Abstract
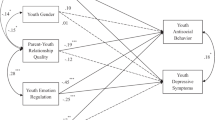
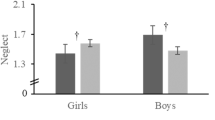
We examined parent emotion dysregulation as part of a model of family emotion-related processes and adolescent psychopathology. Participants were 80 parent–adolescent dyads (mean age = 13.6; 79 % African-American and 17 % Caucasian) with diverse family composition and socioeconomic status. Parent and adolescent dyads self-reported on their emotion regulation difficulties and adolescents reported on their perceptions of parent invalidation (i.e., punishment and neglect) of emotions and their own internalizing and externalizing behaviors. Results showed that parents who reported higher levels of emotion dysregulation tended to invalidate their adolescent’s emotional expressions more often, which in turn related to higher levels of adolescent emotion dysregulation. Additionally, adolescent-reported emotion dysregulation mediated the relation between parent invalidation of emotions and adolescent internalizing and externalizing behaviors. Potential applied implications are discussed.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achenbach, T. M. (1991). Manual for the Child Behavior Checklist/4-18 and 1991 Profile. Burlington, VT: University of Vermont Department of Psychiatry.
Aldao, A., Nolen-Hoeksema, S., & Schweizer, S. (2010). Emotion-regulation strategies across psychopathology: A meta-analytic review. Clinical Psychology Review, 30, 217–237.
Arnett, J. J. (1999). Adolescent storm and stress, reconsidered. American Psychologist, 54, 317–326.
Batson, C. D., O’Quin, K., Fultz, J., Vanderplas, M., & Isen, A. M. (1983). Influence of self-reported distress and empathy on egoistic versus altruistic motivation to help. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 45, 706–718.
Berking, M., Orth, U., Wupperman, P., Meier, L., & Caspar, F. (2008). Prospective effects of emotion-regulation skills on emotional adjustment. Journal of Counseling Psychology, 55, 485–494.
Buckholdt, K., Parra, G., & Jobe-Shields, L. (2009). Emotion regulation as a mediator of the relation between emotion socialization and deliberate self-harm. American Journal of Orthopsychiatry, 79, 482–490.
Buckholdt, K., Parra, G., & Jobe-Shields, L. (2010). Emotion dysregulation as a mechanism through which parental magnification of sadness increases risk for binge eating and limited control of eating behaviors. Eating Behaviors, 11, 122–126.
Cole, P. M., & Tan, P. Z. (2007). Emotion socialization from a cultural perspective. In J. E. Grusec & P. D. Hastings (Eds.), Handbook of socialization: Theory and research (pp. 516–542). New York: Guilford.
Davis, M. H., Luce, C., & Kraus, S. J. (1994). The heritability of characteristics associated with dispositional empathy. Journal of Personality, 62, 369–391.
Dumas, J. E. (2005). Mindfulness-based parent training: Strategies to lessen the grip of automaticity in families with disruptive children. Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology, 34, 779–791.
Duncan, L. G., Coatsworth, J. D., & Greenberg, M. T. (2009). A model of mindful parenting: Implications for parent–child relationships and prevention research. Clinical Child and Family Psychology Review, 12, 255–270.
Dunsmore, J. C., & Halberstadt, A. G. (2009). The dynamic cultural context of emotion socialization. In J. A. Mancini & K. A. Roberto (Eds.), Pathways of human development: Explorations of change (pp. 171–190). New York: Rowman & Littlefield Publishers.
Ehrenreich, J., Goldstein, C., Wright, L., & Barlow, D. (2009). Development of a unified protocol for the treatment of emotional disorders in youth. Child and Family Behavior Therapy, 31, 20–37.
Eisenberg, N., Cumberland, A., & Spinrad, T. L. (1998). Parental socialization of emotion. Psychological Inquiry, 9, 241–273.
Eisenberg, N., Fabes, R. A., Shepard, S. A., Guthrie, I. K., Murphy, B. C., & Reiser, M. (1999). Parental reactions to children’s negative emotions: Longitudinal relations to quality of children’s social functioning. Child Development, 70, 513–534.
Eisenberg, N., Valiente, C., Morris, A. S., Fabes, R. A., Cumberland, A., Reiser, M., et al. (2003). Longitudinal relations among parental emotional expressivity, children’s regulation, and quality of socioemotional functioning. Developmental Psychology, 39, 3–19.
Fabes, R. A., Eisenberg, N., & Bernzweig, J. (1990). The Coping with Children’s Negative Emotions Scale: Procedures and scoring. Available from authors. Arizona State University.
Gottman, J. M., Katz, L. F., & Hooven, C. (1996). Parental meta-emotion philosophy and the emotional life of families: Theoretical models and preliminary data. Journal of Family Psychology, 10, 243–268.
