Abstract
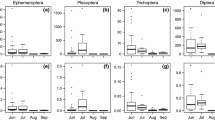
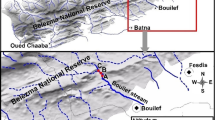
Riffle beetles (Coleoptera: Elmidae) are freshwater insects, and both adult and larval stages primarily inhabit running water. Therefore, environmental factors such as current velocity and substrate characteristics are crucial for the habitat of elmid beetles. The effects of substrate size structure, water depth, current velocity, and distance from terrestrial areas were evaluated for the adult and larval abundance of three common riffle beetles, Stenelmis nipponica Nomura, Zaitzevia awana (Kono), and Zaitzeviaria brevis (Nomura), and other cohabiting aquatic insects in a middle reach of the Mukogawa River, western Japan. The substrate size structure was summarized using principal component analysis, and the effects of environmental factors were analyzed using best subsets multiple regression. In summer (August), the three elmid species tended to be more abundant in the shallow quadrats of coarse-grained substrates, and substrate preference differed among species and stages. Current velocity and proximity to the terrestrial area were not significant for S. nipponica and Z. brevis, whereas adult Z. awana preferred faster-flowing currents and needed to the distance from the terrestrial areas. In winter (December), only the substrate size structure affected the abundance of adult elmid beetles. Although elmid beetles require highly sensitive habitats, they are easily surveyed. Therefore, they are convenient indicators of riverbed environments.
Implications for insect conservation
Preference of substrate sand size as their habitat differ among stages and seasons. Diverse substrate condition would be needed to conserve elmid beetles.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguilera-Giraldo IA, Vásquez-Ramos JM (2019) Distribución espacial y temporal de Elmidae (Insecta: Coleoptera) y su relación con los parámetros fisicoquímicos en el río Ocoa, Meta, Colombia. Rev Acad Colomb Cienc Ex Fis Nat 43:108–119
Bowles DE, Barr CB, Stanford R (2003) Habitat and phenology of the endangered riffle beetle Heterelmis comalensis and a coexisting species, Microcylloepus pusillus, (Coleoptera: Elmidae) at Comal Springs, Texas, USA. Arch Hydrobiol 156:361–383
Braun BM, Pires MM, Stenert C, Maltchik L, Kotzian CB (2018) Effects of riparian vegetation width and substrate type on riffle beetle community structure. Entomol Sci 21:66–75
Brown HP (1987) Biology of riffle beetles. Annu Rev Entomol 32:253–273
Burgherr P, Ward JV (2001) Longitudinal and seasonal distribution patterns of the benthic fauna of an alpine glacial stream (Val Roseg, Swiss Alps). Freshw Biol 46:1705–1721
Collier KJ (2004) Invertebrate community dynamics in soft-bottomed streams of northern New Zealand: a spatio-temporal hierarchy. New Zeal J Mar Fresh 38:1–18
Collier KJ, Quinn JM (2003) Land-use influences macroinvertebrate community response following a pulse disturbance. Freshw Biol 48:1462–1481
Cooke M, Longley G, Gibson R (2015) Spring association and microhabitat preferences of the Comal Springs riffle beetle (Heterelmis comalensis). Southwest Nat 60:110–121
Degani G, Herbst GN, Ortal R, Bromley HJ, Levanon D, Netzer Y, Harari N, Glazman H (1993) Relationship between current velocity, depth and the invertebrate community in a stable river system. Hydrobiologia 263:163–172
Dietrich F, Waringer JA (1999) Distribution patterns and habitat characterization of Elmidae and Hydraenidae (Insecta: Coleoptera) in the Weidlingbach near Vienna, Austria. Int Rev Hydrobiol 84:1–15
Elliott JM (2008) The ecology of riffle beetles (Coleoptera: Elmidae). Freshw Rev 1:189–203
Godbout L, Hynes HBN (1982) The three dimensional distribution of the fauna in a single riffle in a stream in Ontario. Hydrobiologia 97:87–96
González-Córdoba M, Zúñiga MC, Giraldo LP, Ramírez YP, Chará J (2020) Sensibilidad de Elmidae (Insecta: Coleoptera) a la perturbación del hábitat y la calidad fisicoquímica del agua en ambientes lóticos de los Andes colombianos. Rev Biol Trop 68:601–622
Hayashi M, Sota T (2019) Physical gills in Elmidae (Coleoptera: Byrrhoidea): Structure and evolutionary pattern of plastron in Stenelmis and related genera. Entomol Sci 22:157–160
Jäch MA, Balke M (2008) Global diversity of water beetles (Coleoptera) in freshwater. Hydrobiologia 595:419–442
Kawai T, Tanida K (2005) Aquatic insects of Japan: Manual with keys and illustrations. Tokai University press, Kanagawa. (In Japanese.)
