Abstract
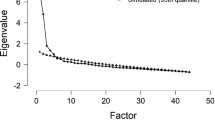
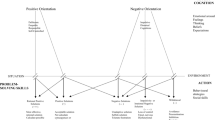
The study develops and evaluates the interpersonal problem-solving inventory for elementary school students (IPSI). In particular, the study employs a multidimensional interpersonal problem-solving model that is based on the cognitive-affective-behavioral approach to construct a process measure of interpersonal problem-solving inventory for 4th and 5th grade students, especially for elementary school settings in Vietnam. The inventory is a 4-point Likert-type scale consisting of 44 items and five dimensions. The IPSI was administered to a total elementary student sample that consisted of 786 Vietnamese elementary students in fourth and fifth grades (ages: 9–12, M = 10.11, SD = 0.75). The reliability of the IPSI was reported (Cronbach’s α = 0.90; McDonald’s ω = 0.82). EFA was conducted on the first dataset to explore the emerging factor structure of the IPSI. The EFA results suggested an exclusive five-factor solution. CFA was examined on the second dataset to define the theory-driven five-factor structure of the IPSI. The CFA findings indicated that the IPSI consented to the five-factor structure as similar as the EFA results. The assessment of the five-factor model endorsed that five of the six global fit indices (χ2/df = 1.406 < 2, P < 0.001; CFI = 0.928; TLI = 0.924; GFI = 0.875; RMSEA = 0.032 < 0.05; and SRMR = 0.049 < 0.05) are statistically acceptable, suggesting a good fitting model. The results suggest that the scale has acceptable internal reliability and construct validity. Applicability and limitations of the IPSI are discussed. Subsequent studies and possible improvements are proposed.
Highlights
-
The IPSI scale was developed to assess individual problem-solving skills of elementary-age school students to real-life interpersonal issues.
-
The construct validity of the IPSI scale for Vietnamese fourth and fifth grade student samples were analysed using EFA and CFA techniques.
-
The results of examining Cronbach’s coefficient alpha levels indicated that the subscale scores on the IPSI verify good internal consistencies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asún, R. A., Rdz-Navarro, K., & Alvarado, J. M. (2016). Developing multidimensional likert scales using item factor analysis: the case of four-point items. Sociological Methods & Research, 45(1), 109–133.
Çam, S., & Tümkaya, S. (2008). Development of interpersonal problem solving inventory for high school students: The validity and reliability process. International Journal of Human Sciences, 5(2), 1–17.
Dereli-İman, E. (2013). The social problem-solving questionnaire: Evaluation of psychometric properties among Turkish primary school students. Egitim Arastirmalari - Eurasian Journal of Educational Research, 52, 97–116.
Dunn, T. J., Baguley, T., & Brunsden, V. (2014). From alpha to omega: A practical solution to the pervasive problem of internal consistency estimation. British Journal of Psychology, 105(3), 399–412.
D’Zurilla, T. J., & Nezu, A. M. (2001). Problem-solving therapies. In K. S. Dobson (Ed.), Handbook of Cognitive Behavioural Therapies (pp. 211-245). New York, London: The Guildford Press.
D’Zurilla, T. J., & Maydeu-Olivares, A. (1995). Conceptual and methodological issues in social problem-solving assessment. Behavior Therapy, 26, 409–432.
D’Zurilla, T. J. (1986). Problem-solving therapy: A social competence approach to clinical intervention. New York: Springer.
D’Zurilla, T. J., Nezu, A. M., & Maydeu-Olivares, A. (1996). Manual for the social problem solving inventory-revised (SPSI-R). In press, North Tonawanda, N.Y: Multi-Health Systems, INC.
D’Zurilla, T. J., Nezu, A. M., & Maydeu-Olivares, A. (2002). Social Problem-Solving Inventory-Revised (SPSI–R): Technical manual. North Tonawanda, NY: Multi-Health Systems Inc.
D’Zurilla, T. J., Nezu, A. M., & Maydeu-Olivares, A. (2004). What is social problem-solving?: Meaning, models, and measures. In E. C. Chang, T. J. D.,Zurilla, & L. Sanna (Eds.), Social problem-solving: Theory, research, and training (pp. 11−27). Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
D’Zurilla, T. J., & Nezu, A. M. (1990). Development and preliminary evaluation of the Social Problem-Solving Inventory. Psychological Assessment: A Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 2, 156–163.
Frauenknecht, M., & Black, D. A. (1995). Social Problem Solving Inventory for Adolescents (SPSI-A): Development and preliminary psychometric evaluation. Journal of Personality Assessment, 64, 522–539.
Goss-Sampson, M. A. (2020). Statistical Analysis in JASP 0.14: A Guide for Students. Available online: https://jasp-stats.org/jasp-materials/(accessed March 15 2019).
Hair, J., Black, W., Babin, B., & Anderson, R. (2010). Multivariate data analysis. Pearson Prentice Hall.
