Abstract
Objectives
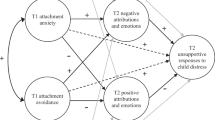
This study aimed to identify factors, namely adult attachment and childhood parenting experiences, to investigate individual differences in parenting behavior using an infant simulator paradigm.
Methods
One hundred and eighteen college-aged females completed questionnaires about adult attachment, how their parents responded to negative emotions, and attitudes about infant crying. Participants then interacted with a distressed infant simulator, while their behavior with the simulator and physiology were recorded.
Results
Attachment avoidance was associated with less infant-oriented beliefs and more parent-oriented beliefs about infant crying. Adult attachment avoidance was also associated with greater physiological reactivity during the task, more physiological regulation, and increased caregiving behaviors. Attachment anxiety was related to a decrease in heart rate during the task. Remembered nonsupportive parental reactions were associated with more parent-oriented beliefs about infant crying as well as more caregiving during the task. However, caregiving quality was not related to any variables of interest in the study.
Conclusions
Implications addressing potential intervention programs using the infant simulator and targeting at-risk populations to understand individual differences in parenting are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ablow, J. C., Marks, M. S., Feldman, S. S., & Hufman, L. C. (2013). Associations between first-time expectant women’s representations of attachment and their physiological reactivity to infant cry. Child Development, 84, 1373–1391. https://doi.org/10.1111/cdev.12135.
Ainsworth, M. D. S. (1979). Infant-mother attachment. American Psychologist, 34(10), 932–937. https://doi.org/10.1037/0003-066x.34.10.932.
Bakermans-Kranenburg, M. J., Alink, L. R. A., Biro, S., Voorthuis, A., & van Ijzendoorn, M. H. (2015). The leiden infant simulator assessment (LISSA): parenting an infant simulator as your own baby. Infant and Child Development, 24, 220–227. https://doi.org/10.1002/icd.1905.
Bartlett, E., & McMahon, C. (2016). The cognitive affective, and physiological impact of infant crying: a comparison of two Laboratory methodologies. Journal of Reproductive and Infant Psychology, 34, 196–209. https://doi.org/10.1080/02646838.2015.1113515.
Behrens, K. Y., Haltigan, J. D., & Bahm, N. I. G. (2016). Infant attachment, adult attachment, and maternal sensitivity: Revisiting the intergenerational transmission gap. Attachment & Human Development, 18, 337–353. https://doi.org/10.1080/14616734.2016.1167095.
Belsky, J., Conger, R., & Capaldi, D. M. (2009). The intergenerational transmission of parenting: Introduction to the special section. Developmental Psychology, 45, 1201–1204. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0016245.
Berlin, L. J., Cassidy, J., & Appleyard, K. (2008). The influence of early attachments on other relationships. In J. Cassidy & P. R. Shaver (Eds), Handbook of attachment: theory, research, and clinical applications. 2nd edn. (pp. 333–347). New York, NY: Guilford Press.
Berntson, G. G., Quigley, K. S., & Lozano, D. (2007). Cardiovascular psychophysiology. In J. T. Cacioppo, L. G. Tassinary & G. G. Berntson (Eds), Handbook ofpsychophysiology (pp. 182–210). New York, NY: Cambridge University Press.
Bowlby, J. (1973). Attachment and loss: Vol.2: separation anxiety and anger. New York, NY: BasicBooks.
Bruning, S., & McMahon, C. (2009). The impact of infant crying on young women: a randomized controlled study. Journal of Reproductive and Infant Psychology, 27, 206–220. https://doi.org/10.1080/02646830802350856.
Braungart-Rieker, J. M., Garwood, M. M., Powers, B. P., & Wang, X. (2001). Parental sensitivity, infant affect, and affect regulation: predictors of later attachment. Child Development, 72, 252–270. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-8624.00277.
Buckholdt, K. E., Parra, G. R., & Jobe-Shields, L. (2014). Intergenerational transmission of emotional dysregulation through parental invalidation of emotions: implications for adolescent internalizing and externalizing behaviors. Journal of Child and Family Studies, 23, 324–332. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-013-9768-4.
Castro, V. L., Halberstadt, A. G., Lozada, F. T., & Craig, A. B. (2015). Parents’ emotion-related beliefs, behaviours, and skills predict children’s recognition of emotion. Infant and Child Development, 24, 1–22. https://doi.org/10.1002/icd.1868.
Clark, R. (1999). The parent-child early relational assessment: a factorial validity study. Educational and Psychological Measurement, 59, 821–846. https://doi.org/10.1177/00131649921970161.
Chopik, W. J., Edelstein, R. S., & Fraley, R. C. (2013). From the cradle to the grave: age differences in attachment from early adulthood to old age. Journal of Personality, 81, 171–183. 10.111/j.1467-6494.2012.00793.x.
