Abstract
Purpose
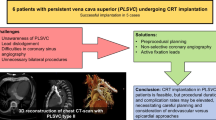
The persistent left superior vena cava (PLSVC) is usually asymptomatic and creates a challenge when detected incidentally during cardiac resynchronization therapy defibrillator (CRT-D) implantation. The purpose of our cases is to show different anatomical variables of PLSVC and different strategies used for CRT-D implantation.
Methods
Four cases of PLSVC were presented. Pre-procedural bilateral venography was done to define anatomical variant of PLSVC. The side of approach and vein of approach were chosen according to the anatomical variant. Major challenges, electrical parameters, procedural times, long-term follow up, and complications were addressed.
Results
Two cases were de novo CRT-D implantation. One case was an extraction/re-implantation of the coil lead, and one case was an upgrading. In one case, CRT-D implantation was followed by AVN ablation. All cases had successful devices implantation. Two cases had isolated PLSVC: one of them had right approach and the other had left approach. One case had double SVC with no connecting brachiocephalic veins and underwent a left-sided approach. One case had double SVC with a small connecting brachiocephalic vein and had a left approach for implantation with using the small brachiocephalic vein for the RV lead. Electrical parameters were acceptable for all leads implanted. Long-term follow-up was done for 6 months to 5 years. One complication occurred (acute atrial lead dislodgement).
Conclusions
In our case series, the presence of PLSVC did not preclude successful placement of pacemaker/defibrillator leads using standard tools. Bilateral venography helped to decide the side and vein of lead insertion.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data support the published claims and comply with field standards.
References
Zhong YL, Long X-M, Jiang L-Y, He B-F, Lin H, Luo P, et al. Surgical treatment of dextroversion, isolated persistent left superior vena cava draining into the left atrium. J Card Surg. 2015;30(10):767–70.
Elison B, Evans D, Zanders T, Jeanmonod R. Persistent left superior vena cava draining into the pulmonary venous system discovered after central venous catheter placement. Am J Emerg Med. 2014;32(8):943.e1–3.
Lai YC, Goh JC, Lim SH, Seah TG. Difficult pulmonary artery catheterization in a patient with persistent left superior vena cava. Anaesth Intensive Care. 1998;26(6):671–3.
Tak T, Crouch E, Drake GB. Persistent left superior vena cava: incidence, significance and clinical correlates. Int J Cardiol. 2002;82(1):91–3. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-5273(01)00586-1.
Schummer W, Schummer C, Frober R. Persistent left superior vena cava and central venous catheter position: clinical impact illustrated by four cases. SurgRadiol Anat. 2003;25(3–4):315–21. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-003-0138-6.
Golzio PG, Franco E, Chiribiri A. Atrio-ventricular synchronization by single VDD lead inserted through persistent left superior vena cava in patient with Turner's syndrome. Pacing ClinElectrophysiol. 2006;29(10):1181–2. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1540-8159.2006.00513.x.
Schummer W, Schummer C, Fröber R. Persistent left superior vena cava and central venous catheter position: clinical impact illustrated by four cases. SurgRadiol Anat. Jul-Aug 2003;25(3–4):315–21.
Sinha SK, Goel A, Razi M, et al. Permanent pacemaker implantation in patients with isolated persistent left superior vena cava from a right-sided approach: technical considerations and follow-up outcome. Cardiol Res. 2019;10(1):18–23. https://doi.org/10.14740/cr784.
Anselmino M, Marocco MC, Amellone C, Massa R. Hybrid right-left cardiac resynchronization therapy defibrillator implantation in persistent left superior vena cava. Europace. 2009;11(4):533–4. https://doi.org/10.1093/europace/eun371.
Zerbe F, Bornakowski J, Sarnowski W. Pacemaker electrode implantation in patients with left superior vena cava. Br Heart J. 1992;67:65–6.
Gaba D, Kittusamy P, Ho RT, Pavri B, Greenspon AJ. Permanent pacing from a left ventricular vein in a patient with persistent left superior vena cava and absent right superior vena cava. J Intervent Card Electrophysiol. 2003;9:357–60.
Daccarett M, Pai RK, Abedin M, Segerson NM, Hamdan MH. A novel technique for right ventricular lead placement in a patient with a persistent left superior vena cava. Europace. 2007;9:200–1.
Williams TA Jr, Abe O, Mitre CA, Kassotis J. Low defibrillation threshold in a patient with a dual-coil defibrillator lead implanted through a persistent left superior vena cava. Pacing ClinElectrophysiol. 2012;35(9):e274–5. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1540-8159.2012.03432.
Beig JR, Dar MI, Tramboo NA, Hafeez I, Lone AA, Rather HA. An innovation in pacemaker lead implantation via persistent left superior vena cava: the "3D alpha curve" stylet. Pacing ClinElectrophysiol. 2017;40(9):1042–4. https://doi.org/10.1111/pace.13075.
Mora G. A novel method of placing right ventricular leads in patients with persistent left superior vena cava using a conventional J stylet. Indian Pacing Electrophysiol J. 2014;14:65–74.
Kumar S, Moorthy N, Kapoor A, Sinha N. A challenging dual chamber permanent pacemaker implantation in persistent left superior vena cava with absent right superior vena cava. J Cardiol Cases. 2012;5(2):e122–4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jccase.2011.12.003.
Roberts DH, Bellamy CM, Ramsdale DR. Implantation of a dual chamber pacemaker in a patient with persistent left superior vena cava. Int J Cardiol. 1992;36(2):242–3. https://doi.org/10.1016/0167-5273(92)90017-W.
Zardo F, Nicolosi GL, Burelli C, Zanuttini D. Dual-chamber transvenous pacemaker implantation via anomalous left superior vena cava. Am Heart J. 1986;112(3):621–2. https://doi.org/10.1016/0002-8703(86)90534-X.
Chen X, Yu Z, Bai J, Wang W, Qin S, Wang J, et al. Transvenous cardiac implantable electronic device implantation in patients with persistent left superior vena cava in a tertiary center. J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 2018;53(2):255–62. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10840-018-0377-4.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not Applicable.
Consent for publication
Not required as information is anonymized and the submission does not include images that may identify the person.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bontempi, L., Aboelhassan, M., Cerini, M. et al. Technical considerations for CRT-D implantation in different varieties of persistent left superior vena cava. J Interv Card Electrophysiol 61, 517–524 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10840-020-00843-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10840-020-00843-6