Abstract
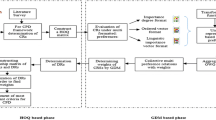
User collaboration has been recognized as a critical factor in successful product development. To select the proper users who have a higher satisfaction to meet product development requirements, this study proposes an integrated approach based on quality function deployment (QFD) and data envelopment analysis (DEA). The proposed approach considers product development requirements, the inner dependencies of user evaluation criteria, and the relationships between requirements and criteria simultaneously and presents them in house of quality (HoQ). For the fuzzy and imprecise information in HoQ, fuzzy weighted average method is employed to determine the weight of each user evaluation criterion. Furthermore, to determine the priorities of users with a large number efficiently, this study implements linguistic variables to assess the weight of each user under each criterion, the DEA method to determine the optimal values of linguistic variables, and the simple additive weighting approach to aggregate the weight of each criteria and the local score of each user with respect to each criterion. An illustrative case is presented to demonstrate the applications of the proposed approach based on QFD and DEA in this paper.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aghdam, M. M., Jelodar, M. J., & Mahdavi, I. (2015). Engineering design requirements ranking in QFD by fuzzy data envelopment analysis. Arth Prabandh: A Journal of Economics and Management, 4(3), 134–150.
Azadi, M., & Saen, R. F. (2013). A combination of QFD and imprecise DEA with enhanced Russell graph measure: A case study in healthcare. Socio-Economic Planning Sciences, 47(4), 281–291.
Bilgram, V., Brem, A., & Voigt, K.-I. (2008). User-centric innovations in new product development—Systematic identification of lead users harnessing interactive and collaborative online-tools. International Journal of Innovation Management, 12(03), 419–458.
Bouchereau, V., & Rowlands, H. (2000). Methods and techniques to help quality function deployment (QFD). Benchmarking: An International Journal, 7(1), 8–20.
Cariaga, I., El-Diraby, T., & Osman, H. (2007). Integrating value analysis and quality function deployment for evaluating design alternatives. Journal of Construction Engineering and Management, 133(10), 761–770.
Chen, L. H., & Ko, W. C. (2009). Fuzzy linear programming models for new product design using QFD with FMEA. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 33(2), 633–647.
Chen, L. H., & Weng, M. C. (2006). An evaluation approach to engineering design in QFD processes using fuzzy goal programming models. European Journal of Operational Research, 172(1), 230–248.
Djelassi, S., & Decoopman, I. (2013). Customers’ participation in product development through crowdsourcing: Issues and implications. Industrial Marketing Management, 42(5), 683–692.
Dursun, M., & Karsak, E. E. (2013). A QFD-based fuzzy MCDM approach for supplier selection. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 37(8), 5864–5875.
Eilat, H., Golany, B., & Shtub, A. (2008). R&D project evaluation: An integrated DEA and balanced scorecard approach. Omega, 36(5), 895–912.
Faems, D., Van Looy, B., & Debackere, K. (2005). Interorganizational collaboration and innovation: Toward a portfolio approach. Journal of Product Innovation Management, 22(3), 238–250.
Franke, N., & Shah, S. (2003). How communities support innovative activities: An exploration of assistance and sharing among end-users. Research Policy, 32(1), 157–178.
Franke, N., Von Hippel, E., & Schreier, M. (2006). Finding commercially attractive user innovations: A test of lead-user theory. Journal of Product Innovation Management, 23(4), 301–315.
Gok, A. (2015). A new approach to minimization of the surface roughness and cutting force via fuzzy TOPSIS, multi-objective grey design and RSA. Measurement, 70, 100–109.
Greer, C. R., & Lei, D. (2012). Collaborative innovation with customers: A review of the literature and suggestions for future research. International Journal of Management Reviews, 14(1), 63–84.
Hadi-Vencheh, A., & Mohamadghasemi, A. (2011). A fuzzy AHP–DEA approach for multiple criteria ABC inventory classification. Expert Systems with Applications, 38(4), 3346–3352.
Jeppesen, L. B., & Frederiksen, L. (2006). Why do users contribute to firm-hosted user communities? The case of computer-controlled music instruments. Organization Science, 17(1), 45–63.
Jeppesen, L. B., & Molin, M. J. (2003). Consumers as co-developers: Learning and innovation outside the firm. Technology Analysis & Strategic Management, 15(3), 363–383.
Karsak, E. E. (2008). Using data envelopment analysis for evaluating flexible manufacturing systems in the presence of imprecise data. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 35(9–10), 867–874.
Karsak, E. E., & Dursun, M. (2014). An integrated supplier selection methodology incorporating QFD and DEA with imprecise data. Expert Systems with Applications, 41(16), 6995–7004.
Karsak, E. E., & Dursun, M. (2015). An integrated fuzzy MCDM approach for supplier evaluation and selection. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 82, 82–93.
Kauffmann, P., Unal, R., Fernandez, A., & Keating, C. (2000). A model for allocating resources to research programs by evaluating technical importance and research productivity. Engineering Management Journal, 12(1), 5–8.
Kausch, C. (2007). A risk-benefit perspective on early customer integration. Contributions to management science (pp. 1–218). Springer.
Kilincci, O., & Onal, S. A. (2011). Fuzzy AHP approach for supplier selection in a washing machine company. Expert Systems with Applications, 38(8), 9656–9664.
