Abstract
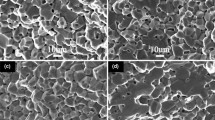
The effects of SiO2, CaO, TiO2, and Nb2O5 additives on the high-frequency magnetic properties of the Mn0.3Zn0.7Fe2O4 (MZFT) ferrites were examined in this study. The content of SiO2 and CaO was kept at 50 ppm and 500 ppm, while that of TiO2 and Nb2O5 varied respectively from 0 to 3000 ppm and from 0 to 300 ppm. All samples surpassed 95 % theoretical density after sintering at 1300 °C with N3T30 composition (50 ppm SiO2, 5000 ppm CaO, 3000 ppm TiO2, and 300 ppm Nb2O5) reporting the highest sintered density. The calculated lattice constants of the ferrites evaluated appeared to be nearly the same (≈0.849 Å) and no second phase was present. It was apparent that the additions of SiO2, CaO, TiO2, and Nb2O5 exerted no notable impact on the microstructures of the ferrites. The average grain size of the samples sintered at 1300 °C ranged from 7.78 μm to 9.76 μm with both intergranular and intragranular pores. Incorporation of partial Ti4+ and Nb5+ ions into the lattices shifted the secondary maximum peak of the μi-T curves from 90 °C to lower temperatures (60 to 70 °C). The initial permeability of the ferrites was strongly dependent on the additives and the sintering temperature. The initial permeability of the MZFT sample sintered at 1275 °C and 1300 °C read respectively 5056 and 5222, and that of the N3T30 sample emerged to be 2917 and 3389. Compared to that of pure MZFT ferrite, the TiO2 and Nb2O5, SiO2 and CaO added compositions displayed a nearly 45 % reduction in total power loss, mainly caused by the electrical insulating layers at the grain boundaries, which lowered the eddy current loss. The N3T30 ferrite sintered at 1275 °C showed the lowest total power losses of 272 mW/cm3 at 50 °C.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Sugimoto, The Past, Present, and Future of Ferrites. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 82, 269–280 (1999)
H. Shokkrollahi, K. Janghorban, Influence of Additives on the Magnetic Properties, Microstructures, and Densification of Mn-Zn Soft Ferrites. Materials Science and Engineering B 141, 91–107 (2007)
P. Hu, H.B. Yang, D.A. Pan, H. Wang, J.J. Tian, S.G. Zhang, X.F. Wang, A.A. Volinsky, Heat treatment Effects on the Microstructure and Microstructure and Magnetic Properties of Mn-Zn Ferrite Powers. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 322, 173–177 (2010)
Z. Yu, K. Sun, L. Li, Y. Liu, Z. Lan, H. Zhang, Influences of Bi2O3 on Microstructure and magnetic Properties of Mn-Zn Ferrites. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 320, 919–923 (2008)
C.S. Liu, J.M. Wu, C.J. Chen, M.J. Tung, Power Loss Properties of Mn-Zn Ferrites Containing Er2O3. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 133, 478–480 (1994)
K. Sun, Z. Lan, Z. Yu, L. Li, H. Ji, Z. Xu, Effects of NiO Addition on the Structural, Microstructural and Electromagnetic Properties of Manganese-Zinc Ferrite. Materials Chemistry and Physics 113, 797–802 (2009)
W. Wang, C. Zang, Q. Jiao, Synthesis, Structure and Electromagnetic Properties of Mn-Zn Ferrite by Sol–gel Combustion Technique. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 349, 116–120 (2014)
N.S. Mitrovie, S.R. Djukie, S. Randjic, Z. Ristanovic, H. Danninger, Soft Magnetic Properties of MnZn Ferrites Prepared by Powder Injection Moulding. Science of Sintering 44, 355–364 (2012)
M.M. Rashad, M.I. Nasr, Controlling the Microstructure and Magnetic Properties of Mn-Zn Ferrites Nanopowders Synthesized by Co-precipitation Method. Electronic Materials Letters 8, 325–329 (2012)
S. Kumar, T.J. Shinde, P.N. Vasambekar, Microwave Synthesis and Characterization of Nanocrystalline Mn-Zn Ferrites. Adv. Mat. Lett. 4, 373–377 (2013)
H. Zhang, Y. Shi, X. Zeng, X.Y. He, Effects of Eu3+ Substitution on Nanosized Mn-Zn Ferrite Powders Synthesized by Combustion Processing. Key Engineering materials 512–515, 1416–1419 (2013)
G.C. Jain, B.K. Das, and S. Kumari, “Effect of Dopant a Mn-Zn Ferrite with GeO2 and SnO2,” IEEE Transactions on Magnetics Mag-16 (1980) 14281433.
