Abstract
Background
The risk of complications has been shown to be lower with subcutaneous implantable defibrillator (S-ICD) than with conventional ICDs. Given the low frequency of complications, experience of how to manage them is limited. In this paper, we describe generator- and lead-related complications recorded in a series of S-ICD patients, and we propose our conservative approach to managing them.
Methods
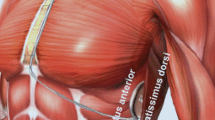
The study cohort consisted of S-ICD patients who were referred to our institution owing to generator- or lead-related complications requiring surgical intervention. With our “shift and cover” approach, the system component involved is moved from its original position to an alternative, more protected location. In the case of the generator, this involves moving it to an intermuscular pocket. In the case of infections at the parasternal scar, the electrode sleeve is moved away from its original location, stitched, and then covered with the muscular fascia.
Results
Fourteen S-ICD patients were referred to our institution owing to system-related complications. Complications involved the generator in 7 cases (deep pocket infections with erosion, extrusion, or pain), the lead in 5 cases (parasternal infections at the xyphoid incision site), and both the generator and the lead in 2 cases. Complications were managed without completely removing the device and resolved in a single surgical session with no intraoperative complications. During defibrillation testing, the first shock at 65 J was effective in all patients. The shock impedance after revision was significantly lower than that measured during first implantation (59 ± 10 Ohm versus 86 ± 24 Ohm, P = 0.013). In all cases, the cosmetic result was satisfactory. No complications or recurrent infections were reported at the 12-month follow-up visit.
Conclusions
The proposed conservative approach was successful in managing S-ICD complications. The revision procedure allowed to optimize the system configuration in terms of the defibrillation vector, resulting in lower shock impedance values and better device positioning.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Weiss R, Knight BP, Gold MR, Leon AR, Herre JM, Hood M, Rashtian M, Kremers M, Crozier I, Lee KL, Smith W, Burke MC. Safety and efficacy of a totally subcutaneous implantable-cardioverter defibrillator. Circulation. 2013;128:944–53.
Priori SG, Blomström-Lundqvist C, Mazzanti A, Blom N, Borggrefe M, Camm J, Elliott PM, Fitzsimons D, Hatala R, Hindricks G, Kirchhof P, Kjeldsen K, Kuck KH, Hernandez-Madrid A, Nikolaou N, Norekvål TM, Spaulding C, Van Veldhuisen DJ, ESC Scientific Document Group. ESC Guidelines for the management of patients with ventricular arrhythmias and the prevention of sudden cardiac death: The Task Force for the Management of Patients with Ventricular Arrhythmias and the Prevention of Sudden Cardiac Death of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Endorsed by: Association for European Paediatric and Congenital Cardiology (AEPC). Eur Heart J. 2015;36:2793–867.
Knops RE, van der Stuijt W, Smeding L. Subcutaneous or transvenous defibrillator therapy. Reply N Engl J Med. 2021;384:678–9.
Rordorf R, Casula M, Pezza L, Fortuni F, Sanzo A, Savastano S, Vicentini A. Subcutaneous versus transvenous implantable defibrillator: an updated meta-analysis. Heart Rhythm. 2021;18:382–91.
Droghetti A, Basso Ricci E, Scimia P, Harizai F, Marini M. Ultrasound-guided serratus anterior plane block combined with the two-incision technique for subcutaneous ICD implantation. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2018;41:517–23.
Winter J, Siekiera M, Shin DI, Meyer C, Kröpil P, Clahsen H, O’Connor S. Intermuscular technique for implantation of the subcutaneous implantable cardioverter defibrillator: long-term performance and complications. Europace. 2017;19:2036–41.
Francia P, Biffi M, Adduci C, Ottaviano L, Migliore F, De Bonis S, Dello Russo A, De Filippo P, Viani S, Bongiorni MG, Caravati F, Lavalle C, Landolina ME, Pisanò E, Giorgi D, Lovecchio M, Valsecchi S, Diemberger I. Implantation technique and optimal subcutaneous defibrillator chest position: a PRAETORIAN score-based study. Europace. 2020;22:1822–9.
