Abstract
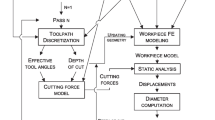
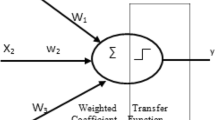
This paper aims to introduce a computer-based estimation and compensation method for diametral errors in cantilever bar turning without additional hardware requirements. In the error estimation method, the error characteristics of workpieces are determined experimentally depending on cutting speed, depth of cut, feed rate, workpiece diameter, length from the chuck and the geometric error sum of CNC lathe. An Artificial Neural Network (ANN) model is trained using these experimental error characteristics for estimation of the error. The ANN model estimated the workpiece dimensional errors with a good accuracy. Error correction is realised via turning of workpieces with a CNC part program which modified based on the estimated error profile. The dimensional errors are reduced approximately by 90% with the proposed method.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Azouzi R., & Guillot M. (1997) On-line prediction of surface finish and dimensional deviation in turning using neural network based sensor fusion. International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture 37(9): 1201–1217
Benardos P. G., Mosialos S., Vosniakos G. C. (2006) Prediction of workpiece elastic deflections under cutting forces in turning. Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing 22: 505–514
Chryssolouris G., Guillot M. (1990) A comparison of statistical and AI approaches to the selection of process parameters in intelligent machining. Transactions of the ASME Journal of Engineering Industry 112: 122–131
El Ouafı A., Guillot M., Bedrouni A. (2000) Accuracy enhancement of multi-axis CNC machines through on-line neurocompensation. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing 11: 535–545
Fan C., Collins E. G., Liu C., Wang B. (2003) Radial error feedback geometric adaptive control for bar turning in CNC turning centers. ASME Journal of Manufacturing Science and Engineering 125: 77–84
Hatamura Y., Nagao T., Mitsuishi M., Kato K., Taguchi S., Okumura T. et al (1993) Development of an intelligent machining center incorporating active compensation for thermal distortion. Annals of CIRP 42: 549–552
Hinduja S., Mladenov D., Burdekin M. (2003) Assessment of force-induced errors in CNC turning. Annals of CIRP 52(1): 329–332
Lippmann R. P. (1987) An introduction to computing with neural nets. IEEE ASSP Magazine 2: 4–22
Li X., Venuvinod P. K., Djorjevich A., Liu Z. (2001) Predicting machining errors in turning using hybrid learning. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology 18: 863–872
Mehrabi M. G., Pszuba P., O’Neal G., Min B. K., Pasek Z., Koren Y. (2002) Geometric error compensation in line boring process. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing 13(5): 371–379
Phan A. V., Baron L., Mayer J. R. R., Cloutier G. (2003) Finite element and experimental studies of diametral errors in cantilever bar turning. Applied Mathematical Modelling 27: 221–232
Rashid M. K. (2005) Simulation study on the improvements of machining accuracy by using smart materials. Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing 21: 249–257
Rashid M. K., Al-Araimi S. A. (2005) Fuzzy algorithm and structural stiffness in error attenuation of intelligent toolpost. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing 16: 277–286
Suneel T. S., Pande S. S. (2000) Intelligent tool path correction for improving profile accuracy in CNC turning. International Journal of Production Research 38(14): 3181–3202
Topal, E. S. (2003). Investigation and computer aided compensation of cutting force induced machining errors in CNC Turning. Ph.D. Thesis, Erciyes University (in Turkish).
Topal E. S., Çoğun C. (2005) A cutting force induced error elimination method for turning operations. Journal of Materials Processing Technology 170: 192–203
Ülker, E., Turanalp, M. E., & Halkaci, H. S. (2009). An artificial immune system approach to CNC tool path generation. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 20, 67–77.
Yang S., Yuan J., Ni J. (1997) Real-time cutting force induced error compensation on a turning center. International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture 37(11): 1597–1610
Zhang J. Y., Liang S. Y., Yao J., Chen J. M., Huang J. L. (2006) Evolutionary optimization of machining processes. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing 17: 203–215
Ziegert J. C., Kalle P. (1994) Error compensation in machine tools; a neural network approach. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing 5: 143–151
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Topal, E.S., Çoğun, C. Computer-based estimation and compensation of diametral errors in CNC turning of cantilever bars. J Intell Manuf 22, 853–865 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-009-0360-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-009-0360-0