Abstract
Purpose
To reduce X-ray radiation injury, we investigated the relation between projection positions and X-ray radiation doses when a coronary sinus mapping electrode was placed.
Methods
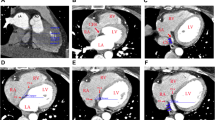
There were 400 patients in whom a coronary sinus mapping electrode was placed for intracardiac electrophysiologic examination or radio-frequency catheter ablation in our hospital between 1 June 2008 and 31 May 2011. The doctors who placed the coronary sinus mapping electrode and the projection positions including posteroanterior, left anterior oblique 45°, and right anterior oblique 30° projection positions were randomly selected. X-ray doses were recorded when the coronary sinus mapping electrode was placed, and then, these were compared between the three projection positions.
Results
The X-ray dose was significantly lower in the right anterior oblique 30° projection position (50.01 ± 11.38 mGy) than in the posteroanterior projection position (68.05 ± 18.85 mGy, q = 12.924, p = 0.000) and the left anterior oblique 45° projection position (71.66 ± 16.95 mGy, q = 15.214, p = 0.000). There were no statistical significances in X-ray doses between the posteroanterior and the left anterior oblique 45° projection positions (p = 0.066) and different operators (p = 0.985).
Conclusion
Based on the results of this study, we suggest that in placing the coronary sinus mapping electrode, the right anterior oblique 30° projection position should be first adopted because it can allow the electrode to be easily placed and reduce the X-ray radiation dose as much as possible.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Miller, Dl, Balter, S., Cole, P. E., Lu, H. T., Schueler, B. A., Geisinger, M., et al. (2003). Radiation doses in interventional radiology procedures: The RAD-IR study: Part I: Overall measures of dose. Journal of Vascular and Interventional Radiology, 14(6), 711–727.
Andreassi, M. G., Cioppa, A., Manfredi, S., Palmieri, C., Botto, N., & Picano, E. (2007). Acute chromosomal DNA damage in human lymphocytes after radiation exposure in invasive cardiovascular procedures. European Heart Journal, 28(18), 2195–2199.
Venneri, L., Rossi, F., Botto, N., Andreassi, M. G., Salcone, N., & Emad, A. (2009). Cancer risk from professional exposure in staff working in cardiac catheterization laboratory: Insights from the National Research Council's Biological Effects of Ionizing Radiation VII Report. American Heart Journal, 157(1), 118–124.
Picano, E., Santoro, G., & Vano, E. (2007). Sustainability in the cardiac cath lab. The International Journal of Cardiovascular Imaging, 23(2), 143–147.
Smith, I. R., Rivers, J. T., Hayes, J., Stafford, W., & Codd, C. (2009). Reassessment of radiation risks from electrophysiology procedures compared to coronary angiography. Heart Lung and Circulation Journal, 18(3), 191–199.
Georges, J. L., Livarek, B., Gibault-Genty, G., Aziza, J. P., Hautecoeur, J. L., & Soleille, H. (2009). Reduction of radiation delivered to patients undergoing invasive coronary procedures. Effect of a programme for dose reduction based on radiation-protection training. Archives of Cardiovascular Diseases, 102(12), 821–827.
McGuire, M. A., Johnson, D. C., Robotion, M., Richards, D. A., Uther, J. B., & Ross, D. L. (1992). Dimensions of the triangle of Koch in human. The American Journal of Cardiology, 70, 829–830.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, G., Huang, Jf., Lu, Hh. et al. Relation between projection positions and X-ray radiation doses during placement of the coronary sinus mapping electrode. J Interv Card Electrophysiol 34, 263–266 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10840-012-9671-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10840-012-9671-8