Gottman, J. M., Katz, L. F., & Hooven, C. (1997). Meta-emotion: How families communicate emotionally. Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc.
Gratz, K. L., & Roemer, L. (2004). Multidimensional assessment of emotion regulation and dysregulation: Development, factor structure, and initial validation of the difficulties in emotion regulation scale. Journal of Psychopathology and Behavior Assessment, 26, 41–54.
Jones, S., Eisenberg, N., Fabes, R. A., & MacKinnon, D. P. (2002). Parents’ reactions to elementary school children’s negative emotions: Relations to social and emotional functioning at school. Merrill-Palmer Quarterly, 48, 133–159.
Kazdin, A., & Weisz, J. (1998). Identifying and developing empirically supported child and adolescent treatments. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 66, 19–36.
Klimes-Dougan, B., & Zeman, J. (2007). Introduction to the special issue of social development: Emotion socialization in childhood and adolescence. Social Development, 16, 203–209.
Kovan, N., Chung, A., & Sroufe, L. (2009). The intergenerational continuity of observed early parenting: A prospective, longitudinal study. Developmental Psychology, 45, 1205–1213.
Larson, R., & Lampman-Petraitis, C. (1989). Daily emotional states as reported by children and adolescents. Child Development, 60, 1250–1260.
Larson, R., Moneta, G., Richards, M., & Wilson, S. (2002). Continuity, stability, and change in daily emotional experience across adolescence. Child Development, 73, 1151–1165.
Linehan, M. M. (1993). Cognitive behavioral treatment of borderline personality disorder. New York: Guilford Press.
Morris, A. S., Silk, J. S., Steinberg, L., Myers, S. S., & Robinson, L. R. (2007). The role of the family context in the development of emotion regulation. Social Development, 16, 361–388.
Morris, A., Silk, J., Steinberg, L., Terranova, A., & Kithakye, M. (2010). Concurrent and longitudinal links between children’s externalizing behavior in school and observed anger regulation in the mother–child dyad. Journal of Psychopathology and Behavioral Assessment, 32, 48–56.
Muthén, L., & Muthén, B. (1998–2006). Mplus user’s guide (4th ed.). Los Angeles: Muthén & Muthén.
Neumann, A., van Lier, P., Gratz, K., & Koot, H. (2010). Multidimensional assessment of emotion regulation difficulties in adolescents using the Difficulties in Emotion Regulation Scale. Assessment, 17, 138–149.
O’Neal, C. R., & Magai, C. (2005). Do parents respond in different ways when children feel different emotions? The emotional context of parenting. Development and Psychopathology, 17, 467–487.
Parra, G. R., Olsen, J. P., Buckholdt, K. E., Jobe-Shields, L. E., & Davis, G. L. (2010). A pilot study of the development of a measure assessing adolescent reactions in the context of emotion socialization. Journal of Child and Family Studies, 19, 596–606.
Pelaez, M., Field, T., Pickens, J., & Hart, S. (2008). Disengaged and authoritarian parenting behavior of depressed mothers with their toddlers. Infant Behavior and Development, 31, 145–148.
Silk, J., Shaw, D., Skuban, E., Oland, A., & Kovacs, M. (2006). Emotion regulation strategies in offspring of childhood-onset depressed mothers. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 47, 69–78.
Suveg, C., Kendall, P. C., Comer, J. S., & Robin, J. (2006). Emotion-focused cognitive-behavioral therapy for anxious youth: a multiple-baseline evaluation. Journal of Contemporary Psychotherapy, 36, 77–85.
Valiente, C., Lemery-Chalfant, K., & Reiser, M. (2007). Pathways to problem behaviors: Chaotic homes, parent and child effortful control, and parenting. Social Development, 16, 249–267.
Weinberg, A., & Klonsky, E. (2009). Measurement of emotion dysregulation in adolescents. Psychological Assessment, 21, 616–621.
Yap, M., Allen, N., & Sheeber, L. (2007). Using an emotion regulation framework to understand the role of temperament and family processes in risk for adolescent depressive disorders. Clinical Child and Family Psychology Review, 10, 180–196.
Zeman, J., Cassano, M., Perry-Parrish, C., & Stegall, S. (2006). Emotion regulation in children and adolescents. Journal of Developmental and Behavioral Pediatrics, 27, 155–168.
Zisser, A., & Eyberg, S. M. (2010). Treating oppositional behavior in children using parent–child interaction therapy. In A. E. Kazdin & J. R. Weisz (Eds.), Evidence-based psychotherapies for children and adolescents (2nd ed., pp. 179–193). New York: Guilford.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Buckholdt, K.E., Parra, G.R. & Jobe-Shields, L. Intergenerational Transmission of Emotion Dysregulation Through Parental Invalidation of Emotions: Implications for Adolescent Internalizing and Externalizing Behaviors. J Child Fam Stud 23, 324–332 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-013-9768-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-013-9768-4