Abstract
Background
Damage to the cardiac conduction system requiring permanent pacemaker (PPM) implantation is a known adverse outcome of transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR). A permanent-temporary pacemaker (PTPM) is a device that involves an active-fixation lead attached to an external pulse generator taped to the skin. We reviewed the utility of PTPMs as a temporary bridge measure after TAVR in patients with conduction abnormalities that do not meet conventional criteria for PPM placement.
Methods
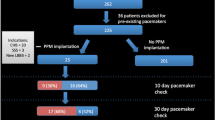
Between January 01, 2013 and December 31, 2015, we analyzed 67 patients who received PTPM after TAVR. Baseline demographics, comorbidities, type and size of the valve, pre-TAVR electrocardiograms (ECGs), post-TAVR ECGs at 1 day, 1 month, and 6 months, and pacemaker interrogation results were reviewed for each patient if available.
Results
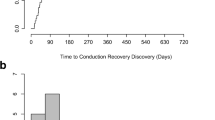
The mean age of patients was 80.5 ± 9.1 years. PTPM were placed for 2.3 ± 2.4 days. Among these patients, 44.8% (n = 30) received a PPM prior to discharge. Male gender (OR 2.84, 95% CI 1.05–7.69, p = 0.05) and an increase in QRS duration post-TAVR (p = 0.01) were associated with PPM placement. Pacemaker interrogation data of 11 patients with PPM revealed that 27% (n = 3) had < 1% V-pacing requirements and < 10% A-pacing requirements.
Conclusions
In post-TAVR patients who develop conduction abnormalities that do not meet conventional PPM implantation indications, PTPM safely provides a time period for further assessment and may prevent unnecessary PPM implantation. Male gender and an increase in QRS duration post-TAVR are associated with PPM implantation. Additionally, some patients may recover from their conduction disturbances and demonstrate low pacemaker utilization.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Leon MB, Smith CR, Mack M, Miller DC, Moses JW, Svensson LG, et al. Transcatheter aortic-valve implantation for aortic stenosis in patients who cannot undergo surgery. N Engl J Med. 2010;363(17):1597–607. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1008232.
Leon MB, Smith CR, Mack MJ, Makkar RR, Svensson LG, Kodali SK, et al. Transcatheter or surgical aortic-valve replacement in intermediate-risk patients. N Engl J Med. 2016;374(17):1609–20. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1514616.
Smith CR, Leon MB, Mack MJ, Miller DC, Moses JW, Svensson LG, et al. Transcatheter versus surgical aortic-valve replacement in high-risk patients. N Engl J Med. 2011;364(23):2187–98. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1103510.
Walther T, Hamm CW, Schuler G, Berkowitsch A, Kotting J, Mangner N, et al. Perioperative results and complications in 15,964 transcatheter aortic valve replacements. Prospective Data From the GARY Registry J Am Coll Cardiol. 2015;65(20):2173–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2015.03.034.
Genereux P, Head SJ, Van Mieghem NM, Kodali S, Kirtane AJ, Xu K, et al. Clinical outcomes after transcatheter aortic valve replacement using valve academic research consortium definitions: a weighted meta-analysis of 3,519 patients from 16 studies. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012;59(25):2317–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2012.02.022.
Webb JG, Altwegg L, Boone RH, Cheung A, Ye J, Lichtenstein S, et al. Transcatheter aortic valve implantation: impact on clinical and valve-related outcomes. Circulation. 2009;119(23):3009–16. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.108.837807.
Popma JJ, Adams DH, Reardon MJ, Yakubov SJ, Kleiman NS, Heimansohn D, et al. Transcatheter aortic valve replacement using a self-expanding bioprosthesis in patients with severe aortic stenosis at extreme risk for surgery. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014;63(19):1972–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2014.02.556.
Meredith Am IT, Walters DL, Dumonteil N, Worthley SG, Tchetche D, Manoharan G, et al. Transcatheter aortic valve replacement for severe symptomatic aortic stenosis using a repositionable valve system: 30-day primary endpoint results from the REPRISE II study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014;64(13):1339–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2014.05.067.
Siontis GC, Juni P, Pilgrim T, Stortecky S, Bullesfeld L, Meier B, et al. Predictors of permanent pacemaker implantation in patients with severe aortic stenosis undergoing TAVR: a meta-analysis. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014;64(2):129–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2014.04.033.
Nazif TM, Dizon JM, Hahn RT, Xu K, Babaliaros V, Douglas PS, et al. Predictors and clinical outcomes of permanent pacemaker implantation after transcatheter aortic valve replacement: the PARTNER (Placement of AoRtic TraNscathetER Valves) trial and registry. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2015;8(1 Pt A):60–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcin.2014.07.022.
Guetta V, Goldenberg G, Segev A, Dvir D, Kornowski R, Finckelstein A, et al. Predictors and course of high-degree atrioventricular block after transcatheter aortic valve implantation using the CoreValve Revalving System. Am J Cardiol. 2011;108(11):1600–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjcard.2011.07.020.
Sovari AA, Shehata M. Heart block following transcatheter aortic valve implantation: a matter of right bundle branch integrity? Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. 2016;14(6):663–5. https://doi.org/10.1586/14779072.2016.1168694.
Haworth P, Behan M, Khawaja M, Hutchinson N, de Belder A, Trivedi U, et al. Predictors for permanent pacing after transcatheter aortic valve implantation. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2010;76(5):751–6. https://doi.org/10.1002/ccd.22457.
