Abstract
Introduction
Substrate-based radiofrequency ablation for treatment of atrial fibrillation (AF) is still under development. The purpose of this study was to investigate the different characteristics and distribution of complex fractionated atrial electrograms (CFAE) in both atria in patients with paroxysmal and persistent AF.
Methods and Results
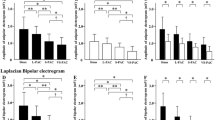
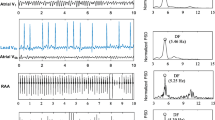
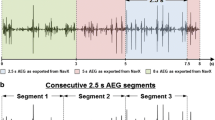
The NavX™ system was used to map the left and right atria and the coronary sinus in 20 AF patients (ten persistent). An automated algorithm calculates the average time interval between consecutive deflections (complex fractionated electrogram (CFE) mean). All recordings were visually inspected off-line and interpreted either as continuous, fragmented, mixed CFAE, or non-CFAE, and their locations were determined. Electrograms with intermittent CFAE characteristics were also regarded as non-CFAEs. There were more CFAEs in persistent AF than in paroxysmal AF (52% vs. 44% of total registrations, p < 0.05), and CFAEs were more widespread in both atria in persistent AF patients. There were also more continuous CFAEs (70% vs. 59% of total CFAEs, p < 0.05), and less mixed and intermittent CFAEs (22% vs. 30% and 16% vs. 21% of total CFAEs, respectively, p < 0.05) in persistent AF. Fragmented CFAEs had more high-voltage signals than other groups. Employing the automated algorithm for CFAE mapping, a CFE mean cut-off value of ≤80 ms provides a sensitivity and specificity of 87.4% and 81.2%, respectively.
Conclusions
CFAEs distribute in preferential areas and arrange in different patterns in both atria. Patients with persistent AF have more continuous CFAEs and higher temporal signal stability than patients with paroxysmal AF.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Haissaguerre, M., Jais, P., Shah, D. C., Garrigue, S., Takahashi, A., Lavergne, T., et al. (2000). Electrophysiological end point for catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation initiated from multiple pulmonary venous foci. Circulation, 101, 1409–1417.
Verma, A., Marrouche, N. F., & Natale, A. (2004). Pulmonary vein antrum isolation: Intracardiac echocardiography-guided technique. Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 15, 1335–1340.
Pappone, C., Oreto, G., Rosanio, S., Vicedomini, G., Tocchi, M., Gugliotta, F., et al. (2000). Circumferential radiofrequency ablation of pulmonary vein ostia: A new anatomic approach for curing atrial fibrillation. Circulation, 102, 2619–2628.
Pachon, M. J., Pachon, M. E., Pachon, M. J., Lobo, T. J., Pachon, M. Z., Vargas, R. N., et al. (2004). A new treatment for atrial fibrillation based on spectral analysis to guide the catheter RF-ablation. Europace, 6, 590–601.
Nademanee, K., McKenzie, J., Kosar, E., Schwab, M., Sunsaneewitayakul, B., Vasavakul, T., et al. (2004). A new approach for catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation: mapping of the electrophysiologic substrate. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 43, 2044–2053.
Oral, H., Chugh, A., Good, E., Wimmer, A., Dey, S., Gadeela, N., et al. (2007). Radiofrequency catheter ablation of chronic atrial fibrillation guided by complex electrograms. Circulation, 115, 2606–2612.
Schmitt, C., Estner, H., Hecher, B., Luik, A., Kolb, C., Karch, M., et al. (2007). Radiofrequency ablation of complex fractionated atrial electrograms (CFAE): Preferential sites of acute termination and regularization in paroxysmal and persistent atrial fibrillation. Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 18, 1039–1046.
Nademanee, K., Schwab, M., Porath, J., & Abbo, A. (2006). How to perform electrogram-guided atrial fibrillation ablation. Heart Rhythm, 3, 981–984.
Elayi, C. S., Verma, A., Di Biase, L., Ching, C. K., Patel, D., Barrett, C., et al. (2008). Ablation for longstanding permanent atrial fibrillation: results from a randomized study comparing three different strategies. Heart Rhythm, 5, 1658–1664.
Deisenhofer, I., Estner, H., Reents, T., Fichtner, S., Bauer, A., Wu, J., et al. (2008). Does electrogram guided substrate ablation add to the success of pulmonary vein isolation in patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation? A prospective, randomized study. Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 20, 514–521.
Estner, H. L., Hessling, G., Ndrepepa, G., Wu, J., Reents, T., Fichtner, S., et al. (2008). Electrogram-guided substrate ablation with or without pulmonary vein isolation in patients with persistent atrial fibrillation. Europace, 10, 1281–1287.
Oral, H., Chugh, A., Yoshida, K., Sarrazin, J. F., Kuhne, M., Crawford, T., et al. (2009). A randomized assessment of the incremental role of ablation of complex fractionated atrial electrograms after antral pulmonary vein isolation for long-lasting persistent atrial fibrillation. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 53, 782–789.