Lüthje, C. (2004). Characteristics of innovating users in a consumer goods field: An empirical study of sport-related product consumers. Technovation, 24(9), 683–695.
Lüthje, C., & Herstatt, C. (2004). The Lead User method: An outline of empirical findings and issues for future research. Social Science Electronic Publishing, 34(5), 553–568.
Lüthje, C., Herstatt, C., & Von Hippel, E. (2005). User-innovators and "local" information: The case of mountain biking. Research Policy, 34(6), 951–965.
Li, Y. L., Tang, J. F., & Luo, X. G. (2010). An ECI-based methodology for determining the final importance ratings of customer requirements in MP product improvement. Expert Systems with Applications, 37(9), 6240–6250.
Lin, M.-J. J., & Huang, C.-H. (2012). The impact of customer participation on NPD performance: The mediating role of inter-organisation relationship. Journal of Business & Industrial Marketing, 28(1), 3–15.
Liu, F.-H. F., & Hai, H. L. (2005). The voting analytic hierarchy process method for selecting supplier. International Journal of Production Economics, 97(3), 308–317.
Liu, S.-T. (2005). Rating design requirements in fuzzy quality function deployment via a mathematical programming approach. International Journal of Production Research, 43(3), 497–513.
Mehrjerdi, Y. Z., Owlia, M., & Dorodzani, A. T. (2012). Evaluation and ranking the relative importance of design requirements by combining QFD and DEA techniques (case study: Tile industry of Iran). International Journal of Industrial Engineering, 23(2), 175–186.
Miotti, L., & Sachwald, F. (2003). Co-operative R&D: Why and with whom?: An integrated framework of analysis. Research Policy, 32(8), 1481–1499.
Nieto, M. J., & Santamaría, L. (2007). The importance of diverse collaborative networks for the novelty of product innovation. Technovation, 27(6), 367–377.
Noguchi, H., Ogawa, M., & Ishii, H. (2002). The appropriate total ranking method using DEA for multiple categorized purposes. Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics, 146(1), 155–166.
Olson, E. L., & Bakke, G. (2001). Implementing the lead user method in a high technology firm: A longitudinal study of intentions versus actions. Journal of Product Innovation Management, 18(6), 388–395.
Ramanathan, R., & Yunfeng, J. (2009). Incorporating cost and environmental factors in quality function deployment using data envelopment analysis. Omega, 37(3), 711–723.
Schaarschmidt, M., & Kilian, T. (2014). Impediments to customer integration into the innovation process: A case study in the telecommunications industry. European Management Journal, 32(2), 350–361.
Schreier, M., Oberhauser, S., & Prügl, R. (2007). Lead users and the adoption and diffusion of new products: Insights from two extreme sports communities. Marketing Letters, 18(1–2), 15–30.
Schreier, M., & Prügl, R. (2008). Extending lead-user theory: Antecedents and consequences of consumers’ lead userness. Journal of Product Innovation Management, 25(4), 331–346.
Shanmugam, R., & Johnson, C. (2007). At a crossroad of data envelopment and principal component analyses. Omega, 35(4), 351–364.
Song, L. J., Yang, Y., Zhang, X. D., & Yang, J. (2007). Preference-based algorithm for collaborative design partners evaluation & selection. Computer Integrated Manufacturing Systems, 13(10), 2053–2059.
Von Hippel, E. (1986). Lead users: A source of novel product concepts. Management Science, 32(7), 791–805.
Wang, C. H., & Wu, H. S. (2016). A novel framework to evaluate programmable logic controllers: A Fuzzy MCDM perspective. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 27(2), 315–324.
Wang, W.-L., Yang, Y., & Wang, M.-K. (2007). RS and SVM- based partner selection research for customer collaborative innovation. Jisuanji Gongcheng yu Yingyong(Computer Engineering and Applications), 42(29), 245–248.
Wang, Y.-M., & Chin, K.-S. (2011). Technical importance ratings in fuzzy QFD by integrating fuzzy normalization and fuzzy weighted average. Computers & Mathematics with Applications, 62(11), 4207–4221.
Wang, Y., Chin, K., & Yang, J. (2007). Three new models for preference voting and aggregation. Journal of the Operational Research Society, 58(10), 1389–1393.
Wang, Y. M., Liu, J., & Elhag, T. M. S. (2008). An integrated AHP–DEA methodology for bridge risk assessment. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 54(3), 513–525.
Yang, J., Yang, Y., Wang, W., Zhao, X., & Song, L. (2008). Evaluation of collaborative innovative customer based on PWNN model and its application. Computer Integrated Manufacturing Systems, 14(5), 882–890.
Zadeh, L. A. (1975). The concept of a linguistic variable and its application to approximate reasoning. Information Sciences, 8(3), 199–249.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by The Key Project of Academic Humanities and Social Science of Anhui Education Department (SK2017A0120), and The Scientific Research Starting Foundation of Anhui Polytechnic University for Talent Introduction (2016YQQ008). The author would like to thank the anonymous reviewers and the editor for their constructive comments and suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X. User selection for collaboration in product development based on QFD and DEA approach. J Intell Manuf 30, 2231–2243 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-017-1386-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-017-1386-3