Chronaki, G., Garner, M., Hadwin, J. A., Thompson, M. J. J., Chin, C. Y., & Sonuga-Barke, E. J. S. (2015). Emotion-recognition abilities and behavior problem dimensions in preschoolers: Evidence for a specific role for childhood hyperactivity. Child Neuropsychology, 21, 25–40. https://doi.org/10.1080/09297049.2013.863273.
Conger, R. D., Belsky, J., & Capaldi, D. M. (2009). The intergenerational transmission of parenting: closing comments for the special section. Developmental Psychology, 45, 1276–1283. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0016911.
Crouch, J. L., Skowronski, J. J., Milner, J. S., & Harris, B. (2008). Parental responses to infant crying: The influence of child physical abuse risk and hostile priming. Child Abuse & Neglect, 32, 702–710. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chiabu.2007.11.002.
Crowell, J. A., Fraley, R. C., & Roisman, G. I. (2016). Mesaurement of individual differences in adult attachment. In J. Cassidy & P. R. Shaver (Eds), Handbook of attachment: theory, research, and clinical applications (pp. 598–635). New York, NY: The Guilford Press.
Dawson, M. E., Schell, A. M., & Filion, D. L. (2007). The electrodermal system. In J. T. Cacioppo, L. G. Tassinary & G. G. Berntson (Eds), Handbook of psychophysiology (pp. 159–181). New York, NY: Cambridge University Press.
de Cock, E. S. A., Henrichs, J., Rijk, C. H. A. M., & van Bakel, H. J. A. (2015). Baby please stop crying: An experimental approach to infant crying, affect, and expected parenting self-efficacy. Journal of Reproductive and Infant Psychology, 33, 414–425. https://doi.org/10.1080/02646838.2015.1024212.
Devos, T., Blanco, K., Rico, F., & Dunn, R. (2008). The role of parenthood and college education in the self-concept of college students: explicit and implicit assessments of gendered aspirations. Sex Roles, 59, 214–228. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11199-008-9430-6.
Eisenberg, N., Hofer, C., & Vaughan, J. (2007). Effortful control and its socioemotional consequences. In J. J. Gross (Ed.), Handbook of emotion regulation (pp. 287–306). New York, NY: The Guilford Press.
Fabes, R. A., Eisenberg, N., & Bernzweig, J. (1990). Coping with Children’s Negative Emotions Scale (CCNES): description and scoring. Tempe, AZ: Arizona State University.
Fabes, R. A., Leonard, S. A., Kupanoff, K., & Martin, C. L. (2001). Parental coping with children’s negative emotions: relations with children’s emotional and social responding. Child Development, 72, 907–920. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-8624.00323.
Fraley, R. C., Waller, N. G., & Brennan, K. A. (2000). An item-response theory analysis of self-report measures of adult attachment. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 78, 350–365. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.78.2.350.
George, C., & Solomon, J. (1996). Representational models of relationships: Links between caregiving and attachment. Infant Mental Health Journal, 17, 198–216. 10.1002(SICI)1097-0355(199623)17:3<198::AID-IMHJ2>3.0CO;2-L.
Groh, A. M., & Roisman, G. I. (2009). Adults’ autonomic and subjective emotional responses to infant vocalizations: The role of secure base script knowledge. Developmental Psychology, 45, 889–893. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0014943.
Gnilka, P. B., Ashby, J. S., & Noble, C. M. (2013). Adaptive and maladaptive perfectionism as mediators of adult attachment styles and depression, hopelessness, and life satisfaction. Journal of Counseling & Development, 91, 78–86. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1556-6676.2013.00074.x.
Haltigan, J. D., Leerkes, E. M., Burney, R. V., O’Brien, M., Supple, A. J., & Calkins, S. D. (2012). The infant crying questionnaires: initial factor structure and validation. Infant Behavior & Development, 35, 876–883. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.infbeh.2012.06.001.
Hamilton, J. L., Kleiman, E. M., Rubenstein, L. M., Strange, J. P., Flynn, M., Abramson, L. Y., & Alloy, L. B. (2016). Deficits in emotional clarity and vulnerability to peer victimization and internalizing symptoms among early adolescents. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 45, 183–194. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10964-015-0260-x.
Hazan, C., & Shaver, P. R. (1994). Attachment as an organizational framework for research on close relationships. Psychological Inquiry, 5, 1–22. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15327965pli0501_1.
Hill-Soderland, A. L., Mills-Koonce, W. R., Propper, C., Calkins, S. D., Granger, D. A., Ginger, A. M., & Cox, M. J. (2008). Parasympathetic and sympathetic responses to the strange situation in infants and mothers form avoidant and securely attached dyads. Developmental Psychobiology, 50, 361–376. https://doi.org/10.1002/dev.20302.
