Abstract
Introduction
We reviewed our experience in managing intracardiac ultrasound-detected left atrial thrombus and analyzed the impact of the timing of heparin therapy on thrombus incidence.
Methods and Results
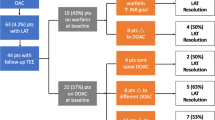
We identified 508 patients undergoing ablation procedures for atrial fibrillation in which intracardiac ultrasound was used. All patients received unfractionated heparin during the procedure: 31 patients before the first transseptal puncture (preTS1), 257 between the first and second transseptal punctures (TS1–TS2), and 220 following both punctures (postTS2). By using intracardiac echocardiography (ICE), thrombus was detected in 30 of these 508 patients (5.9%). Of these, 29 were in the left atrium and constituted our study group. In 21 patients, the thrombi were successfully aspirated from the left atrium using strong suction through the transseptal sheath. All patients in whom thrombi were aspirated did well without neurological event or death. When patients received heparin therapy either preTS1 or TS1–TS2, there was a significant decrease in the occurrence of ICE-detected left atrial thrombus compared with those who received heparin postTS2 (0 of 31 patients (0%) preTS, 9 of 257 (3.5%) TS1–TS2, and 20 of 220 (9.1%) postTS2; (preTS1 vs postTS2, p = 0.01; preTS2 [preTS1 and TS1–TS2] vs postTS2, p < 0.001).
Conclusion
Early administration of intravenous heparin, specifically before transseptal puncture, decreases the incidence of left atrial thrombi.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ACT:
-
activated coagulation time
- ICE:
-
intracardiac echocardiography
- TS:
-
transseptal puncture
- EPS:
-
electrophysiologic study
- TEE:
-
transesophageal echocardiography
- MHz:
-
megahertz
- CHI2 :
-
ҳ 2 test
- preTS1:
-
prior–before the first transseptal puncture
- TS1–TS2:
-
between the first and second transseptal puncture
- postTS2:
-
after the second transseptal
References
Cappato, R., Calkins, H., Chen, S. A., Davies, W., Iesaka, Y., Kalman, J., et al. (2005). Worldwide survey on the methods, efficacy, and safety of catheter ablation for human atrial fibrillation. Circulation, 111, 1100–1105.
Haissaguerre, M., Jais, P., Shah, D. C., Takahashi, A., Hocini, M., Quiniou, G., et al. (1998). Spontaneous initiation of atrial fibrillation by ectopic beats originating in the pulmonary veins. New England Journal of Medicine, 339, 659–666.
Packer, D. L., Asirvatham, S., & Munger, T. M. (2003). Progress in nonpharmacologic therapy of atrial fibrillation. Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 14, S296–S309.
Nademenee, K., McKenzie, J., Kosar, E., Schwab, M., Sunsaneewitayakul, B., Vasavakul, T., et al. (2004). A new approach for catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation: mapping of the electrophysiologic substrate. Journal of American College of Cardiology, 43, 2044–2053.
Pappone, C., & Rosanio, S. (2003). Evolution of non-pharmacological curative therapy for atrial fibrillation. Where do we stand today? International Journal of Cardiology, 88, 135–142.
Wazni, O., Rossillo, A., Marrouche, N., Saad, E., Martin, D., Bhargava, M., et al. (2005). Embolic events and char formation during pulmonary vein isolation in patients with atrial fibrillation: Impact of different anticoagulation regimens and importance of intracardiac echo imaging. Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 16, 576–581.
Hynes, B. J., Mart, C., Artman, S., Pu, M., & Naccarelli, G. V. (2004). Role of intracardiac ultrasound in interventional electrophysiology. Current Opinion in Cardiology, 19, 52–57.
Kautzner, J., & Peichl, P. (2007). Intracardiac echocardiography in electrophysiology. Herzschrittmachertherapie & Elektrophysiologie, 18, 140–146.
Ren, J., & Marchlinski, F. (2007). Utility of intracardiac echocardiography in left heart ablation for tachyarrhythmias. Echocardiography, 24, 533–540.