Burke MC, Gold MR, Knight BP, Barr CS, Theuns DAMJ, Boersma LVA, Knops RE, Weiss R, Leon AR, Herre JM, Husby M, Stein KM, Lambiase PD. Safety and efficacy of the totally subcutaneous implantable defibrillator: 2-year results from a pooled analysis of the IDE study and EFFORTLESS Registry. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2015;65:1605–15.
Lambiase PD, Theuns DA, Murgatroyd F, Barr C, Eckardt L, Neuzil P, Scholten M, Hood M, Kuschyk J, Brisben AJ, Carter N, Stivland TM, Knops R, Boersma LVA. Subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillators: long-term results of the EFFORTLESS study. Eur Heart J. 2022;28:ehab921.
Ziacchi M, Bisignani G, Palmisano P, Scalone A, Martignani C, Elvira Mocavero P, Caravati F, Della Cioppa N, Mazzuero A, Pecora D, Vicentini A, Landolina ME, Debonis S, Scimia P, Lovecchio M, Valsecchi S, Diemberger I, Droghetti A. Serratus anterior plane block in subcutaneous implantable cardioverter defibrillator implantation: a case-control analysis. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2020;31:144–9.
Droghetti A, Fusco P, Marini M, Harizai F, Scimia P. Ultrasound-guided serratus anterior plane block and parasternal block in cooperative sedation for S-ICD implantation. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2019;42:1076–8.
Botto GL, Forleo GB, Capucci A, Solimene F, Vado A, Bertero G, Palmisano P, Pisanò E, Rapacciuolo A, Infusino T, Vicentini A, Viscusi M, Ferrari P, Talarico A, Russo G, Boriani G, Padeletti L, Lovecchio M, Valsecchi S, D’Onofrio A. ‘AIAC S-ICD Why Not’ Survey Investigators. The Italian subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator survey: S-ICD, why not? Europace. 2017;19:1826–32.
Blomström-Lundqvist C, Traykov V, Erba PA, Burri H, Nielsen JC, Bongiorni MG, Poole J, Boriani G, Costa R, Deharo JC, Epstein LM, Sághy L, Snygg-Martin U, Starck C, Tascini C, Strathmore N. European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA) international consensus document on how to prevent, diagnose, and treat cardiac implantable electronic device infections-endorsed by the Heart Rhythm Society (HRS), the Asia Pacific Heart Rhythm Society (APHRS), the Latin American Heart Rhythm Society (LAHRS), International Society for Cardiovascular Infectious Diseases (ISCVID), and the European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ESCMID) in collaboration with the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS). Eur Heart J. 2020;41:2012–32.
Le KY, Sohail MR, Friedman PA, Uslan DZ, Cha SS, Hayes DL, Wilson WR, Steckelberg JM, Baddour LM. Mayo Cardiovascular Infections Study Group. Impact of timing of device removal on mortality in patients with cardiovascular implantable electronic device infections. Heart Rhythm. 2011;8:1678–85.
Lopez JA. Conservative management of infected pacemaker and implantable defibrillator sites with a closed antimicrobial irrigation system. Europace. 2013;15:541–5.
Puri R, Psaltis PJ, Nelson AJ, Sanders P, Young GD. Povidone-iodine irrigation — a possible alternative to lead extraction. Indian Pacing Electrophysiol J. 2011;11:115–9.
Poller WC, Schwerg M, Melzer C. Therapy of cardiac device pocket infections with vacuum-assisted wound closure-long-term follow-up. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2012;35:1217–21.
Kusumoto FM, Schoenfeld MH, Wilkoff BL, Berul CI, Birgersdotter-Green UM, Carrillo R, Cha YM, Clancy J, Deharo JC, Ellenbogen KA, Exner D, Hussein AA, Kennergren C, Krahn A, Lee R, Love CJ, Madden RA, Mazzetti HA, Moore JC, Parsonnet J, Patton KK, Rozner MA, Selzman KA, Shoda M, Srivathsan K, Strathmore NF, Swerdlow CD, Tompkins C, Wazni O. 2017 HRS expert consensus statement on cardiovascular implantable electronic device lead management and extraction. Heart Rhythm. 2017;14:e503–51.
