Abstract
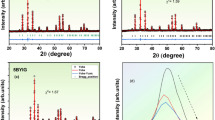
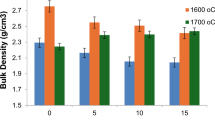
Bi4Ti3O12 (BIT) based ceramics were prepared by hydroxide coprecipitation method and subsequent treatment at 650∘C for 1 h. Calcined BIT was doped with different amounts of WO3 by surface doping using W(C2H5O)6. The amount of dopant modified the sintering behaviour of BIT-based ceramics through a liquid-phase assisted sintering mechanism in the case of low dopant concentration and Zenner effect when high concentration of dopant was used. Consequently, the microstructure and the electrical properties were strongly dependent on the dopant concentration. Doped BIT-based ceramics showed a microstructure composed of very small platelet-like grains and the electrical conductivity was markedly decreased. The high electrical resistivity makes possible the polarization of doped ceramics and relatively good piezoelectric parameters were measured.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
E.C. Subbarao, J. Phys. Chem. Solids, 23, 665 (1962).
T. Takenaka and K. Sakata, J. Appl. Phys., 55, 1092 (1984).
J.F. Scott and C.A. Araujo, Science, 246, 1400 (1989).
B. Aurivillius, Ark. Kemi., 1, 499 (1949).
A. Fouskova and L.E. Cross, J. Appl. Phys., 41, 2834 (1970).
M. Villegas, A.C. Caballero, C. Moure, P. Durán, and J.F. Fernández, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 82, 2411 (1999).
M. Villegas, A.C. Caballero, and J.F. Fernández, Ferroelectrics, 267, 165 (2002).
S.S. Lopatin, T.G. Lupeiko, T.L. Vasil’tsova, N.I. Basenko, and I.M. Berlizev, Inorg. Mater., (Engl. Transl.) 24, 1328 (1988).
H.S. Shulman, M. Testorf, D. Damjanovic, and N. Setter, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 79, 3124 (1996).
J.S. Kim, S.S. Kim, J.K. Kim, and T.K. Song, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys., 41, 6451 (2002).
M. Villegas, C. Moure, J.F. Fernández, and P. Durán, Ceram. Int., 22, 15 (1996).
M. Villegas, T. Jardiel, and G. Farías, 2004 J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 24 1025
I. Radosavljevic, J.S.O. Evans, and A.W. Sleight, J. Solid State Chem., 136, 63 (1998).
S.P. Yordanov, I. Ivanov, and P. Carapanov, J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys., 31, 800 (1998).
A.Q. Jiang, G.H. Li, and L.D. Zhang, J. Appl. Phys., 83, 4878 (1998).
C. Voisard, D. Damjanovic, and N. Setter, J. Europ. Ceram. Soc., 19, 1251 (1999).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Villegas, M., Jardiel, T., Caballero, A.C. et al. Electrical Properties of Bismuth Titanate Based Ceramics with Secondary Phases. J Electroceram 13, 543–548 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10832-004-5155-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10832-004-5155-2