Keane, D., Mansour, M., & Singh, J. (2004). Detection by intracardiac echocardiography of early formation of left atrial thrombus during pulmonary vein isolation. Europace, 6, 109–110.
Marrouche, N., Martin, D., Wazni, O., Gillinov, A., Klein, A., Bhargava, M., et al. (2003). Phased-array intracardiac echocardiography monitoring during pulmonary vein isolation in patients with atrial fibrillation: Impact on outcome and complications. Circulation, 107, 2710–2716.
Okuyama, Y., Kashiwase, K., Mizuno, H., Oka, T., Takeda, Y., Komatsu, S., et al. (2006). Development of thrombus on a transseptal sheath in the left atrium during attempted electrical pulmonary vein isolation for the treatment of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. Europace, 8, 191–192.
Ren, J. F., Marchlinski, F. E., & Callans, D. J. (2004). Left atrial thrombus associated with ablation for atrial fibrillation: Identification with intracardiac echocardiography. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 43, 1861–1867.
Ren, J. F., Marchlinski, F. E., & Callans, D. J. (2006). Real-time intracardiac echocardiographic imaging of the posterior left atrial wall contiguous to anterior wall of the esophagus. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 48, 594 author reply 594–595.
Ren, J. F., Marchlinski, F. E., Callans, D. J., Gerstenfeld, E. P., Dixit, S., Lin, D., et al. (2005). Increased intensity of anticoagulation may reduce risk of thrombus during atrial fibrillation ablation procedures in patients with spontaneous echo contrast. Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 16, 474–477.
Asirvatham, S. J., Bruce, C. J., & Friedman, P. A. (2003). Advances in imaging for cardiac electrophysiology. Coronary Artery Disease, 14, 3–13.
Roman-Gonzalez, J., Asirvatham, S. J., Razavi, M., Packer, D. L., Grice, S. K., Friedman, P. A., et al. (2001). Marked discrepancies between catheter tip temperature registration and pulmonary vein tissue changes during ablation of focal atrial fibrillation in patients. (Abstract 470). PACE, 24, 656.
Asirvatham, S. J. (2007). Pacing maneuvers for nonpulmonary vein sources: part II. Heart Rhythm, 4, 681–685.
Bunch, T. J., Connolly, H. M., Asirvatham, S. J., Brady, P. A., Gersh, B. J., Munger, T. M., et al. (2007). Catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation in patients with the Marfan and Marfan-like syndromes. Journal of Interventional Cardiac Electrophysiology, 20, 15–20.
Martelo, S., D'Avila, A., Ferreira, F., & Saad, E. (2006). Implantation of bilateral carotid artery filters to allow safe removal of left atrial thrombus during ablation of atrial fibrillation. Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 17, 1140–1141.
Asirvatham, S., & Friedman, P. (2006). Silent cerebral thromboembolism with left atria ablation: A lurking danger. Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 17, 8–10.
Chen, S. A., Chiang, C. E., Tai, C. T., Cheng, C. C., Chiou, C. W., Lee, S. H., et al. (1996). Complications of diagnostic electrophysiologic studies and radiofrequency catheter ablation in patients with tachyarrhythmias: An eight-year survey of 3,966 consecutive procedures in a tertiary referral center. American Journal of Cardiology, 77, 41–46.
Epstein, M. R., Knapp, L. D., Martindill, M., Lulu, J. A., Triedman, J. K., Calkins, H., et al. (1996). Embolic complications associated with radiofrequency catheter ablation. Atakr Investigator Group. American Journal of Cardiology, 77, 655–658.
Oral, H., Chugh, A., Ozaydin, M., Good, E., Fortino, J., Sankaran, S., et al. (2006). Risk of thromboembolic events after percutaneous left atrial radiofrequency ablation of atrial fibrillation. Circulation, 114, 759–765.
Asirvatham, S. J. (2007). Ablation for atrial fibrillation: can we decrease thromboembolism without increasing the risk for bleeding? Circulation, 116, 2517–2519.
