Abstract
Purpose
Since the introduction of the Biotronik Linox S/SD leads in 2006, there have been multiple reports of premature lead failure. The purpose of this study was to investigate the longevity of the Linox S/SD leads and to identify the possible predictors of lead failure in a single tertiary implant center.
Methods
We retrospectively reviewed patients who underwent implantation of Linox S/SD leads or Sorin Vigila 1CR/2CR leads (the same Linox S/SD leads marketed by Sorin) at our center. The cumulative lead survival was estimated using the Kaplan-Meier curve, and variables associated with lead failure were assessed by Cox proportional hazard model.
Results
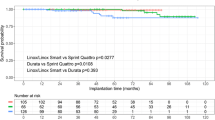
A total of 187 patients (154 (82%) male) underwent Linox S/SD or Vigila 1CR/2CR implantation between 2007 and 2013. During follow-up with a median time of 75 months, nine lead failures were identified (4.8%). The mean and median times from lead implantation to lead failure were 70.7 ± 21 months and 64 (45–111) months, respectively. The cumulative survival probability for the Linox S/SD at 5 years was 97.1% and at 12 years was 90.3%. Non-physiological high-rate sensing was the most common type of lead failure in patients. In two-thirds of these patients, this led to inappropriate shock. We did not find any significant relationships between patients’ clinical and procedural characteristics and lead failure.
Conclusions
At our center, the 5-year lead survival of the Linox S/SD has been better than reports from other centers. The majority of lead failures presented as non-physiological high-rate sensing with subsequent inappropriate therapy.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Khatib SM, Stevenson WG, Ackerman MJ, Bryant WJ, Callans DJ, Curtis AB, et al. 2017 AHA/ACC/HRS Guideline for management of patients with ventricular arrhythmias and the prevention of sudden cardiac death: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines and the Heart Rhythm Society. Circulation. 2018;138:e272–391.
De Maria E, Borghi A, Bonetti L, Fontana PL, Cappelli S. Externalized conductors and insulation failure in Biotronik defibrillator leads: history repeating or a false alarm? World J Clin Cases. 2017;5(2):27–34.
Lam A, Buehler S, Goulouti E, Sweda R, Haeberlin A, Medeiros-Domingo A, et al. Comparison of lead failure manifestation of Biotronik Linox with St. Jude Medical Riata and Medtronic Sprint Fidelis lead. J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 2019;54:161–70.
Biotronik Product Performance Report, 2017. https://www.biotronik.com/en-us/ healthcare-professionals/product-performance-report.
Noti F, Lam A, Klossner N, Seiler J, Servatius H, Medeiros-Domingo A, et al. Failure rate and conductor externalization in the Biotronik Linox/Sorin Vigila implantable cardioverter-defibrillator lead. Heart Rhythm. 2016;13:1075–82.
Padfield GJ, Steinberg C, Karim SS, Tung S, Bennett MT, Le Maitre JP, et al. Early failure of the Biotronik Linox implantable cardioverter-defibrillator lead. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2015;26:274–81.
Howe AJ, McKeag NA, Wilson CM, Ashfield KP, Roberts MJ. Insulation failure of the Linox defibrillator lead: a case report and retrospective review of a single center experience. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2015;26:686–9.
van Malderen SCH, Szili-Torok T, Yap SC, Hoeks SE, Zijlstra F, Theuns DAMJ. Comparative study of the failure rates among 3 implantable defibrillator leads. Heart Rhythm. 2016;13:2299–305.
Manfredi JA, Smithgall SM, Kircher CM, Lollis MA. Insulation failure with externalized conductor of a Linox SD lead: a case report. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2014;25:440–1.
Kawada S, Nishii N, Morimoto Y, Miyoshi A, Tachibana M, Sugiyama H, et al. Comparison of longevity and clinical outcomes of implantable cardioverter-defibrillator leads among manufactures. Heart Rhythm. 2017;14:1496–503.
O’Connor M, Hooks D, Webber M, Shi B, Morrison S, Harding S, et al. Long-term single-center comparison of ICD lead survival: evidence for premature Linox lead failure. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2018;29(7):1024–31.
Marai I, Milman A, Nof E, Gurevitz O, Barlev D, Lipchenca I, et al. Performance of the Linox implantable cardioverter defibrillator leads: a single-center experience. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2019;42(12):1524–8.
McKeag NA, Noad RL, Ashfield K, Wilson CM, McEneaney DJ, Roberts MJD. Prospective assessment of Linox implantable cardioverter defibrillator leads for structural or electrical abnormalities. Adv Ther. 2018;35(5):666–70.
Good ED, Cakulev I, Orlov MV, Hirsh D, Simeles J, Mohr K, et al. Long-term evaluation of Biotronik Linox and Linox (smart) implantable cardioverter defibrillator leads. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2016;27(6):735–42.
Díez DP, Rubín JM, Cuervo DC, Iglesias DG, De La Tassa CM. Analysis of early failure of Biotronik Linox Smart implantable cardioverter-defibrillator leads: a comparative study of three defibrillator leads. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2018;41(9):1165–70.
Guédon-Moreau L, Lacroix D, Sadoul N, Clémenty J, Kouakam C, Hermida JS, et al. A randomized study of remote follow-up of implantable cardioverter defibrillators: safety and efficacy report of the ECOST trial. Eur Heart J. 2013;34(8):605–14.
Varma N, Michalski J, Epstein AE, Schweikert E. Automatic remote monitoring of implantable cardioverter-defibrillator lead and generator performance: the Lumos-T Safely RedUceS RouTine Office Device Follow-Up (TRUST) trial. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2010;3(5):428–36.
Varma N. Remote monitoring for advisories: automatic early detection of silent lead failure. PACE. 2009;32(4):525–7.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alasti, M., Machado, C., Mirzaee, S. et al. Long-term longevity and clinical outcomes of Linox S/SD implantable cardioverter-defibrillator leads: a single-center experience. J Interv Card Electrophysiol 61, 115–121 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10840-020-00787-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10840-020-00787-x