Abstract
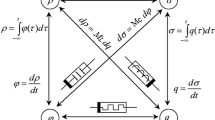
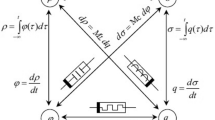
In this work, a charge-based memristor emulator is designed using a single active current mode component Differential Voltage Current Conveyor Transconductance Amplifier with one capacitor and two resistors as passive components. Importantly, the proposed circuit topology can be changed to either grounded or floating configuration using a single switch. Moreover, the proposed memristor design can be operated either in incremental or decremental configuration by using another switch. Therefore, using only two switches, the same circuitry can be utilized to design the floating/grounded incremental/decremental memristor. The pinched hysteresis loop area can be controlled by applying different biasing voltages. Further, the mathematical analysis is performed to drive the theoretical TiO2 based results for the proposed memristor emulator. In addition, simulations confirming the theoretical analysis are conducted in PSPICE using the 180 nm TSMC technology with a supply voltage of ± 0.9 V by varying frequencies and capacitances to obtain a pinched hysteresis loop. The presented circuit performs effectively for frequencies upto 500 MHz while operating with grounded type memristor and 300 MHz with floating type design. To check the ability to remember the history of the proposed memristor, the non-volatility test is performed for both the incremental and decremental configurations. Moreover, the suggested memristor design is applied in an adaptive learning circuit to prove its feasibility in neuromorphic applications.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All relevant data supporting the findings of this study are included within the article and its supplementary information files. However, raw data are available from the authors upon reasonable request and with the permission of the data providers.
References
Chua, L.O.: Memristor: the missing circuit element. IEEE Trans. Circuit Theory 18(5), 507–512 (1971)
Adhikari, S.P., Sah, M.P., Kim, H., Chua, L.O.: Three fingerprint of memristor. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I: Regul. Pap. 60(11), 3008–3021 (2013)
Saleh, S., Koldehofe, B.: On memristors for enabling energy efficient and enhanced cognitive network functions. IEEE Access 10, 129279–129312 (2022)
Liu, X., Zeng, Z.: Memristor crossbar architectures for implementing deep neural networks. Complex Intell. Syst. 8(2), 787–802 (2022)
Li, H.H., Chen, Y., Liu, C., Strachan, J.P., Davila, N.: Looking ahead for resistive memory technology: a broad perspective on ReRAM technology for future storage and computing. IEEE Consum. Electron. Mag. 6(1), 94–103 (2017)
Xue, X., Wang, C., Liu, W., Lv, H., Wang, M., Zeng, X.: A RISC-V processor with area-efficient memristor-based in-memory computing for hash algorithm in blockchain applications. Micromachines 10(8), 541 (2019)
Benatti, L., Zanotti, T., Pavan, P., Puglisi, F.M.: Ultra-low power logic in memory with commercial grade memristors and FPGA-based smart-IMPLY architecture. Microelectron. Eng. 280, 112062 (2023)
Shirinzadeh, S., Soeken, M., Gaillardon, P.-E., Drechsler, R.: Logic synthesis for RRAM-based in-memory computing. IEEE Trans. Comput.-Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 37(7), 1422–1435 (2018)
Strukov, D.B., Snider, G.S., Stewart, D.R., Williams, R.S.: The missing memristor found. Nature 453, 80–83 (2008)
Ilyas, N., Li, D., Li, C., et al.: Analog switching and artificial synaptic behavior of Ag/SiOx:Ag/TiOx/p++-Si memristor device. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 15, 30 (2020)
Chien W.C. et. al.: A Multi-level 40 nm WOX resistive memory with excellent reliability. 2011 International electron devices meeting Tech. Dig., 5–7(2011)