Jones, J. D., Cassidy, J., & Shaver, P. R. (2015). Parents’ self-reported attachment styles: a review of links with parenting behaviors, emotions, and cognitions. Personality and Social Psychology Review, 19, 44–76.
Joosen, K. J., Mesman, J., Bakermans-Kranenburg, M. J., Pieper, S., Zeskind, P. S., & van IJzendoorn, M. H. (2013a). Physiological reactivity to infant crying and observed maternal sensitivity. Infancy, 18, 414–431. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1532-7078.2012.00122.x.
Joosen, K. J., Mesman, J., Bakersman-Kranenburg, M. J., & van IJzendoorn, M. H. (2013b). Maternal overreactive sympathetic nervous system responses to repeated infant crying predicts risk for impulsive harsh discipline of infants. Child Maltreatment, 18, 252–263. https://doi.org/10.1177/1077559513494762.
Kahle, S., Miller, J. G., Lopez, M., & Hastings, P. D. (2016). Sympathetic recovery from anger is associated with emotion regulation. Journal of Experimental Child Psychology, 142, 359–371.
Kopystynska, O., Spinrad, T. L., Seay, D. M., & Eisenberg, N. (2016). The interplay of maternal sensitivity and gentle control when predicting children’s subsequent academic functioning: Evidence of mediation by effortful control. Developmental Psychology, 52, 909–921. https://doi.org/10.1037/dev0000122.
Lang, S. N., Schoppe-Sullivan, S. J., Kotila, L. E., & Kamp Dush, C. M. (2013). Daily parenting engagement among new mothers and fathers: the role of romantic attachment in dual-earner families. Journal of Family Psychology, 27, 862–872. https://doi.org/10.1037/a003-4510.
Leerkes, E. M. (2011). Maternal sensitivity during distressing tasks: a unique predictor of attachment security. Infant Behavior and Development, 34, 443–446. https://doi.org/10.1016/jinfbeh.2011.04.006.
Leerkes, E. M., Parade, S. H., & Burney, R. V. (2010). Origins of mothers’ and fathers’ beliefs about infant crying. Journal of Applied Developmental Psychology, 31, 467–474. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appdev.2010.09.003.
Leerkes, E. M., & Siepak, K. J. (2006). Attachment linked predictors of women’s emotional and cognitive responses to infant distress. Attachment & Human Development, 8, 11–32. https://doi.org/10.1080/14616730600594450.
Leerkes, E. M., Su, J., Calkins, S. D., Supple, A. J., & O’Brien, M. (2016). Pathways by which mothers’ physiological arousal and regulation while caregiving predict sensitivity to infant distress. Journal of Family Psychology, 30, 769–799. https://doi.org/10.1037/fam0000185.
Leerkes, E. M., Supple, A. J., Su, J., & Cavanaugh, A. M. (2015). Links between remembered childhood emotion socialization and adult adjustment: similarities and differences between european american and african american women. Journal of Family Issues, 36, 1854–1877. https://doi.org/10.1177/0192513x13505567.
McKay, E. R., Rosinski, L., Mayes, L. C., Rutherford, H. J. V., & Bridgett, D. J. (2019). Maternal positive responses to a distressed infant simulator predict subsequent negative affect in infants. Infant Behavior and Development, 56, 101299.
Mills-Koonce, W. R., Appleyard, K., Marnett, M., Deng, M., Putallaz, M., & Cox, M. (2011). Adult attachment style and stress as risk factors for early maternal sensitivity and negativity. Infant Mental Health Journal, 32, 277–285. https://doi.org/10.1002/imhj.20296.
Moore, P., & Robin, A. (1981). An approach to parent training for high school students. American Journal of Family Therapy, 9, 61–69.
NICHD Early Child Care Research Network. (1999). Child care and mother-child interaction in the first 3 years of life. Developmental Psychology, 35(6), 1399–1413.
Out, D., Pieper, S., Bakermans-Kranenburg, M. J., & van Ijzendoorn, M. H. (2010). Physiological reactivity to infant crying: a behavioral genetic study. Genes, Brain, and Behavior, 9, 868–876. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1601-183x.2010.00624.x.
Peterson, B. D., Pirritano, M., Tucker, L., & Lampic, C. (2012). Fertility awareness and parenting attitudes amon American male and female undergraduate university students. Human Reproduction, 27, 1375–1382. https://doi.org/10.1093/humrep/des011.
Porges, S. W., Doussard-Roosevelt, J. A., & Maiti, A. K. (1994). Vagal tone and the physiological regulation of emotion. In N. A. Fox (Ed.), The development of emotion regulation: Biological and behavioral considerations (pp. 167–186). Chicago, IL: The Chicago Press.
Rholes, W. S., Simpson, J. A., Blakely, B. S., Lanigan, L., & Allen, E. A. (1997). Adult attachment styles, the desire to have children, and working models of parenthood. Journal of Personality, 65, 357–385.