Kobayashi F (2002) Intrabasinal watershed between Mukogawa and Kakogawa River systems in the western part of the Sanda Basin, Hyogo Prefecture, West Japan. Hum Nat 13:29–35 (In Japanese with English abstract.)
Lloyd F, Sites RW (2000) Microhabitat associations of three species of Dryopoidea (Coleoptera) in an Ozark stream: a comparison of substrate, and simple and complex hydraulic characters. Hydrobiologia 439:103–114
Malmqvist B, Sjöström P (1983) The microdistribution of three beetle species inhabiting a South Swedish stream riffle. Acta Hydrobiol 25/26:409–414
McCreadie JW, Bedwell C (2014) Species composition of local riffle beetle (Coleoptera: Elmidae) assemblages in small coastal streams of the Gulf of Mexico: the influences of local and regional factors. Aquat Ecol 48:127–141
Murvosh CM (1971) Ecology of the water penny beetle Psephenus herricki (DeKay). Ecol Monogr 41:79–96
Nair P, Hunter AH, Worsham MLD, Stehle M, Randy Gibson J, Nowlin WH (2019) Sexual dimorphism in three species of Heterelmis Sharp (Coleoptera: Elmidae). Coleopterists Bull 73:1075–1083
Ogata T (2000) Effect of surfactants to aquatic insects with plastron respiration. Jap J Environ Toxicol 3:83–83 (In Japanese with English abstract.)
Ogata T, Nakajima J (2006) Elmid Beetles of Fukuoka Prefecture, Northern Kyushu, Japan.Bulletin of the Hoshizaki Green Foundation 9:227–243. (In Japanese with English abstract.)
Olsen DA, Townsend CR (2003) Hyporheic community composition in a gravel-bed stream: influence of vertical hydrological exchange, sediment structure and physicochemistry. Freshw Biol 48:1363–1378
Quinn JM, Hickey CW (1990a) Magnitude of effects of substrate particle size, recent flooding, and catchment development on benthic invertebrates in 88 New Zealand rivers. New Zeal J Mar Fresh 24:411–427
Quinn JM, Hickey CW (1990b) Characterisation and classification of benthic invertebrate communities in 88 New Zealand rivers in relation to environmental factors. New Zeal J Mar Fresh 24:387–409
Reice SR (1994) Nonequilibrium determinant of biological community structure. Am Sci 82:424–435
Sato M (1985) Elmidae. In Ueno, Kurosawa, Sato (eds) “Genshoku Nihon kochu Zukan II”, pp.434–440. (In Japanese.)
Shiyake S, Beetle Team of Yamatogawa River Research Group (2008) Fauna and distribution of the riffle beetles(Coleoptera: Elmidae)in Yamatogawa River system, central Japan. Bull Osaka Museum Nat History 62:47–64 (In Japanese with English abstract.)
Thorpe WH (1950) Plastron respiration in aquatic insects. Biol Rev 25:344–390
Tominaga O, Shiyake S, Beetle Team of Yodogawa River Research Group (Project Y2, Osaka Museum of Natural History) (2012) Fauna and distribution of the families of Dryopidae and Elmidae (Coleoptera) in the Yodogawa River system, central Japan. Bull Osaka Museum Nat History 66:19–38 (In Japanese with English abstract.)
Yoshimura M (2012) Effects of forest disturbances on aquatic insect assemblages. Entomol Sci 15:145–154
Yoshitomi H, Shiragane A, Hikida N (1999) The fauna of Elmidae and Dryopidae in the Yahagi River system. Rep Yahagi River Inst 3:95–116 (In Japanese with English summary.)
Acknowledgements
We thank Mr. T. Yasuoka, Mr. D. Yamashita and Mr. D. Nakase for helping with fieldwork. Our cordial thanks are also due to Mr. Tsuyoshi Yagi, Museum of Nature and Human Activities, Sanda, for keeping the voucher specimens.
Funding
No funding was received to assist with the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Mr. J. Fujiwara did the study of conceptualization, investigation, visualization, writing original draft, review & editing. Dr. K. Maeto did the study of analysis, writing original draft, review & editing. Dr. M. Yoshimura did the study of conceptualization, analysis, writing original draft, review & editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Fujiwara, J., Maeto, K. & Yoshimura, M. Effect of environmental factors on the abundance of riffle beetles (Coleoptera: Elmidae) and co-inhabiting aquatic insects within a reach scale, in Japan. J Insect Conserv 26, 893–906 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10841-022-00434-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10841-022-00434-y