, H., Baxter, S. L., McKeown, A., Yang, G., Wu, X., Yan, F., Dong, J., Prasadha, M. K., Pei, J., Ting, M. Y. L., Christina Li, J. Z., Hewett, S., Ian Ziyar, J. D., Shi, A., Zhang, R., Zheng, L., Hou, R., Shi, W., Fu, X., Duan, Y., Huu, V. A. N., Wen, C, Zhang, E. D., Zhang, C. L., Li, O., Wang, X., Singer, M. A., Sun, X., Xu, J., Tafreshi, A., Anthony Lewis, M., Xia, H., Zhang, K. (2018). Identifying medical diagnoses and treatable diseases by image-based deep learning. Cell, 172(5), 1122–1131.e9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2018.02.010
Kim, J., Mastnik, S., & André, E. (2008). EMG-based hand gesture recognition for realtime biosignal interfacing. In Proceedings of the 13th international conference on Intelligent user interfaces—IUI ‘08 (p. 30). ACM Press. https://doi.org/10.1145/1378773.1378778
Kim, M., & Lee, J. Y. (2016). Touch and hand gesture-based interactions for directly manipulating 3D virtual objects in mobile augmented reality. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 75(23), 16529–16550. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-016-3355-9
Kong, W. W., & Ranganath, S. (2008). Signing Exact English (SEE): Modeling and recognition. Pattern Recognition, 41(5), 1638–1652. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2007.10.016
Kong, W. W., & Ranganath, S. (2014). Towards subject independent continuous sign language recognition: A segment and merge approach. Pattern Recognition, 47(3), 1294–1308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2013.09.014
Lee, C.-Y., Batra, T., Baig, M. H., & Ulbricht, D. (2019). Sliced Wasserstein discrepancy for unsupervised domain adaptation. In 2019 IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR) (pp. 10277–10287). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.01053
Liu, T., Yang, Q., & Tao, D. (2017). Understanding how feature structure transfers in transfer learning. In IJCAI (pp. 2365–2371).
Lobov, S., Krilova, N., Kastalskiy, I., Kazantsev, V., & Makarov, V. (2018). Latent factors limiting the performance of sEMG-interfaces. Sensors, 18(4), 1122. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18041122
Long, M., Wang, J., Ding, G., Sun, J., & Yu, P. S. (2013). Transfer feature learning with joint distribution adaptation (pp. 2200–2207). Retrieved November 17, 2021, from https://openaccess.thecvf.com/content_iccv_2013/html/Long_Transfer_Feature_Learning_2013_ICCV_paper.html
Pan, S. J., Tsang, I. W., Kwok, J. T., & Yang, Q. (2011). Domain adaptation via transfer component analysis. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 22(2), 199–210. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNN.2010.2091281
Paudyal, P., Lee, J., Banerjee, A., & Gupta, S. K. S. (2019). A comparison of techniques for sign language alphabet recognition using armband wearables. ACM Transactions on Interactive Intelligent Systems, 9(2–3), 1–26. https://doi.org/10.1145/3150974
Phinyomark, A., Khushaba, R. N., & Scheme, E. (2018). Feature extraction and selection for myoelectric control based on wearable EMG sensors. Sensors, 18(5), 1615. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18051615
Phinyomark, A., Phukpattaranont, P., & Limsakul, C. (2012a). Feature reduction and selection for EMG signal classification. Expert Systems with Applications, 39(8), 7420–7431. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2012.01.102
Phinyomark, A., Phukpattaranont, P., & Limsakul, C. (2012b). Fractal analysis features for weak and single-channel upper-limb EMG signals. Expert Systems with Applications, 39(12), 11156–11163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2012.03.039
Sapsanis, C., Georgoulas, G., & Tzes, A. (2013). EMG based classification of basic hand movements based on time-frequency features. In 21st Mediterranean conference on control and automation (pp. 716–722). https://doi.org/10.1109/MED.2013.6608802
Shin, S.-O., Kim, D., & Seo, Y.-H. (2014). Controlling mobile robot using IMU and EMG sensor-based gesture recognition. In 2014 ninth international conference on broadband and wireless computing, communication and applications (pp. 554–557). Presented at the 2014 ninth international conference on broadband and wireless computing, communication and applications. https://doi.org/10.1109/BWCCA.2014.145