Robles, T. F., & Kane, H. S. (2014). The attachment system and physiology in adulthood: Normative processes, individual differences, and implications for health. Journal of Personality, 82, 515–527. https://doi.org/10.1111/jopy.12052.
Roisman, G. I., Holland, A., Fortuna, K., Fraley, R. C., Clausell, E., & Clarke, A. (2007). The adult attachment interview and self-reports of attachment style: an empirical rapprochement. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 92, 678–697.
Rutherford, H. J. V., Goldberg, B., Luyten, P., Bridgett, D. J., & Mayes, L. C. (2013). Parental reflexive functioning is associated with tolerance of infant distress but not general distress: Evidence for a specific relationship using a simulated baby paradigm. Infant Behavior and Development, 36, 635–641. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.infbeh.2013.06.008.
Scharf, M., & Mayseless (2011). Buds of parenting in emerging adult males: what we learned from our parents. Journal of Adolescent Research, 26, 479–505.
Schoenmaker, C., Huffmeijer, R., van IJzendoorn, M. H., Bakermans-Kranenburg, M. J., van den Dries, L., LInting, M., & Juffer, F. (2015). Attachment and physiological reactivity to infant crying in young adulthood: dissociation between experiential and physiological arousal in insecure adoptees. Physiology & Behavior, 139, 549–556. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physbeh.2014.11.055.
Selcuk, E., Günaydin, G., Sumer, N., Harma, M., Salman, S., Hazan, C., & Ozturk, A. (2010). Self-reported romantic attachment style predicts everyday maternal caregiving behavior at home. Journal of Research in Personality, 44, 544–549.
Scrimgeour, M. B., Davis, E. L., & Buss, K. A. (2016). You get what you get and you don’t throw a fit!: emotion socialization and child physiology jointly predict early prosocial development. Developmental Psychology, 52, 102–116. https://doi.org/10.1037/dev0000071.
Thompson, R. H., Bruzek, J. L., & Cotnoir-Bichelman, N. M. (2011). The role of negative reinforcement in infant caregiving: an experimental simulation. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 44, 295–304. https://doi.org/10.1901/jaba.2011.44-295.
van Anders, S. M., Tolman, R. M., & Volling, B. L. (2012). Baby cries and nurturance affect testosterone in men. Hormones and Behavior, 61, 31–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yhbeh.2011.09.012.
van IJzendoorn, M. H. (1995). Adult attachment representations, parental responsiveness, andinfant attachment: a meta-analysis on the predictive validity of the Adult Attachment Interview. Psychological Bulletin, 117, 387–403. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-2909.117.3.387.
Vecchio, T. D., Walter, A., & O’Leary, S. G. (2009). Affective and physiological factors predicting maternal response to infant crying. Infant Behavior and Development, 32, 117–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.infbeh.2008.10.005.
Verhage, M. L., Schuengel, O., Madigan, S., Fearon, R. M. P., Oosterman, M., Rosalinda, C., & vanIjzendoorn, M. H. (2016). Narrowing the transmission gap: a synthesis of three decades of research on the intergenerational transmission of attachment. Psychological Bulletin, 142, 337–366. https://doi.org/10.1037/bul0000038.
Voorthuis, A., Out, D., van der Veen, R., Bhandari, R., van IJzendoorn, M. H., & Bakermans-Kranenburg, M. J. (2013). One doll fits all: validation of the leiden infant simulator sensitivity assessment (LISSA). Attachment & Human Development, 15, 603–617. https://doi.org/10.1080/1466734.2013.820897.
Wei, M., Russell, D. W., Mallinckrodt, B., & Vogel, D. L. (2007). The experiences in close relationship scale (ECR)-short form: reliability, validity, and factor structure. Journal of Personality Assessment, 88, 187–204. https://doi.org/10.1080/00223890701268041.
Zeifman, D. M. (2001). An ethological analysis of human infant crying: answering Tinbergen’s four questions. Developmental Psychobiology, 39, 265–285. https://doi.org/10.1002/dev.1005.
Zoline, S. S., & Jason, L. A. (1985). Preventive parent education for high school students. Journal of Clinical Child Psychology, 14, 119–123.
Author Contributions
MP: assisted with study design and execution, assisted with data analysis, and wrote the paper. EM: assisted with study design and execution, data analysis, and writing of manuscript. GL: assisted with behavioral coding. NE: assisted with study design and execution, assisted with data analysis, collaborated in the writing and editing of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the Science and Engineering Research Center, Texas Christian University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the Texas Christian University institutional research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pruitt, M.M., McKay, E.R., Lelakowska, G. et al. The Infant Simulator Paradigm with Non-Parents: Attitudes, Physiology, and Observed Caregiving. J Child Fam Stud 29, 2515–2529 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-019-01643-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-019-01643-x