Abstract
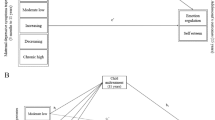
This study tests a model of intergenerational influences on childhood depressed mood that proposes (1) indirect and direct paths from maternal drug use to offspring depressed mood; and (2) pathway from maternal maladaptive personality attributes to offspring depressed mood via adverse child-rearing practices. A cross-sectional two-generational design was employed. Data was obtained utilizing structured questionnaires administered by trained interviewers in the homes of the participants. The sample was comprised of African American and Puerto Rican children (N = 210) and their mothers living in New York City. Using structural equation modeling, the analysis showed that maladaptive personality attributes are associated with adverse maternal child-rearing practices, which, in turn, are related to depressed mood in the offspring. Maternal drug use had a direct effect on offspring depressed mood. Maternal drug use also had an indirect path to offspring depressed mood via maladaptive personality attributes and adverse maternal child-rearing practices. The total effects analysis indicated that adverse maternal child-rearing practices was the strongest predictor of childhood depressed mood. This finding was consistent with the proximal position of the latent construct within the model. Maternal personality attributes and drug use were of lesser importance, but still statistically significant. The results suggest that maternal drug use and maladaptive personality attributes pose risks for the future depressive mood of children. The relative strength of positive maternal involvement with offspring should be the focus of preventive and therapeutic intervention efforts.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abaied, J. L., & Rudolph, K. D. (2014). Family relationships, emotional processes, and adolescent depression. In S. Richards & M. O’Hara (Eds.), The Oxford handbook of depression and comorbidity (pp. 460–475). New York: Oxford University Press.
Achenbach, T. M. (1991). Manual for the child behavior checklist 4–18 and 1991 profile. Burlington, VT: University of Vermont Department of Psychiatry.
Asgeirsdottir, B. B., Sigfusdottir, I. D., Gudjonsson, G. H., & Sigurdsson, J. F. (2011). Associations between sexual abuse and family conflict/violence, self-injurious behavior, and substance use: The mediating role of depressed mood and anger. Child Abuse and Neglect, 35, 210–219.
Baron, R. M., & Kenny, D. A. (1986). The moderator-mediator variable distinction in social psychological research: Conceptual, strategic, and statistical considerations. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 51, 1173–1182.
Bebbington, P., Jonas, S., Kuipers, E., King, M., Cooper, C., Brugha, T., & Jenkins, R. (2011). Childhood sexual abuse and psychosis: Data from a cross-sectional national psychiatric survey in England. The British Journal of Psychiatry, 199, 29–37.
Beydoun, H. A., Beydoun, M. A., Kaufman, J. S., Lo, B., & Zonderman, A. B. (2012). Intimate partner violence against adult women and its association with major depressive disorder, depressive symptoms and postpartum depression: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Social Science and Medicine, 75, 959–975.
Brook, J. S., Brook, D. W., Gordon, A. S., Whiteman, M., & Cohen, P. (1990). The psychosocial etiology of adolescent drug use: A family interactional approach. Genetic, Social, and General Psychology Monographs, 116, 111–267.
Brook, D. W., Brook, J. S., Zhang, C., Cohen, P., & Whiteman, M. (2002). Drug use and the risk of major depressive disorder, alcohol dependence, and substance use disorders. Archives of General Psychiatry, 59, 1039–1044.
Byrne, B. M. (1998). Structural equation modeling with LISREL, RELIS and SIMPLIS: Basic concepts, applications and programming. Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Caserta, M. T., Wyman, P. A., Wang, H., Moynihan, J., & O’Connor, T. G. (2011). Associations among depression, perceived self-efficacy, and immune function and health in preadolescent children. Development and Psychopathology, 23, 1139–1147.
Clark, D. B., Cornelius, J., Wood, D. S., & Vanyukov, M. (2004). Psychopathology risk transmission in children of parents with substance use disorders. American Journal of Psychiatry, 161, 685–691.
Cole, D. A. (1990). Relation of social and academic competence to depressive symptoms in childhood. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 99, 422–429.