Kok, L. C., Mangrum, J. M., Haines, D. E., & Mounsey, J. P. (2002). Cerebrovascular complication associated with pulmonary vein ablation. Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 13, 764–767.
Kalman, J. M., Fitzpatrick, A. P., Olgin, J. E., Chin, M. C., Lee, R. J., Scheinman, M. M., et al. (1997). Biophysical characteristics of radiofrequency lesion formation in vivo: Dynamics of catheter tip-tissue contact evaluated by intracardiac echocardiography. American Heart Journal, 133, 8–18.
Asirvatham, S., & Narayan, O. (2006). Advanced catheter mapping and navigation systems. In S. Huang, & M. Wood (Eds.), Catheter ablation of cardiac arrhythmias. Philadelphia: Saunders/Elsevier.
Black, I. W. (2000). Spontaneous echo contrast: where there’s smoke there’s fire. Echocardiography, 17, 373–382.
Bunch, T. J., Asirvatham, S. J., Friedman, P. A., Monahan, K. H., Munger, T. M., Rea, R. F., et al. (2005). Outcomes after cardiac perforation during radiofrequency ablation of the atrium. Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 16, 1172–1179.
Demolin, J. M., Eick, O. J., Munch, K., Koullick, E., Nakagawa, H., & Wittkampf, F. H. (2002). Soft thrombus formation in radiofrequency catheter ablation. Pacing and Clinical Electrophysiology, 25, 1219–1222.
Wyse, D. (2007). Anticoagulation in atrial fibrillation: A contemporary viewpoint. Heart Rhythm, 4, S34–S39.
Carasso, S., Kuperstein, R., Konen, E., Glikson, M., & Feinberg, M. (2006). Plowing the atrium and growing thrombi: Two cases of large atrial thrombi following ablative and surgical procedure for atrial fibrillation. European Journal of Echocardiography, 7, 383–386.
Bulava, A., Slavik, L., Fiala, M., Heinc, P., Skvarilova, M., Lukl, J., et al. (2004). Endothelial damage and activation of the hemostatic system during radiofrequency catheter isolation of pulmonary veins. Journal of Interventional Cardiac Electrophysiology, 10, 271–279.
Lim, B., Venkatachalam, K., Jahangir, A., Johnson, S., & Asirvatham, S. (2008). Concurrent application of charge using a novel circuit helps prevent heat-related coagulum formation during radiofrequency ablation. Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology.
Kilicaslan, F., Verma, A., Saad, E., Rossillo, A., Davis, D., Prasad, S., et al. (2006). Transcranial Doppler detection of microembolic signals during pulmonary vein antrum isolation: Implications for titration of radiofrequency energy. Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 17, 495–501.
Wazni, O. M., Beheiry, S., Fahmy, T., Barrett, C., Hao, S., Patel, D., et al. (2007). Atrial fibrillation ablation in patients with therapeutic international normalized ratio: Comparison of strategies of anticoagulation management in the periprocedural period. Circulation, 116, 2531–2534.
Lim, B., Venkatachalam, K., Jahangir, A., & Asirvatham, S. (2007). Mechanism of coagulum formation in radiofrequency ablation and a novel method to prevent it. JACC, 49, 422A.
Lickfett, L., Hackenbroch, M., Lewalter, T., Selbach, S., Schwab, J., Yang, A., et al. (2006). Cerebral diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging: A tool to monitor the thrombogenicity of left atrial catheter ablation. Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 17, 1–7.
Hockstad, E., & Gornick, C. C. (1994). Mildly symptomatic pulmonary emboli associated with electrophysiologic procedures. Indications for anticoagulant use. Chest, 106, 1908–1911.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bruce, C.J., Friedman, P.A., Narayan, O. et al. Early heparinization decreases the incidence of left atrial thrombi detected by intracardiac echocardiography during radiofrequency ablation for atrial fibrillation. J Interv Card Electrophysiol 22, 211–219 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10840-008-9270-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10840-008-9270-x