Roux, J.-F., Gojraty, S., Bala, R., Liu, C. F., Hutchinson, M. D., Dixit, S., et al. (2008). Complex fractionated electrogram distribution and temporal stability in patients undergoing atrial fibrillation ablation. Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 19, 815–820.
Scherr, D., Dalal, D., Cheema, A., Nazarian, S., Almasry, I., Bilchick, K., et al. (2009). Long- and short-term temporal stability of complex fractionated atrial electrograms in human left atrium during atrial fibrillation. Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 20, 13–21.
Konings, K. T., Smeets, J. L., Penn, O. C., Wellens, H. J., & Allessie, M. A. (1997). Configuration of unipolar atrial electrograms during electrically induced atrial fibrillation in humans. Circulation, 95, 1231–1241.
Park, J. H., Pak, H.-N., Kim, S. K., Jang, J. K., Choi, J. I., Lim, H. E., et al. (2009). Electrophysiologic characteristics of complex fractionated atrial electrograms in patients with atrial fibrillation. Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 20, 266–272.
Stiles, M. K., Brooks, A. G., Kuklik, P., John, B., Dimitri, H., Lau, D. H., et al. (2008). High-density mapping of atrial fibrillation in humans: Relationship between high-frequency activation and electrogram fractionation. Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 19, 1245–1253.
Stiles, M. K., Brooks, A. G., John, B., Shashidinar, Wilson, L., Kuklik, P., et al. (2008). The effect of electrogram duration on quantification of complex fractionated atrial electrograms and dominant frequency. Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 19, 252–258.
Matsuo, S., Lellouche, N., Wright, M., Bevilacqua, M., Knecht, S., Nault, I., et al. (2009). Clinical predictors of termination and clinical outcome of catheter ablation for persistent atrial fibrillation. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 54, 788–795.
Oral, H., Knight, B. P., Tada, H., Özaydin, M., Chugh, M., Hassan, S., et al. (2002). Pulmonary vein isolation for paroxysmal and persistent atrial fibrillation. Circulation, 105, 1077–1081.
Liu, X., Shi, H.-F., Tan, H.-W., Wang, X.-H., Li, Z., & Gu, J.-N. (2009). Decreased connexin 43 and increased fibrosis in atrial regions susceptible to complex fractionated atrial electrograms. Cardiology, 114, 22–29.
Lin, J., Scherlag, B. J., Zhou, J., Lu, Z., Patterson, E., Jackman, W. M., et al. (2007). Autonomic mechanism to explain complex fractionated atrial electrograms (CFAE). Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 18, 1197–1205.
Lu, Z., Scherlag, B. J., Lin, J., Niu, G., Ghias, M., Jackman, W. M., et al. (2008). Autonomic mechanism for complex fractionated atrial electrograms: Evidence by fast Fourier transform analysis. Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 19, 835–842.
Katrisis, D., Giazitzoglou, E., Sougiannis, D., Voridis, E., & Po, S. S. (2009). Complex fractionated atrial electrograms at anatomic sites of ganglionated plexi in atrial fibrillation. Europace, 11, 308–315.
Tada, H., Yoshida, K., Chugh, A., Boonyapisit, W., Crawford, T., Sarrazin, J.-F., et al. (2008). Prevalence and characteristics of continuous electrical activity in patients with paroxysmal and persistent atrial fibrillation. Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 19, 606–612.
Nademanee, K. (2007). Trials and travails of electrogram-guided ablation of chronic atrial fibrillation. Circulation, 115, 2592–2594.
Off, M. K., Solheim, E., Schuster, P., Hoff, P. I., Ohm, O.-J., & Chen, J. (2008). Detection of complex fractionated electrograms by an automated algorithm (abstr). Heart Rhythm, 5, S171.
Wu, J., Estner, H., Luik, A., Ücer, E., Reents, T., Pflaumer, A., et al. (2008). Automatic 3D mapping of complex fractionated atrial electrograms (CFAE) in patients with paroxysmal and persistent atrial fibrillation. Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 19, 897–903.
Chen, J., Off, M. K., Solheim, E., Hoff, P. I., Schuster, P., & Ohm, O.-J. (2009). Spatial relationships between the pulmonary veins and sites of complex fractionated atrial electrograms during atrial fibrillation. Pacing and Clinical Electrophysiology, 32, S190–S193.
Acknowledgements
This study was partly supported by the Norwegian Foundation for Health and Rehabilitation (Solheim). Schuster received an educational grant from Biosense Webster, and Solheim and Chen have served on the St. Jude Medical advisory board. There are no other conflicts of interest to be disclosed.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Eivind Solheim and Morten Kristian Off contributed equally to this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Solheim, E., Off, M.K., Hoff, P.I. et al. Characteristics and distribution of complex fractionated atrial electrograms in patients with paroxysmal and persistent atrial fibrillation. J Interv Card Electrophysiol 28, 87–93 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10840-010-9479-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10840-010-9479-3