Abstract
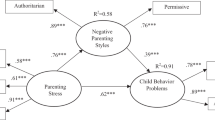
This study examined the influence of various factors on the behavioral problems of adolescents affected by HIV while considering the agreement between adolescent and parent reports on problem behaviors. A total of 136 families each with one parent living with HIV (PLH) and one child aged 13–18 were included. Structural equation modeling was used to explore relationships between selected family measures and adolescent’s problem behaviors. The correlation between the PLH and adolescent-reported behavioral problem measures was low (β = 0.11). PLH-reported adolescent problem behaviors were negatively related to PLH-reported parental bonding (β = −0.39), family routines (β = −0.26), and positively associated with family conflict (β = 0.21). Adolescent-reported family participation was associated with self-reported problem behaviors (β = −0.35). Our study reported discrete perceptions of adolescent problem behaviors from parents’ and adolescents’ points of view. Future intervention efforts should emphasize family contextual factors to improve behavioral outcomes in adolescents affected by HIV.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achenbach, T. M., & Rescorla, L. (2001). Manual for the ASEBA school-age forms & profiles. Burlington, VT: Achenbach System of Empirically Based Assessment.
Achenbach, T. M., & Ruffle, T. M. (2000). The child behavior checklist and related forms for assessing behavioral/emotional problems and competencies. Pediatrics in Review, 21(8), 265–271.
Acock, A. C. (2013). Discovering structural equation modeling using Stata (Revised edition). College Station, TX: Stata Press.
Agnew, R. (1992). Foundation for a general strain theory of crime and delinquency. Criminology, 30(1), 47–88.
Aseltine, R. H., Gore, S., & Gordon, J. (2000). Life stress, anger and anxiety, and delinquency: an empirical test of general strain theory. Journal of Health and Social Behavior, 41(3), 256–275.
Baca, C. B., Vickrey, B. G., Hays, R. D., Vassar, S. D., & Berg, A. T. (2010). Differences in child versus parent reports of the child’s health‐related quality of life in children with epilepsy and healthy siblings. Value in Health, 13(6), 778–786.
Billioud, S. (2007). Confucianism, “cultural tradition” and official discourses in China at the start of the new century. China Perspectives, 3, 50–65.
Bloom, B. L. (1985). A factor analysis of self‐report measures of family functioning. Family Process, 24(2), 225–239.
Bloom, B. L., & Naar, S. (1994). Self‐report measures of family functioning: extensions of a factorial analysis. Family Process, 33(2), 203–216.
Brislin, R. W. (1970). Back-translation for cross-cultural research. Journal of Cross-cultural Psychology, 1(3), 185–216.
Cao, Y., Chen, X., & Fan, R. (2011). Toward a Confucian family-oriented health care system for the future of China. Journal of Medicine and Philosophy, 36(5), 452–465.
Chi, P., & Li, X. (2013). Impact of parental HIV/AIDS on children’s psychological well-being: a systematic review of global literature. AIDS and Behavior, 17(7), 2554–2574.
Chi, P., Li, X., Tam, C. C., Du, H., Guoxiang, Z., & Zhao, J. (2015). Parenting mediates the impact of caregivers’ distress on children’s well-being in families affected by HIV/AIDS. AIDS and Behavior, 19(11), 2130–2139. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10461-015-1104-0.
Cremeens, J., Eiser, C., & Blades, M. (2006). Factors influencing agreement between child self-report and parent proxy-reports on the Pediatric Quality of Life Inventory™ 4.0 (PedsQL™) Generic Core Scales. Health and Quality of Life Outcomes, 4, 58.
Crespo, C., Santos, S., Canavarro, M. C., Kielpikowski, M., Pryor, J., & Féres-Carneiro, T. (2013). Family routines and rituals in the context of chronic conditions: a review. International Journal of Psychology, 48(5), 729–746.
Davis, E., Nicolas, C., Waters, E., Cook, K., Gibbs, L., Gosch, A., & Ravens-Sieberer, U. (2007). Parent-proxy and child self-reported health-related quality of life: using qualitative methods to explain the discordance. Quality of Life Research, 16(5), 863–871.
Eisenberg, M. E., Olson, R. E., Neumark-Sztainer, D., Story, M., & Bearinger, L. H. (2004). Correlations between family meals and psychosocial well-being among adolescents. Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine, 158(8), 792–796.
Erhart, M., Ellert, U., Kurth, B. M., & Ravens-Sieberer, U. (2009). Measuring adolescents’ HRQoL via self reports and parent proxy reports: an evaluation of the psychometric properties of both versions of the KINDL-R instrument. Health and Quality of Life Outcomes, 7, 77.
Ewart, C. K. (1991). Social action theory for a public health psychology. American Psychologist, 46(9), 931–946.
