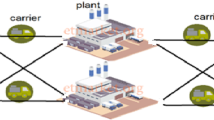
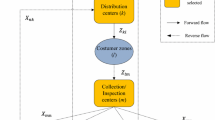
Abstract
A green supply chain with a well-designed network can strongly influence the performance of supply chain and environment. The designed network should lead the supply chain to efficient and effective management to meet the efficient profit, sustainable effects on environment and customer needs. The proposed mathematical model in this paper identifies locations of productions and shipment quantity by exploiting the trade-off between costs, and emissions for a dual channel supply chain network. Due to considering different prices and customers zones for channels, determining the prices and strategic decision variables to meet the maximum profit for the proposed green supply chain is contemplated. In this paper, the transportation mode as a tactical decision has been considered that can affect the cost and emissions. Lead time and lost sales are considered in the modeling to reach more reality. The developed mathematical model is a mixed integer non-linear programming which is solved by GAMS. Due to NP-hard nature of the proposed model and long run time for large-size problems by GAMS, artificial immune system algorithm based on CLONALG, genetic and memetic algorithms are applied. Taguchi technique is used for parameter tuning of all meta-heuristic algorithms. Results demonstrate the strength of CLONALG rather than the other methods.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amini, M., & Li, H. (2015). The impact of dual-market on supply chain configuration for new products. International Journal of Production Research, 53(18), 5669–5684. doi:10.1080/00207543.2015.1058537.
Aras, N., & Aksen, D. (2008). Locating collection centers for distance- and incentive-dependent returns. International Journal of Production Economics, 111(2), 316–333. doi:10.1016/j.ijpe.2007.01.015.
Bai, C., & Sarkis, J. (2010). Green supplier development: Analytical evaluation using rough set theory. Journal of Cleaner Production, 18(12), 1200–1210. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2010.01.016.
Bersini, H., & Varela, F. (1991). Hints for adaptive problem solving gleaned from immune networks. In H.-P. Schwefel & R. Männer (Eds.), Parallel problem solving from nature (Vol. 496, pp. 343–354). Berlin Heidelberg: Springer. Lecture Notes in Computer Science.
Büyüközkan, G., & Berkol, Ç. (2011). Designing a sustainable supply chain using an integrated analytic network process and goal programming approach in quality function deployment. Expert Systems with Applications, 38(11), 13731–13748. doi:10.1016/j.eswa.2011.04.171.
Cardoso, S. R., Barbosa-Póvoa, A. P. F. D., & Relvas, S. (2013). Design and planning of supply chains with integration of reverse logistics activities under demand uncertainty. European Journal of Operational Research, 226(3), 436–451. doi:10.1016/j.ejor.2012.11.035.
Chaabane, A., Ramudhin, A., & Paquet, M. (2012). Design of sustainable supply chains under the emission trading scheme. International Journal of Production Economics, 135(1), 37–49. doi:10.1016/j.ijpe.2010.10.025.
Chan, F. T. S., Swarnkar, R., & Tiwari, M. K. (2005). Fuzzy goal-programming model with an artificial immune system (AIS) approach for a machine tool selection and operation allocation problem in a flexible manufacturing system. International Journal of Production Research, 43(19), 4147–4163. doi:10.1080/00207540500140823.
Corsano, G., Vecchietti, A. R., & Montagna, J. M. (2011). Optimal design for sustainable bioethanol supply chain considering detailed plant performance model. Computers and Chemical Engineering, 35(8), 1384–1398. doi:10.1016/j.compchemeng.2011.01.008.
Cutello, V., & Nicosia, G. (2002). An Immunological Approach to Combinatorial Optimization Problems. In F. Garijo, J. Riquelme, & M. Toro (Eds.), Advances in artificial intelligence—IBERAMIA 2002 (Vol. 2527, pp. 361–370). Berlin Heidelberg: Springer. Lecture Notes in Computer Science.
Dasgupta, D., & Nino, F. (2008). Immunological computation: Theory and applications. USA: Auerbach Publications.
Davis, P. S., & Ray, T. L. (1969). A branch-bound algorithm for the capacitated facilities location problem. Naval Research Logistics Quarterly, 16(3), 331–344. doi:10.1002/nav.3800160306.
de Castro, L. N., & Von Zuben, F. J. (2002). Learning and optimization using the clonal selection principle. Evolutionary Computation, IEEE Transactions on, 6(3), 239–251. doi:10.1109/TEVC.2002.1011539.
Dekker, R., Bloemhof, J., & Mallidis, I. (2012). Operations research for green logistics—An overview of aspects, issues, contributions and challenges. European Journal of Operational Research, 219(3), 671–679. doi:10.1016/j.ejor.2011.11.010.
