Abstract
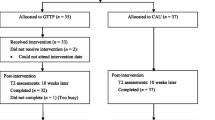
This brief report describes results from an efficacy test of Adolescent ParentWays program, an intervention developed for parents of adolescents ages 13–16 years who have symptoms of behavioral problems and social difficulties. Families were assigned to one of three groups. The in-person treatment group included parents who attended a 10 week, multiple session intervention program (n = 26), an online only treatment group (n = 29) that was given access to a web-based version of the program, or a wait-listed control group (n = 22). Pre- and post- testing of parents and their adolescent child was conducted. The Adolescent ParentWays intervention program was associated with several significant pre-post differences, including enhanced parent–adolescent relationship quality, increased parent knowledge and monitoring, and lower perceived stress for parents. Significant differences in the outcome variables were found for the in-person treatment group and for the on-line only versions of the program, versus a wait-listed control group. This demonstrates the effectiveness of the Adolescent ParentWays intervention program. The findings support the important role of parents in shaping adolescent behaviors and the positive impact of parenting training programs—both in-person traditional models and well as online versions—in promoting positive parent–adolescent relationships. The merits of using online parent training programs are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abidin, R. R. (1995). Parenting stress index, third edition: Professional manual. Odessa, FL: Psychological Assessment Resources Inc.
Achenbach, T., & Edelbrock, C. (1980). Child behavior checklist: CBCL.-T. Achenbach, University of Vermont.
Bergman, L. R., & Magnusson, D. (1997). A person-oriented approach in research ondevelopmental psychopathology. Development and Psychopathology, 9, 291–319.
Boivin, M., & Hymel, S. (1997). Peer experiences and social self-perceptions: A sequential model. Developmental Psychology, 33, 135–145.
Bowers, J. R., Mitchell, E. T., Hardesty, J. L., & Hughes, R. (2011). A review of online divorce education programs. Family Court Review, 49, 776–787.
Brendgen, M., Vitaro, F., & Bukowski, W. M. (1998). Affiliation with delinquent friends: Contributions of parents, self-esteem, delinquent behavior, and rejection by peers. Journal of Early Adolescence, 18, 244–265.
Brown, B. (1990). Peer groups. In S. Feldman & G. Elliott (Eds.), At the threshold: The developing adolescent (pp. 171–196). Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
Burke, K., Brennan, L., & Cann, W. (2012). Promoting protective factors for young adolescents: ABCD Parenting Young Adolescence Program randomized controlled trial. Journal of Adolescence, 35, 1315–1328.
Burke, K., Brennan, L., & Roney, S. (2010). A randomised controlled trial of the efficacy of the ABCD Parenting Young Adolescence Program: Rationale and methodology. Child and Adolescent Psychiatry and Mental Health, 4(22), 1–14.
Cain, D. S., & Combs-Orme, T. (2005). Family structure effects on parenting stress and practices in the African American family. Journal of Sociology and Social Welfare, 32, 19–40.
Carney, J. V. (2000). Bullied to death: Perceptions of peer abuse and suicidal behaviour during adolescence. School Psychology International, 21, 213–223.
Collins, W. A., Maccoby, E. E., Steinberg, L., Hetherington, E. M., & Bornstein, M. H. (2000). Contemporary research on parenting: The case for nature and nurture. American Psychologist, 55, 218–232.
Community Preventive Services Task Force. (2012). Improving adolescent health through interventions targeted to parents and other caregivers. American Journal of Preventive Medicine, 42, 327–328.
Cox, M. J., & Paley, B. (1997). Families as systems. Annual Review of Psychology, 48, 243–267.
Cox, M. J., & Paley, B. (2003). Understanding families as systems. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 12, 193–196.
Dekovic, M., & Meeus, W. (1997). Peer relations in adolescence—effects of parenting and adolescents self-concept. Journal of Adolescence, 20, 163–176.
DeRosier, M. E., (2002). Group interventions and exercises for enhancing children’s communication, cooperation, and confidence. Sarasota, FL: Professional Resources Press.
DeRosier, M. E., & Gilliom, M. (2007). Effectiveness of a parent training program for improving children’s social behavior. Journal of Child and Family Studies, 16, 660–670.
DeRosier, M. E., Kupersmidt, J. B., & Patterson, C. J. (1994). Children’s academic and behavioral adjustment as a function of the chronicity and proximity of peer rejection. Child Development, 65(6), 1799–1813.