Fang, X., Li, X., Stanton, B., Hong, Y., Zhang, L., Zhao, G., & Lin, D. (2009). Parental HIV/AIDS and psychosocial adjustment among rural Chinese children. Journal of Pediatric Psychology, 34(10), 1053–1062.
Fiese, B. H. (2007). Routines and rituals: opportunities for participation in family health. Occupation, Participation and Health, 27(1), 41–49.
Formoso, D., Gonzales, N. A., & Aiken, L. S. (2000). Family conflict and children’s internalizing and externalizing behavior: protective factors. American Journal of Community Psychology, 28(2), 175–199.
Hagan, J., & Foster, H. (2001). Youth violence and the end of adolescence. American Sociological Review, 66(6), 874–899.
Holroyd, E. (2001). Hong Kong Chinese daughters’ intergenerational caregiving obligations. Social Science & Medicine, 53(9), 1125–1134.
Jensen, E. W., James, S. A., Boyce, W. T., & Hartnett, S. A. (1983). The family routines inventory: Development and validation. Social Science & Medicine, 17(4), 201–211.
Kuperminc, G. P., Wilkins, N. J., Jurkovic, G. J., & Perilla, J. L. (2013). Filial responsibility, perceived fairness, and psychological functioning of Latino youth from immigrant families. Journal of Family Psychology, 27(2), 173–182.
Lee, M. B., Lester, P., & Rotheram-Borus, M. J. (2002). The relationship between adjustment of mothers with HIV and their adolescent daughters. Clinical Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 7(1), 71–84.
Lee, S. J., Detels, R., Rotheram-Borus, M. J., Duan, N., & Lord, L. (2007). Depression and social support among HIV-affected adolescents. AIDS Patient Care and STDs, 21(6), 409–417.
Li, L., Sun, S., Wu, Z., Wu, S., Lin, C., & Yan, Z. (2007). Disclosure of HIV status is a family matter: field notes from China. Journal of Family Psychology, 21(2), 307–314.
Li, L., Wu, S., Wu, Z., Sun, S., Cui, H., & Jia, M. (2006). Understanding family support for people living with HIV/AIDS in Yunnan, China. AIDS and Behavior, 10(5), 509–517.
Li, X., Barnett, D., Fang, X., Lin, X., Zhao, G., Zhao, J., & Stanton, B. (2009). Lifetime incidences of traumatic events and mental health among children affected by HIV/AIDS in rural China. Journal of Clinical Child & Adolescent Psychology, 38(5), 731–744. https://doi.org/10.1080/15374410903103601.
Li, L., Wu, Z. Y., Wu, S., Jia, M. H., Lieber, E., & Lu, Y. (2008). Impacts of HIV/AIDS stigma on family identity and interactions in China. Families, Systems & Health, 26(4), 431–442.
Li, L., Ji, G., Liang, L. J., Ding, Y., Tian, J., & Xiao, Y. (2011). A multilevel intervention for HIV-affected families in China: Together for Empowerment Activities (TEA). Social Science & Medicine, 73(8), 1214–1221.
Li, L., Liang, L. J., Ji, G., Wu, J., & Xiao, Y. (2014). Effect of a family intervention on psychological outcomes of children affected by parental HIV. AIDS and Behavior, 18(11), 2051–2058.
Lin, S. (2008). Forced savings, social safety net, and family support: a new old-age security system for China. Chinese Economy, 41(6), 10–44.
Mellins, C. A., Brackis-Cott, E., Dolezal, C., Leu, C. S., Valentin, C., & Meyer-Bahlburg, H. F. (2008). Mental health of early adolescents from high-risk neighborhoods: the role of maternal HIV and other contextual, self-regulation, and family factors. Journal of Pediatric Psychology, 33(10), 1065–1075.
Ministry of Health, People’s Republic of China (2011). 2011 Estimates for the HIV/AIDS epidemic in China. http://www.unaids.org.cn/pics/20130521161757.pdf. Accessed 25 Sep 2017.
Murphy, D. A., Herbeck, D. M., Marelich, W. D., & Shuster, M. A. (2010). Predictors of sexual behavior among early and middle adolescents affected by maternal HIV. International Journal of Sexual Health, 22(3), 195–204.
Murphy, D. A., Marelich, W. D., Herbeck, D. M., & Payne, D. L. (2009). Family routines and parental monitoring as protective factors among early and middle adolescents affected by maternal HIV/AIDS. Child Development, 80(6), 1676–1691.
Murphy, D. A., Roberts, K. J., & Herbeck, D. M. (2013). Adolescent response to having an HIV-infected mother. AIDS Care, 25(6), 715–720.
Moretti, M. M., Obsuth, I., Craig, S. G., & Bartolo, T. (2015). An attachment-based intervention for parents of adolescents at risk: mechanisms of change. Attachment & Human Development, 17(2), 119–135.
Parker, G., Tupling, H., & Brown, L. B. (1979). A parental bonding instrument. British Journal of Medical Psychology, 52(1), 1–10.