Roten L, Wenaweser P, Delacretaz E, Hellige G, Stortecky S, Tanner H, et al. Incidence and predictors of atrioventricular conduction impairment after transcatheter aortic valve implantation. Am J Cardiol. 2010;106(10):1473–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjcard.2010.07.012.
De Carlo M, Giannini C, Bedogni F, Klugmann S, Brambilla N, De Marco F, et al. Safety of a conservative strategy of permanent pacemaker implantation after transcatheter aortic CoreValve implantation. Am Heart J. 2012;163(3):492–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ahj.2011.12.009.
Erkapic D, Kim WK, Weber M, Mollmann H, Berkowitsch A, Zaltsberg S, et al. Electrocardiographic and further predictors for permanent pacemaker requirement after transcatheter aortic valve implantation. Europace. 2010;12(8):1188–90. https://doi.org/10.1093/europace/euq094.
Boerlage-Van Dijk K, Kooiman KM, Yong ZY, Wiegerinck EM, Damman P, Bouma BJ, et al. Predictors and permanency of cardiac conduction disorders and necessity of pacing after transcatheter aortic valve implantation. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2014;37(11):1520–9. https://doi.org/10.1111/pace.12460.
Lever N, Ferguson JD, Bashir Y, Channon KM. Prolonged temporary cardiac pacing using subcutaneous tunnelled active-fixation permanent pacing leads. Heart. 2003;89(2):209–10.
Kornberger A, Schmid E, Kalender G, Stock UA, Doernberger V, Khalil M, et al. Bridge to recovery or permanent system implantation: an eight-year single-center experience in transvenous semipermanent pacing. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2013;36(9):1096–103. https://doi.org/10.1111/pace.12175.
Braun MU, Rauwolf T, Bock M, Kappert U, Boscheri A, Schnabel A, et al. Percutaneous lead implantation connected to an external device in stimulation-dependent patients with systemic infection--a prospective and controlled study. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2006;29(8):875–9. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1540-8159.2006.00454.x.
Dawood FZ, Boerkircher A, Rubery B, Hire D, Soliman EZ. Risk of early mortality after placement of a temporary-permanent pacemaker. J Electrocardiol. 2016;49(4):530–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelectrocard.2016.05.004.
Zei PC, Eckart RE, Epstein LM. Modified temporary cardiac pacing using transvenous active fixation leads and external re-sterilized pulse generators. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006;47(7):1487–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2006.01.006.
de Cock CC, Van Campen CM, In't Veld JA, Visser CA. Utility and safety of prolonged temporary transvenous pacing using an active-fixation lead: comparison with a conventional lead. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2003;26(5):1245–8.
Chihrin SM, Mohammed U, Yee R, Gula LJ, Klein GJ, Skanes AC, et al. Utility and cost effectiveness of temporary pacing using active fixation leads and an externally placed reusable permanent pacemaker. Am J Cardiol. 2006;98(12):1613–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjcard.2006.07.041.
Steinberg JS, Fischer A, Wang P, Schuger C, Daubert J, McNitt S, et al. The clinical implications of cumulative right ventricular pacing in the multicenter automatic defibrillator trial II. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2005;16(4):359–65. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1540-8167.2005.50038.x.
Barsheshet A, Moss AJ, McNitt S, Jons C, Glikson M, Klein HU, et al. Long-term implications of cumulative right ventricular pacing among patients with an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator. Heart Rhythm. 2011;8(2):212–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hrthm.2010.10.035.
Dizon JM, Nazif TM, Hess PL, Biviano A, Garan H, Douglas PS, et al. Chronic pacing and adverse outcomes after transcatheter aortic valve implantation. Heart. 2015;101(20):1665–71. https://doi.org/10.1136/heartjnl-2015-307666.
Urena M, Webb JG, Eltchaninoff H, Munoz-Garcia AJ, Bouleti C, Tamburino C, et al. Late cardiac death in patients undergoing transcatheter aortic valve replacement: incidence and predictors of advanced heart failure and sudden cardiac death. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2015;65(5):437–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2014.11.027.
Mouillet G, Lellouche N, Lim P, Meguro K, Yamamoto M, Deux JF, et al. Patients without prolonged QRS after TAVI with CoreValve device do not experience high-degree atrio-ventricular block. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2013;81(5):882–7. https://doi.org/10.1002/ccd.24657.
van der Boon RM, Van Mieghem NM, Theuns DA, Nuis RJ, Nauta ST, Serruys PW, et al. Pacemaker dependency after transcatheter aortic valve implantation with the self-expanding Medtronic CoreValve System. Int J Cardiol. 2013;168(2):1269–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcard.2012.11.115.
Simms AD, Hogarth AJ, Hudson EA, Worsnop VL, Blackman DJ, O'Regan DJ, et al. Ongoing requirement for pacing post-transcatheter aortic valve implantation and surgical aortic valve replacement. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2013;17(2):328–33. https://doi.org/10.1093/icvts/ivt175.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leong, D., Sovari, A.A., Ehdaie, A. et al. Permanent-temporary pacemakers in the management of patients with conduction abnormalities after transcatheter aortic valve replacement. J Interv Card Electrophysiol 52, 111–116 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10840-018-0345-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10840-018-0345-z