Diabat, A., & Govindan, K. (2011). An analysis of the drivers affecting the implementation of green supply chain management. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 55(6), 659–667. doi:10.1016/j.resconrec.2010.12.002.
Ebrahim, R. M., Razmi, J., & Haleh, H. (2009). Scatter search algorithm for supplier selection and order lot sizing under multiple price discount environment. Advances in Engineering Software, 40(9), 766–776. doi:10.1016/j.advengsoft.2009.02.003.
Elhedhli, S., & Merrick, R. (2012). Green supply chain network design to reduce carbon emissions. Transportation research Part D Transport and Environment, 17(5), 370–379. doi:10.1016/j.trd.2012.02.002.
Eltayeb, T. K., Zailani, S., & Ramayah, T. (2011). Green supply chain initiatives among certified companies in Malaysia and environmental sustainability: Investigating the outcomes. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 55(5), 495–506. doi:10.1016/j.resconrec.2010.09.003.
Ernst & Young, (2001). Global online retailing: An Ernst and Young special report.
Fahimnia, B., Farahani, R. Z., & Sarkis, J. (2013). Integrated aggregate supply chain planning using memetic algorithm—A performance analysis case study. International Journal of Production Research, 51(18), 5354–5373. doi:10.1080/00207543.2013.774492.
Fahimnia, B., Sarkis, J., Choudhary, A., & Eshragh, A. (2015a). Tactical supply chain planning under a carbon tax policy scheme: A case study. International Journal of Production Economics, 164, 206–215. doi:10.1016/j.ijpe.2014.12.015.
Fahimnia, B., Sarkis, J., & Eshragh, A. (2015). A tradeoff model for green supply chain planning: A leanness-versus-greenness analysis. Omega, 54, 173–190. doi:10.1016/j.omega.2015.01.014.
Farmer, J. D., Packard, N. H., & Perelson, A. S. (1986). The immune system, adaptation, and machine learning. Physica D Nonlinear Phenomena, 22(1–3), 187–204. doi:10.1016/0167-2789(86)90240-X.
Forrest, S., Perelson, A. S., Allen, L., & Cherukuri, R. (1994). Self-nonself discrimination in a computer. In 1994 IEEE Computer Society Symposium on Research in Security and Privacy, 1994: Proceedings, 16–18 May 1994 (pp. 202–212). doi:10.1109/RISP.1994.296580.
Forrester Report (2000). Channel conflict crumbles.
Gen, M., Altiparmak, F., & Lin, L. (2006). A genetic algorithm for two-stage transportation problem using priority-based encoding. OR Spectrum, 28(3), 337–354. doi:10.1007/s00291-005-0029-9.
Geoffrion, A. M., & Graves, G. W. (1974). Multicommodity distribution system design by Benders decomposition. Management Science, 20(5), 822–844. doi:10.1287/mnsc.20.5.822.
Giarola, S., Shah, N., & Bezzo, F. (2012). A comprehensive approach to the design of ethanol supply chains including carbon trading effects. Bioresource Technology, 107, 175–185. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2011.11.090.
Goldberg, D. E. (1989). Genetic algorithms in search, optimization and machine learning. USA: addison-wesley longman publishing co., inc.
Guillén-Gosálbez, G., & Grossmann, I. (2010). A global optimization strategy for the environmentally conscious design of chemical supply chains under uncertainty in the damage assessment model. Computers and Chemical Engineering, 34(1), 42–58. doi:10.1016/j.compchemeng.2009.09.003.
Gumus, A. T., Guneri, A. F., & Keles, S. (2009). Supply chain network design using an integrated neuro-fuzzy and MILP approach: A comparative design study. Expert Systems with Applications, 36(10), 12570–12577. doi:10.1016/j.eswa.2009.05.034.
Hiremath, N. C., Sahu, S., & Tiwari, M. (2013). Multi objective outbound logistics network design for a manufacturing supply chain. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 24(6), 1071–1084. doi:10.1007/s10845-012-0635-8.
Hsieh, C.-L., Liao, S.-H., & Ho, W.-C. (2014). Multi-objective dual-sale channel supply chain network design based on NSGA-II. In M. Ali, J.-S. Pan, S.-M. Chen, & M.-F. Horng (Eds.), Modern Advances in Applied Intelligence (Vol. 8481, pp. 479–489). Switzerland: Springer International Publishing. Lecture Notes in Computer Science.
Hsu, C. W., & Hu, A. H. (2008). Green supply chain management in the electronic industry. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 5(2), 205–216. doi:10.1007/BF03326014.
Hugo, A., & Pistikopoulos, E. N. (2005). Environmentally conscious long-range planning and design of supply chain networks. Journal of Cleaner Production, 13(15), 1471–1491. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2005.04.011.