Corona, M., McCarty, C., Cauce, A. M., Robins, R. W., Widaman, K. F., & Conger, R. D. (2012). The relation between maternal and child depression in Mexican American families. Hispanic Journal of Behavioral Sciences, 34, 539–556.
Costello, A., Edelbrock, C., Kalas, R., Kessler, R., & Klaric, S. H. (1982). The diagnostic interview schedule for children, parent version (rev.). Worcester, MA: University of Massachusetts Medical Center.
Cummings, J. R., & Druss, B. G. (2011). Racial/ethnic differences in mental health service use among adolescents with major depression. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 50, 160–170.
Derogatis, L. R., Lipman, R. S., Rickels, K., Uhlenhuth, E. H., & Covi, L. (1974). The Hopkins Symptom Checklist (HSCL): A self-report symptom inventory. Behavioral Science, 19, 1–15.
Diamantopoulos, A., & Siguaw, J. A. (2000). Introducing LISREL. London: Sage Publications.
Dubowitz, H., Kim, J., Black, M. M., Weisbart, C., Semiatin, J., & Magder, L. S. (2011). Identifying children at high risk for a child maltreatment report. Child Abuse and Neglect, 35, 96–104.
Dwairy, M. (2010). Parental inconsistency: A third cross-cultural research on parenting and psychological adjustment of children. Journal of Child and Family Studies, 19, 23–29.
Fernando, K., Carter, J. D., Frampton, C. M., Luty, S. E., McKenzie, J., Mulder, R. T., & Joyce, P. R. (2011). Childhood-, teenage-, and adult-onset depression: Diagnostic and individual characteristics in a clinical sample. Comprehensive Psychiatry, 52, 623–629.
Goh, S., Dong, Z., Zhang, Y., DiMauro, S., & Peterson, B. S. (2014). Mitochondrial dysfunction as a neurobiological subtype of autism spectrum disorder: Evidence from brain imaging. JAMA Psychiatry, 71, 665–671.
Goodman, S. H., Rouse, M. H., Connell, A. M., Broth, M. R., Hall, C. M., & Heyward, D. (2011). Maternal depression and child psychopathology: A meta-analytic review. Clinical Child and Family Psychology Review, 14, 1–27.
Gough, H. G. (1957). The California psychological inventory. Palo Alto, CA: Consulting Psychologists Press.
Günther, T., Konrad, K., De Brito, S. A., Herpertz-Dahlmann, B., & Vloet, T. D. (2011). Attentional functions in children and adolescents with ADHD, depressive disorders, and the comorbid condition. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 52, 324–331.
Hankin, B. L., Fraley, R. C., Lahey, B. B., & Waldman, I. D. (2005). Is depression best viewed as a continuum or discrete category? A taxometric analysis of childhood and adolescent depression in a population-based sample. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 114, 96–110.
Johnston, L. D., Bachman, J. G., & O’Malley, P. M. (1994). Monitoring the future: Questionnaire responses from the nation’s high school seniors, 1991. Ann Arbor, MI: University of Michigan, Institute for Social Research.
Kelleher, I., Lynch, F., Harley, M., Molloy, C., Roddy, S., Fitzpatrick, C., & Cannon, M. (2012). Psychotic symptoms in adolescence index risk for suicidal behavior: Findings from 2 population-based case-control clinical interview studies. Archives of General Psychiatry, 69, 1277–1283.
Kelley, M. L., Pearson, M. R., Trinh, S., Klostermann, K., & Krakowski, K. (2011). Maternal and paternal alcoholism and depressive mood in college students: Parental relationships as mediators of ACOA-depressive mood link. Addictive Behaviors, 36, 700–706.
Kelloway, K. E. (1998). Using LISREL for structural equation modeling: A researcher’s guide. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications.
Kendler, K. S., & Gardner, C. O. (2014). Sex differences in the pathways to major depression: A study of opposite-sex twin pairs. American Journal of Psychiatry, 171, 426–435.
Kendler, K. S., Sundquist, K., Ohlsson, H., Palmér, K., Maes, H., Winkleby, M. A., & Sundquist, J. (2012). Genetic and familial environmental influences on the risk for drug abuse: A national Swedish adoption study. Archives of General Psychiatry, 69, 690–697.