DeRosier, M. E., & Markus, S. R. (2005). Building friendships and combatting bullying: Effectiveness of S.S.GRIN at one year follow-up. Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology, 34, 140–150.
File, T. (2013). Computer and internet use in the United States. Current Population Survey Reports, P20-568. U.S. Census Bureau,Washington, DC.
Galambos, N. L., Barker, E. T., & Almeida, D. M. (2003). Parents do matter: Trajectories of change in externalizing and internalizing problems in early adolescence. Child Development, 74, 578–594.
Hair, E. C., Moore, K. A., Garrett, S. B., Kinukawa, A., Lippman, L., & Michelson, E. (2006). The parent–adolescent relationship scale. In K. A. Moore & L. H. Lippman (Eds.), What do children need to flourish?: Conceptualizing and measuring indicators of positive development (pp. 183–202). New York: Springer.
Hayes, L., Smart, D., Toumbourou, J. W., & Sanson, A. (2004). Parenting influences on adolescent alcohol use (pp. 1–104). Melbourne: Australian Institute of Family Studies.
Kacir, C., & Gordon, D. (1999). Parenting Adolescents Wisely: The effectiveness of an interactive videodisk parent training program in Appalachia. Child and Family Behavior Therapy, 21, 1–22.
Kan, M. L., & McHale, S. M. (2007). Clusters and correlates of experiences with parents and peers in early adolescence. Journal of Research on Adolescence, 17, 565–586.
Mounts, N. S. (2011). Parental management of peer relationships and early adolescents’ social skills. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 40(4), 416–427.
Nowak, C., & Heinrichs, N. (2008). A comprehensive meta-analysis of Triple P—positive parenting program using hierarchical linear modeling: Effectiveness and moderating variables. Clinical Child and Family Psychology Review, 11, 114–144.
Pacifici, C., Delaney, R., White, L., Nelson, C., & Cummings, K. (2006). Web-based training for foster, adoptive, and kinship parents. Children and Youth Services Review, 28, 1329–1343.
Parke, R. D., Burks, V. M., Carson, J. L., Neville, B., & Boyum, L. A. (1994). Family-peer relationships: A tripartite model. In R. D. Parke & S. G. Kellam (Eds.), Exploring family relationships with other social contexts (pp. 115–145). Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Reitz, E., Prinzie, P., Dekovic, M., & Buist, K. L. (2007). The role of peer contacts in the relationship between parental knowledge and adolescents’ externalizing behaviors: A latent growth curve modeling approach. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 36, 623–624.
Schramm, D. G., & McCaulley, G. (2012). Divorce education for parents: A comparison of online and in-person delivery methods. Journal of Divorce and Remarriage, 53, 602–617.
Spera, C. (2005). A review of the relationship among parenting practices, parenting styles, and adolescent school achievement. Educational Psychology Review, 17, 125–146.
Spooner, C. (1999). Causes and correlates of adolescent drug abuse and implications for treatment. Drug and Alcohol Review, 18, 453–475.
Swanson, J., Valiente, C., Lemery-Chalfant, K., & O’Brien, T. C. (2011). Predicting early adolescents’ academic achievement, social competence, and physical health from parenting, ego resilience, and engagement coping. Journal of Early Adolescence, 31, 548–576.
Taylor, L. C., Clayton, J. D., & Rowley, S. J. (2004). Academic socialization: Understanding parental influences on children’s school-related development in the early years. Review of General Psychology, 8, 163–178.
Updegraff, K. A., McHale, S. M., Crouter, A. C., & Kupanoff, K. (2001). Parents’ involvement in adolescents’ peer relationships: A comparison of mothers’ and fathers’ roles. Journal of Marriage and the Family, 63, 655–668.
U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. (2013). Available at: https://www.healthypeople.gov/2020/topics-objectives/topic/Adolescent-Health.
Wade, S. L., Carey, J., & Wolfe, C. R. (2006). The efficacy of an online cognitive-behavioral family intervention in improving child behavior and social competence following pediatric brain injury. Rehabilitation Psychology, 51, 179–189.
Woodward, L. J., & Fergusson, D. M. (2000). Childhood peer relationship problems and later risks of educational under-achievement and unemployment. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 41, 191–201.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Taylor, L.C., Leary, K.A., Boyle, A.E. et al. Parent Training and Adolescent Social Functioning: A Brief Report. J Child Fam Stud 24, 3030–3037 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-014-0106-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-014-0106-2