Jamshidi, R., Fatemi Ghomi, S. M. T., & Karimi, B. (2012). Multi-objective green supply chain optimization with a new hybrid memetic algorithm using the Taguchi method. Scientia Iranica, 19(6), 1876–1886. doi:10.1016/j.scient.2012.07.002.
Kara, S. S., & Onut, S. (2010). A stochastic optimization approach for paper recycling reverse logistics network design under uncertainty. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 7(4), 717–730. doi:10.1007/BF03326181.
Kephart, J. O. A. (1994). biologically inspired immune system for computers. In Artificial Life IV: proceedings of the fourth international workshop on the synthesis and simulation of living systems (pp. 130–139).
Khalifehzadeh, S., Seifbarghy, M., & Naderi, B. (2014). Solving a fuzzy multi objective model of a production-distribution system using meta-heuristic based approaches. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 1–15, doi:10.1007/s10845-014-0964-x.
Kumar, A., Prakash, A., Shankar, R., & Tiwari, M. K. (2006). Psycho-Clonal algorithm based approach to solve continuous flow shop scheduling problem. Expert Systems with Applications, 31(3), 504–514. doi:10.1016/j.eswa.2005.09.059.
Kumar, S., Teichman, S., & Timpernagel, T. (2011). A green supply chain is a requirement for profitability. International Journal of Production Research, 50(5), 1278–1296. doi:10.1080/00207543.2011.571924.
Le, T., & Lee, T.-R. (2013). Model selection with considering the CO2 emission alone the global supply chain. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 24(4), 653–672. doi:10.1007/s10845-011-0613-6.
Lee, H. L., & Billington, C. (1992). Managing supply chain inventory: Pitfalls and opportunities. MIT Sloan Management Review, 33(3), 65–73.
Liu, B., Zhang, R., & Xiao, M. (2010). Joint decision on production and pricing for online dual channel supply chain system. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 34(12), 4208–4218. doi:10.1016/j.apm.2010.04.018.
Mallidis, I., Dekker, R., & Vlachos, D. (2012). The impact of greening on supply chain design and cost: a case for a developing region. Journal of Transport Geography, 22, 118–128. doi:10.1016/j.jtrangeo.2011.12.007.
Markovits-Somogyi, R., Nagy, Z., & Török, Á. (2009). Greening supply chain management. Acta Technica Jaurinensis, 2(3).
Melo, M. T., Nickel, S., & Saldanha-da-Gama, F. (2009). Facility location and supply chain management–A review. European Journal of Operational Research, 196(2), 401–412. doi:10.1016/j.ejor.2008.05.007.
Min, H., & Kim, I. (2012). Green supply chain research: Past, present, and future. Logistics Research, 4(1–2), 39–47. doi:10.1007/s12159-012-0071-3.
Mirzapour Al-e-hashem, S. M. J., Baboli, A., & Sazvar, Z. (2013). A stochastic aggregate production planning model in a green supply chain: Considering flexible lead times, nonlinear purchase and shortage cost functions. European Journal of Operational Research, 230(1), 26–41. doi:10.1016/j.ejor.2013.03.033.
NPD Group, (2004). Who’s buying direct and why: consumers tell all. http://www.npdtechworld.com.
Panigrahi, B. K., Yadav, S. R., Agrawal, S., & Tiwari, M. K. (2007). A clonal algorithm to solve economic load dispatch. Electric Power Systems Research, 77(10), 1381–1389. doi:10.1016/j.epsr.2006.10.007.
Pinto-Varela, T., Barbosa-Póvoa, A. P. F. D., & Novais, A. Q. (2011). Bi-objective optimization approach to the design and planning of supply chains: Economic versus environmental performances. Computers and Chemical Engineering, 35(8), 1454–1468. doi:10.1016/j.compchemeng.2011.03.009.
Pishvaee, M. S., Farahani, R. Z., & Dullaert, W. (2010a). A memetic algorithm for bi-objective integrated forward/reverse logistics network design. Computers and Operations Research, 37(6), 1100–1112. doi:10.1016/j.cor.2009.09.018.
Pishvaee, M., Kianfar, K., & Karimi, B. (2010b). Reverse logistics network design using simulated annealing. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 47(1–4), 269–281. doi:10.1007/s00170-009-2194-5.
Pishvaee, M. S., & Rabbani, M. (2011). A graph theoretic-based heuristic algorithm for responsive supply chain network design with direct and indirect shipment. Advances in Engineering Software, 42(3), 57–63. doi:10.1016/j.advengsoft.2010.11.001.
Pishvaee, M. S., & Razmi, J. (2012). Environmental supply chain network design using multi-objective fuzzy mathematical programming. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 36(8), 3433–3446. doi:10.1016/j.apm.2011.10.007.
Pishvaee, M. S., Razmi, J., & Torabi, S. A. (2012). Robust possibilistic programming for socially responsible supply chain network design: A new approach. Fuzzy Sets and Systems, 206, 1–20. doi:10.1016/j.fss.2012.04.010.