Stegeman, D. F., Kleine, B. U., Lapatki, B. G., & Van Dijk, J. P. (2012). High-density surface EMG: Techniques and applications at a motor unit level. Biocybernetics and Biomedical Engineering, 32(3), 3–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0208-5216(12)70039-6
Stival, F., Michieletto, S., Cognolato, M., Pagello, E., Müller, H., & Atzori, M. (2019). A quantitative taxonomy of human hand grasps. Journal of NeuroEngineering and Rehabilitation, 16(1), 28. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12984-019-0488-x
Sun, B., Feng, J., & Saenko, K. (2016). Return of frustratingly easy domain adaptation. In Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence (Vol. 30, No. 1). Retrieved November 12, 2021, from https://ojs.aaai.org/index.php/AAAI/article/view/10306
Sun, B., & Saenko, K. (2015). Subspace distribution alignment for unsupervised domain adaptation. In Proceedings of the British machine vision conference 2015 (pp. 24.1–24.10). British Machine Vision Association. https://doi.org/10.5244/C.29.24
Vijayalakshmi, P., & Aarthi, M. (2016). Sign language to speech conversion. In 2016 international conference on recent trends in information technology (ICRTIT) (pp. 1–6). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICRTIT.2016.7569545
Vinayak, Murugappan, S., Liu, H., & Ramani, K. (2013). Shape-It-Up: Hand gesture based creative expression of 3D shapes using intelligent generalized cylinders. Computer-Aided Design, 45(2), 277–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cad.2012.10.011
Vuletic, T., Duffy, A., Hay, L., McTeague, C., Campbell, G., & Grealy, M. (2019). Systematic literature review of hand gestures used in human computer interaction interfaces. International Journal of Human–Computer Studies, 129, 74–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhcs.2019.03.011
Wang, J., Chen, Y., Hao, S., Feng, W., & Shen, Z. (2017). Balanced distribution adaptation for transfer learning. In 2017 IEEE international conference on data mining (ICDM) (pp. 1129–1134). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICDM.2017.150
Wang, J., Feng, W., Chen, Y., Yu, H., Huang, M., & Yu, P. S. (2018). Visual domain adaptation with manifold embedded distribution alignment. In Proceedings of the 26th ACM international conference on multimedia (pp. 402–410). https://doi.org/10.1145/3240508.3240512
Wang, P., Li, Y., & Vasconcelos, N. (2021). Rethinking and improving the robustness of image style transfer. In 2021 IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR) (pp. 124–133). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR46437.2021.00019
Yan, H., Ding, Y., Li, P., Wang, Q., Xu, Y., & Zuo, W. (2017). Mind the class weight bias: Weighted maximum mean discrepancy for unsupervised domain adaptation. In 2017 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR) (pp. 945–954). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2017.107
Yu, Z., Zhao, J., Wang, Y., He, L., & Wang, S. (2021). Surface EMG-based instantaneous hand gesture recognition using convolutional neural network with the transfer learning method. Sensors, 21(7), 2540. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21072540
Zhang, Y., Chen, Y., Yu, H., Yang, X., & Lu, W. (2020). Learning effective spatial-temporal features for sEMG armband-based gesture recognition. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 7(8), 6979–6992. https://doi.org/10.1109/JIOT.2020.2979328
Zhang, Y., Chen, Y., Yu, H., Yang, X., Sun, R., & Zeng, B. (2021). A feature adaptive learning method for high-density sEMG-based gesture recognition. Proceedings of the ACM on Interactive, Mobile, Wearable and Ubiquitous Technologies, 5(1), 1–26. https://doi.org/10.1145/3448114
Zhuang, F., Qi, Z., Duan, K., Xi, D., Zhu, Y., Zhu, H., Xiong, H., & He, Q. (2021). A comprehensive survey on transfer learning. Proceedings of the IEEE, 109(1), 43–76. https://doi.org/10.1109/JPROC.2020.3004555
Funding
This paper was supported by “the Fundamental Research for the Central Universities” [Chinese Ministry of Education (Grant No. 2020GFZD014)].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors of this publication declare there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kou, H., Shi, H. & Zhao, H. Subspace and second-order statistical distribution alignment for cross-domain recognition of human hand motions. J Intell Manuf (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-023-02150-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-023-02150-z