K. Janghorban, H. Shokrollahi, Influence of V2O5 Addition on the Grain Growth and Magnetic Properties of Mn-Zn High permeability Ferrites. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 308, 238–242 (2007)
Y.C. Lin, D. Gan, P. Shen, Microstructure of Zirconia-(MnZn Ferrite) Composites. Materials Science and Engineering A188, 327–334 (1994)
J. Nie, H. Li, Z. Feng, H. He, The Effect of Nano-SiO2 on the magnetic Properties of the Low Power Loss Manganese-Zinc Ferrites,”. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 265, 172–175 (2003)
H.N. Ji, Z.W. Lan, Z. Yu, Y.J. Zhi, and Z. Liu, “Effect of Ti-Substitution on Temperature Dependence and Magnetic Disaccommodation of MnZn Ferrites,” Proceedings of 2009 I.E. International Conference on Applied Superconductivity and Electromagnetic Devices, Chengdu, China, September 25–27, 2009, pp. 344–347
V.T. Zaspalis, V. Tsakaloudi, M. Kolenbrander, The Effect of Dopants on the Incremental Permeability of Mn-Zn Ferrites. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 313, 29–36 (2007)
H. Inaba, T. Abe, Y. Kitano, J. Shimomura, Magnetic Properties and the Grain Boundary Structure of Mn-Zn Ferrites with the Addition of Nb2O5. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 133, 487–489 (1994)
V.T. Zaspalis, E. Antoniadis, E. Papazoglou, V. Tsakaloudi, L. Nalbandian, C.A. Sikalidis, The effect of Nb2O5 dopant on the Structural and Magnetic Properties of MnZn Ferrites. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 250, 98–109 (2002)
H. Ji, Z. Lan, Z. Yu, K. Sun, L. Li, Influence of Sn-substitution on Temperature Dependence and Magnetic Disaccommodation of Manganese-zinc Ferrites. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 321, 2121–2124 (2009)
A. Huang, H. He, Z. Feng, Effects of SnO2 Addition on the Magnetic Properties of Manganese Zinc Ferrites. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 301, 331–335 (2006)
J. Fan, F.R. Sale, The Microstructures, Magnetic Properties and Impedance Analysis of Mn-Zn Ferrites Doped with B2O3. Journal of the European Ceramic Society 20, 2743–2751 (2000)
O. Mirzaee, M.A. Golozar, A. Shafyei, Influence of V2O5 as an Effective Dopant on the Microstructure Development and magnetic Properties of Ni0.64Zn0.36Fe2O4 Soft Ferrites. Materials Characterization 59, 638–641 (2008)
24 . X.L. Fu, Q.K. Xing, Z.J. Peng, C.B. Wang, Z.Q. Fu, L.H. Qi, H.Z. Miao, “Microstructure and Electromagnetic Properties of Mn-Zn Ferrites with Low Melting Point Nonmagnetic Sb3+ Ions,” International Journal of Modern Physics 27 (2013) 1350003 (12 pages).
S. Park, J.C. Lee, J.H. Lee, Y.J. Chung, J.U. Seo, The Effects of Nb2O5 and TiO2 on Electrical and magnetic properties of Mn-Zn Ferrites. Phys. Stat. Sol. (c) 1, 3619–3622 (2004)
R.T. Willey, J.T. Mullin, Effects of Titanium Concentration on Disaccommodation Spectra of MnZn Ferrite. IEEE Transactions on Magnetic 19, 2007–2009 (1983)
J. Topfer, H. Kahnt, P. Nauber, S. Senz, D. Hesse, Microstructural Effects in Low Loss Power Ferrites. Journal of European Ceramic Society 25, 3045–3049 (2005)
H. Li, Z. Feng, H. He, Q. Zhu, J. Jiang, J. Nie, X. Yu, Effects of Fe2+ content I Raw Materials on Mn-Zn Ferrite Magnetic Properties. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 237, 153–157 (2001)
C. Beatrice, F. Fiorillo, F.J. Landgraf, V. Lazaro-colan, S. Janasi, J. Leicht, Magnetic Loss, Permeability Dispersion, and Role of Eddy Currents in Mn-Zn Sintered Ferrites. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 320, e865–e868 (2008)
C. Beatrice, O. Bottauscio, M. Chiampi, F. Fiorillo, and A. Manzin, “Magnetic Loss Analysis in Mn-Zn Ferrite Core, “Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 304 (2006) e743-e745.
D. Stoppels, Developments in Soft magnetic Power Ferrites. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 160, 323–328 (1996)
V. Zaspalis, V. Tsakaloudi, E. Papazoglou, M. Kolenbrander, R. Guenther, P.V.D. Valk, Development of a New MnZn-ferrite Soft Magnet Material for High Temperature Power Applications. Journal of Electroceramics 13, 585–591 (2004)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, SF., Hsu, YF. & Chen, CH. Effects of Nb2O5, TiO2, SiO2, and CaO additions on the loss characteristics of Mn-Zn Ferrite. J Electroceram 33, 172–179 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10832-014-9943-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10832-014-9943-z