Pishvaee, M. S., Torabi, S. A., & Razmi, J. (2012b). Credibility-based fuzzy mathematical programming model for green logistics design under uncertainty. Computers and Industrial Engineering, 62(2), 624–632. doi:10.1016/j.cie.2011.11.028.
Quariguasi Frota Neto, J., Walther, G., Bloemhof, J., van Nunen, J. A. E. E., & Spengler, T. (2009). A methodology for assessing eco-efficiency in logistics networks. European Journal of Operational Research, 193(3), 670–682. doi:10.1016/j.ejor.2007.06.056.
Rajabalipour Cheshmehgaz, H., Desa, M., & Wibowo, A. (2013). A flexible three-level logistic network design considering cost and time criteria with a multi-objective evolutionary algorithm. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 24(2), 277–293. doi:10.1007/s10845-011-0584-7.
Rajabalipour Cheshmehgaz, H., Islam, M. N., & Desa, M. (2014). A polar-based guided multi-objective evolutionary algorithm to search for optimal solutions interested by decision-makers in a logistics network design problem. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 25(4), 699–726. doi:10.1007/s10845-012-0714-x.
Samadhi, T. M. A. A., & Hoang, K. (1998). Partners selection in a shared-CIM system. International Journal of Computer Integrated Manufacturing, 11(2), 173–182. doi:10.1080/095119298130903.
Shapiro, J. F. (2007). Modeling the supply chain (Vol. 2). USA: Cengage Learning.
Sousa, R., Shah, N., & Papageorgiou, L. G. (2008). Supply chain design and multilevel planning–An industrial case . Computers and Chemical Engineering, 32(11), 2643–2663. doi:10.1016/j.compchemeng.2007.09.005.
Taguchi, G., Chowdhury, S., & Taguchi, S. (2000). Robust engineering. USA: McGraw-Hill Professional.
Tiwari, M. K., Raghavendra, N., Agrawal, S., & Goyal, S. K. (2010). A Hybrid Taguchi-Immune approach to optimize an integrated supply chain design problem with multiple shipping. European Journal of Operational Research, 203(1), 95–106. doi:10.1016/j.ejor.2009.07.004.
Tunali, S., Ozfirat, P. M., & Ay, G. (2011). Setting order promising times in a supply chain network using hybrid simulation-analytical approach: An industrial case study. Simulation Modelling Practice and Theory, 19(9), 1967–1982. doi:10.1016/j.simpat.2011.04.014.
Wang, F., Lai, X., & Shi, N. (2011). A multi-objective optimization for green supply chain network design. Decision Support Systems, 51(2), 262–269. doi:10.1016/j.dss.2010.11.020.
Xu, H., Liu, Z. Z., & Zhang, S. H. (2012). A strategic analysis of dual-channel supply chain design with price and delivery lead time considerations. International Journal of Production Economics, 139(2), 654–663. doi:10.1016/j.ijpe.2012.06.014.
Yeh, W.-C. (2005). A hybrid heuristic algorithm for the multistage supply chain network problem. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 26(5–6), 675–685. doi:10.1007/s00170-003-2025-z.
Yeh, W.-C. (2006). An efficient memetic algorithm for the multi-stage supply chain network problem. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 29(7–8), 803–813. doi:10.1007/s00170-005-2556-6.
Yeh, W.-C., & Chuang, M.-C. (2011). Using multi-objective genetic algorithm for partner selection in green supply chain problems. Expert Systems with Applications, 38(4), 4244–4253. doi:10.1016/j.eswa.2010.09.091.
Yezheng, L., & Zhengping, D. (2012). Revenue Sharing Contract in Dual Channel Supply Chain in Case of Free Riding. In J. Watada, T. Watanabe, G. Phillips-Wren, R. J. Howlett, & L. C. Jain (Eds.), Intelligent decision technologies (Vol. 16, pp. 459–465). Berlin Heidelberg: Springer. Smart Innovation, Systems and Technologies.
Yu, J., Gan, M., Ni, S., & Chen, D. (2015). Multi-objective models and real case study for dual-channel FAP supply chain network design with fuzzy information. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 1–15. doi:10.1007/s10845-015-1115-8.
Zhao, R., Neighbour, G., Han, J., McGuire, M., & Deutz, P. (2012). Using game theory to describe strategy selection for environmental risk and carbon emissions reduction in the green supply chain. Journal of Loss Prevention in the Process Industries, 25(6), 927–936. doi:10.1016/j.jlp.2012.05.004.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barzinpour, F., Taki, P. A dual-channel network design model in a green supply chain considering pricing and transportation mode choice. J Intell Manuf 29, 1465–1483 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-015-1190-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-015-1190-x