Pedersen, S., & Revenson, T. A. (2005). Parental illness, family functioning, and adolescent well-being: a family ecology framework to guide research. Journal of Family Psychology, 19(3), 404–409.
Rarick, C. A. (2009). The historical roots of Chinese cultural values and managerial practices. Journal of International Business Research, 8(2), 59–66.
Revenson, T. A., AbraÃdo-Lanza, A. F., Majerovitz, S. D., & Jordan, C. (2005). Couples coping with chronic illness: what’s gender got to do with it? Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
Rosenberg, M. (1965). Society and the adolescent self-image. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
Rotheram-Borus, M. J., Stein, J. A., Jiraphongsa, C., Khumtong, S., Lee, S. J., & Li, L. (2010). Benefits of family and social relationships for Thai parents living with HIV. Prevention Science, 11(3), 298–307.
Rotheram-Borus, M. J., Weiss, R., Alber, S., & Lester, P. (2005). Adolescent adjustment before and after HIV-related parental death. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 73(2), 221–229.
Sherr, L., Cluver, L. D., Betancourt, T. S., Kellerman, S. E., Richter, L. M., & Desmond, C. (2014). Evidence of impact: health, psychological and social effects of adult HIV on children. AIDS, 28(Suppl. 3), 251–259.
Sherr, L., & Mueller, J. (2009). Where is the evidence base? Mental health issues surrounding bereavement and HIV in children. Journal of Public Mental Health, 7(4), 31–39.
Short, S. E., & Goldberg, R. E. (2015). Children living with HIV-infected adults: estimates for 23 countries in sub-Saharan Africa. PLoS One, 10(11), e0142580.
Spagnola, M., & Fiese, B. H. (2007). Family routines and rituals: a context for development in the lives of young children. Infants & Young Children, 20(4), 284–299.
Stein, D., Williamson, D. E., Birmaher, B., Brent, D. A., Kaufman, J., Dahl, R. E., & Ryan, N. D. (2000). Parent-child bonding and family functioning in depressed children and children at high risk and low risk for future depression. Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 39(11), 1387–1395.
The U.S. President’s Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief (PEPFAR) (2017). Orphans and vulnerable children. https://www.pepfar.gov/press/258063.htm. Accessed 25 Sep 2017.
Thurman, T. R., Kidman, R., & Taylor, T. M. (2015). Bridging the gap: the impact of home visiting programs for orphans and vulnerable children on social grant uptake in South Africa. Children and Youth Services Review, 48, 111–116.
USAID (2016). Orphans and vulnerable children affected by HIV and AIDS. https://www.usaid.gov/what-we-do/global-health/hiv-and-aids/technical-areas/orphans-and-vulnerable-children-affected-hiv#section1. Accessed 25 Sep 2017.
Van Der Ende, J., Verhulst, F. C., & Tiemeier, H. (2012). Agreement of informants on emotional and behavioral problems from childhood to adulthood. Psychological Assessment, 24(2), 293–300.
Van Roy, B., Groholt, B., Heyerdahl, S., & Clench-Aas, J. (2010). Understanding discrepancies in parent-child reporting of emotional and behavioral problems: Effects of relational and socio-demographic factors. BMC Psychiatry, 10, 56.
Yu, Y., Li, X., Zhang, L., Zhao, J., Zhao, G., Zheng, Y., & Stanton, B. (2013). Domestic chores workload and depressive symptoms among children affected by HIV/AIDS in China. AIDS Care, 25(5), 632–639.
Zhang, W., & Fuligni, A. J. (2006). Authority, autonomy, and family relationships among adolescents in urban and rural China. Journal of Research on Adolescence, 16(4), 527–537.
Zhao, J., Li, X., Qiao, S., Zhao, G., Zhang, L., & Stanton, B. (2015). Parental HIV disclosure: from perspectives of children affected by HIV in Henan China. AIDS Care, 27(4), 416–423. https://doi.org/10.1080/09540121.2014.978733.
Zolkoski, S. M., & Bullock, L. M. (2012). Resilience in children and youth: a review. Children and Youth Services Review, 34(12), 2295–2303.
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by National Institute of Child Health & Human Development/NIH (grant number R01HD068165). We would like to thank our project team members in Anhui, China for their contributions to this study.
Author contributions
L.L. designed and executed the study, guided the data analyses and result interpretation. W.S.C. analyzed the data and wrote part of the results. C.-W.L. collaborated in the writing of the manuscript. C.L. collaborated in the writing of the study and editing of the final manuscript. Y.X. and G.J. conducted the fieldwork and collaborated in the writing of the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, L., Comulada, W.S., Lan, CW. et al. Behavioral Problems Reported by Adolescents and Parents from HIV Affected Families in China. J Child Fam Stud 27, 365–373 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-017-0906-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-017-0906-2