Lewis, G., Rice, F., Harold, G. T., Collishaw, S., & Thapar, A. (2011). Investigating environmental links between parent depression and child depressive/anxiety symptoms using an assisted conception design. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 50, 451–459.
MacKinnon, D. P., Lockwood, C. M., Hoffman, J. M., West, S. G., & Sheets, V. (2002). A comparison of methods to test mediation and other intervening variable effects. Psychological Methods, 7, 83–104.
McConley, R. L., Mrug, S., Gilliland, M. J., Lowry, R., Elliott, M. N., Schuster, M. A., & Franklin, F. A. (2011). Mediators of maternal depression and family structure on child BMI: Parenting quality and risk factors for child overweight. Obesity, 19, 345–352.
McDonald, R., Dodson, M. C., Rosenfield, D., & Jouriles, E. N. (2011). Effects of a parenting intervention on features of psychopathy in children. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 39, 1013–1023.
Michl, L. C., McLaughlin, K. A., Shepherd, K., & Nolen-Hoeksema, S. (2013). Rumination as a mechanism linking stressful life events to symptoms of depression and anxiety: Longitudinal evidence in early adolescents and adults. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 122, 339–352.
Muthén, L. K., & Muthén, B. O. (2010). Mplus users’ guide (6th ed.). Los Angeles, CA: Muthén & Muthén.
Otowa, T., Gardner, C. O., Kendler, K. S., & Hettema, J. M. (2013). Parenting and risk for mood, anxiety and substance use disorders: A study in population-based male twins. Social Psychiatry and Psychiatric Epidemiology, 48, 1841–1849.
Owens, M., Stevenson, J., Hadwin, J. A., & Norgate, R. (2012). Anxiety and depression in academic performance: An exploration of the mediating factors of worry and working memory. School Psychology International, 33, 433–449.
Pearlin, L. I., Lieberman, M. A., Menaghan, E. G., & Mullan, J. T. (1981). The stress process. Journal of Health and Social Behavior, 22, 337–356.
Pérez-Fuentes, G., Olfson, M., Villegas, L., Morcillo, C., Wang, S., & Blanco, C. (2013). Prevalence and correlates of child sexual abuse: A national study. Comprehensive Psychiatry, 54, 16–27.
Pikó, B. F., & Balázs, M. Á. (2012). Control or involvement? Relationship between authoritative parenting style and adolescent depressive symptomatology. European Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 21, 149–155.
Reinke, W. M., Eddy, J. M., Dishion, T. J., & Reid, J. B. (2012). Joint trajectories of symptoms of disruptive behavior problems and depressive symptoms during early adolescence and adjustment problems during emerging adulthood. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 40, 1123–1136.
Richardson, G. A., Goldschmidt, L., Larkby, C., & Day, N. L. (2013). Effects of prenatal cocaine exposure on child behavior and growth at 10 years of age. Neurotoxicology and Teratology, 40, 1–8.
Schaefer, E. S. (1965). Children’s report of parental behavior: An inventory. Child Development, 36, 413–424.
Schaefer, E. S., Edgerton, M., & Comstock, M. S. (1976). Parent interview. Unpublished manuscript, The University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill.
Schaefer, E. S., & Finkelstein, N. W. (1975). Child behavior toward parents: An inventory and factor analysis. Paper presented at the Annual Meeting of the American Psychological Association, Chicago, IL.
Shanahan, L., Copeland, W. E., Costello, E. J., & Angold, A. (2011). Child-, adolescent-and young adult-onset depressions: Differential risk factors in development? Psychological Medicine, 41, 2265–2274.
Acknowledgments
This study is supported by NIH research Grants DA05702 and DA12374, and Research Scientist Award DA00244, all to Dr. Judith Brook from the National Institute on Drug Abuse. The authors wish to thank Dr. Stephen J. Finch for his insightful review of this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brook, D.W., Lee, J.Y., Morojele, N.K. et al. Predictors of Childhood Depressed Mood: A Two-Generational Study. J Child Fam Stud 24, 2786–2794 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-014-0082-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-014-0082-6