Hartup, W. W., & Sancilio, M. F. (1986). Children’s friendships. In E. Schopler & G. B. Mesibov (Eds.), Social behaviour in autism (pp. 61–80). New York: Plenum.
Heppner, P. P., & Petersen, C. H. (1982). The development and implications of a personal problem-solving inventory. Journal of Counselling Psychology, 29(1), 66–75.
Hooper, D., Coughlan, J., & Mullen, M. R. (2008). Structural Equation Modelling: Guidelines for Determining Model Fit. The Electronic Journal of Business Research Methods, 6(1), 53–60.
James, S., Hunsley, J., & Hemsworth, D. (2002). Factor structure of the relationship belief inventory. Cognitive Therapy and Research, 26(6), 729–744.
Kasik, L. (2014). Development of social problem solving—A longitudinal study (2009–2011) in a Hungarian context. European Journal of Developmental Psychology, 12(2), 142–158.
Kathryn, S. W. (2011). Understanding how social and emotional skill deficits contribute to school failure. Preventing School Failure, 55(1), 10–16.
Maydeu-Olivares, A., & D’Zurilla, T. J. (1996). A factor-analytic study of the Social Problem-Solving Inventory: An integration of the theory and data. Cognitive Therapy and Research, 20(6), 115–133.
McMurran, M., & McGuire, J. (2011). Social problem solving and offending evidence, evaluation and evolution. New York: Wiley.
Nguyen, C. K. (2019). Development of the teacher rating scale of interpersonal problem solving in adolescents. Current Psychology, 40, 5175–5184.
Nguyen, C. K., & Nguyen, T. M. L. (2017). Development of the social problem solving measure of adolescents’ competences in dealing with interpersonal problems. HNUE Journal of Science, Educational Sciences, 62(12), 12–24.
Nguyen, C. K., & Nguyen, T. M. L. (2020). Development and psychometric properties of a social problem solving test for adolescents. Journal of Rational-Emotive & Cognitive-Behavior Therapy, 38(1), 76–95.
Nguyen, C. K., Tran, T. H., & Nguyen, T. M. L. (2020b). The interpersonal problem-solving measure for elementary school students: development and preliminary evaluation in a third grade student sample. Journal of Rational-Emotive & Cognitive-Behavior Therapy, 39, 14–34.
Nguyen, C. K., Tran, T. H., & Nguyen, T. M. L. (2020a). The development of a social problem-solving test for elementary school students. Journal of Rational-Emotive & Cognitive-Behavior Therapy, 39, 35–57.
Nguyen, C. K., Tran, T. H., & Nguyen, T. M. L. (2018). The problem-solving ability of 4th and 5th grade elementary school students: the situation and factors affecting. Paper presented in the Proceedings the sixth international conference on school psychology: the role of school psychology in promoting well-being of students and families, Hanoi: Vietnam.
Semrud-Clikeman, M. (2007). Social competence in children. New York: Springer.
Shujja, S., Malik, F., & Khan, N. (2015). Social competence scale for adolescents (SCSA): Development and validation within cultural perspective. Journal of Behavioural. Sciences, 25(1), 59–77.
Spence, S. H. (1991). Developments in the assessment of social skills and social competence in children. Behavior Change, 8(4), 148–166.
Tepeli, K., & Yılmaz, E. (2013). Social problem solving skills of children in terms of maternal acceptance-rejection levels. US-China Education Review, 3(8), 581–592.
Wakeling, H. (2007). The psychometric validation of the social problem-solving inventory -revised with UK incarcerated sexual offenders. Sex Abuse, 19(3), 217–236.
Wentzel, R. R. (1991). Relation between social competence and academic achievement in early adolescence. Child Development, 62(5), 1066–1078.
Werner, C., & Schermelleh-Engel, K. (2010). Deciding Between Competing Models: Chi-Square Difference Tests. Available online: https://www.psychologie.uzh.ch/dam/jcr:ffffffff-b371-2797-0000-00000fda8f29/chisquare_diff_en.pdf(accessed April 10, 2019).
Yong, A. G., & Pearce, S. (2013). A beginner’s guide to factor analysis: focusing on exploratory factor analysis. Tutorials in Quantitative Methods for Psychology, 9(2), 79–94.
Zsolnai, A., Kasik, L., & Braunitzer, G. (2014). Coping strategies at the ages 8, 10 and 12. Educational Psychology, 35(1), 73–92.
Acknowledgements
The preparation of this manuscript was supported in part by the Research Group on Assessment and Education for Children with Developmental Disorders, Hanoi National University of Education. The authors would like to thanks Hanoi National University of Education.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in the study involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, as revised in 2008. We also confirm that the submission protocol of the study has been approved by the institutional ethics committee at Hanoi National University of Education (HNUE) and the Ministry of Education and Training, Vietnam.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Do, T.T., Nguyen, C.K., Nguyen, M.L.T. et al. The Development and Validation of the Interpersonal Problem-Solving Inventory for Elementary School Students. J Child Fam Stud 31, 3359–3371 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-022-02407-w
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-022-02407-w