Brouwer TF, Driessen AHG, Olde Nordkamp LRA, Kooiman KM, de Groot JR, Wilde AAM, Knops RE. Surgical management of implantation-related complications of the subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator. JACC Clin Electrophysiol. 2016;2:89–96.
Baddour LM, Weiss R, Mark GE, El-Chami MF, Biffi M, Probst V, Lambiase PD, Miller MA, McClernon T, Hansen LK, Knight BP. Diagnosis and management of subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator infections based on process mapping. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2020;43:958–65.
Francia P, Adduci C, Angeletti A, Ottaviano L, Perrotta L, De Vivo S, Bongiorni MG, Migliore F, Russo AD, De Filippo P, Caravati F, Nigro G, Palmisano P, Viani S, D’Onofrio A, Lovecchio M, Valsecchi S, Ziacchi M. Acute shock efficacy of the subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator according to the implantation technique. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2021;32:1695–703.
D’Onofrio A, Pieragnoli P, Biffi M, Nigro G, Migliore F, Francia P, De Filippo P, Capucci A, Botto GL, Giammaria M, Palmisano P, Pisanò E, Bisignani G, La Greca C, Sarubbi B, Sala S, Viscusi M, Landolina M, Lovecchio M, Valsecchi S, Bongiorni MG. “S-ICD Rhythm Detect″ Investigators. Subcutaneous implantable cardioverter defibrillator implantation: an analysis of Italian clinical practice and its evolution. Int J Cardiol. 2018;272:162–7.
Amin AK, Gold MR, Burke MC, Knight BP, Rajjoub MR, Duffy E, Husby M, Stahl WK, Weiss R. Factors associated with high-voltage impedance and subcutaneous implantable defibrillator ventricular fibrillation conversion success. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2019;12:e006665.
Heist EK, Belalcazar A, Stahl W, Brouwer TF, Knops RE. Determinants of subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-Defibrillator efficacy: a computer modeling study. JACC Clin Electrophysiol. 2017;3:405–14.
Biffi M, Bongiorni MG, D’Onofrio A, Manzo M, Pieragnoli P, Palmisano P, Ottaviano L, Perego GB, Pangallo A, Lavalle C, Bonfantino V, Nigro G, Landolina ME, Katsouras G, Diemberger I, Viani S, Bianchi V, Lovecchio M, Valsecchi S, Ziacchi M. “S-ICD Rhythm Detect” Investigators. Is 40 joules enough to successfully defibrillate with subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillators? JACC Clin Electrophysiol. 2021;7:767–76.
Boersma L, Barr C, Knops R, Theuns D, Eckardt L, Neuzil P, Scholten M, Hood M, Kuschyk J, Jones P, Duffy E, Husby M, Stein K, Lambiase PD. EFFORTLESS Investigator Group. Implant and midterm outcomes of the subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator registry: The EFFORTLESS study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2017;70:830–41.
van der Stuijt W, Quast ABE, Baalman SWE, de Wilde KC, Brouwer TF, Wilde AAM, Knops RE. Complications related to elective generator replacement of the subcutaneous implantable defibrillator. Europace. 2021;23:395–9.
Smietana J, Frankel DS, Serletti JM, Arkles J, Pothineni NVK, Marchlinski FE, Schaller RD. Subserratus implantation of the subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator. Heart Rhythm. 2021;18:1799–804.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Luca Auricchio (Boston Scientific) for his valuable collaboration in the critical revision of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
Dr. Andrea Droghetti and Dr. Luca Ottaviano are consultants for Boston Scientific. The other authors report no conflicts.
Informed consent
Before the procedure, each patient signed an informed consent form approved by the institutional review board.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Droghetti, A., Pecora, D., Maffè, S. et al. “Shift and cover technique”: conservative management of complications for the rescue of S-ICD subcutaneous implantable defibrillator systems. J Interv Card Electrophysiol (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10840-022-01312-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10840-022-01312-y