Wang, C., He, W., Tong, Y., et al.: Investigation and manipulation of different analog behaviors of memristor as electronic synapse for neuromorphic applications. Sci. Rep. 6, 22970 (2016)
Chang, Y.F., Fowler, B., Chen, Y.C., et al.: Demonstration of synaptic behaviors and resistive switching characterizations by proton exchange reactions in silicon oxide. Sci. Rep. 6, 21268 (2016)
Gogoi, H.J., Mallajosyula, A.T.: A comparative study on the forming methods of chalcogenide memristors to optimize the resistive switching performance. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 53(44), 445108 (2020)
Chanthbouala, A., Garcia, V., Cherifi, R.O., et al.: A ferroelectric memristor. Nat. Mater. 11(10), 860–864 (2012)
Kim, H., Sah, M.P., Yang, C., Cho, S., Chua, L.O.: Memristor emulator for memristor circuit applications. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Reg. Pap. 59(10), 2422–2431 (2012)
Yu, D., Iu, H.H.-C., Fitch, A.L., Liang, Y.: A floating memristor emulator based relaxation oscillator. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I: Reg. Pap. 61(10), 2888 (2014)
Kanyal, G., Kumar, P., Paul, S.K., Kumar, A.: OTA based high frequency tunable resistorless grounded and floating memristor emulators. AEU-Int. J. Electron. C. 92, 124–145 (2018)
Kumar, K., Nagar, B.C., Pradhan, G.: Single OTA-based tunable resistorless grounded memristor emulator and its application. J. Comput. Electron. 22, 549–559 (2023)
Ranjan, R.K., Niranjan, R., Bhuwal, N., Khateb, F.: Single DVCCTA based high frequency incremental/decremental memristor emulator and its application. AEU—Int. J. Electron. Commun. 82, 177–190 (2017)
Ranjan, R.K., Rani, N., Pal, R., Paul, S.K., Kanyal, G.: Single CCTA based high frequency floating and grounded type of incremental/decremental memristor emulator and its application. Microelectron. J. 60, 119–128 (2017)
Ayten, U.E., Minaei, S., Sagba, M.: Memristor emulator circuits using single CBTA. AEU Int. J. Electron. Commun. 82, 109–118 (2017)
Petrović, P.B.: Floating incremental/decremental flux-controlled memristor emulator circuit based on single VDTA. Anal. Integr. Circuits Signal Process 96(3), 417–433 (2018)
Vista, J., Ranjan, A.: Flux controlled floating memristor employing VDTA: incremental or decremental operation. IEEE Trans. Computer-Aided Des. Int. Circuits Syst. 40(2), 364–372 (2021)
Liu, X., Zeng, Z., Wen, S.: Implementation of memristive neural network with full-function Pavlov associative memory. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I, Reg. Pap. 63(9), 1454–1463 (2016)
Borghetti, J., Snider, G.S., Kuekes, P.J., Yang, J.J., Stewart, D.R., Williams, R.S.: Memristive’ switches enable ‘stateful’ logic operations via material implication. Nature 464(7290), 873–876 (2010)
Zhang, Y., Shen, Y., Wang, X.P., Cao, L.N.: A novel design for memristor-based logic switch and crossbar circuits, IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Reg. Papers 62(5), 1402–1411 (2015)
Waser, R., Dittmann, R., Staikov, G., Szot, K.: Redox-based resistive switching memories—Nanoionic mechanisms, prospects, and challenges. Adv. Mater. 21(25–26), 2632–2663 (2009)
Baghel V. S. and Akashe S.: Low Power Memristor Based 7T SRAM Using MTCMOS Technique. 2015 Fifth International Conference on Advanced Computing & Communication Technologies, Haryana, India, 222–226(2015).
Itoh, M., Chua, L.O.: Memristor oscillators. Int. J. Bifurcation Chaos 18(11), 3183–3206 (2008)
Bao, B.C., Liu, Z., Xu, J.P.: Steady periodic memristor oscillator with transient chaotic behaviours. Electron. Lett. 46(3), 237–238 (2010)
Pan, C., Hong, Q., Wang, X.: A novel memristive chaotic neuron circuit and its application in chaotic neural networks for associative memory. IEEE Trans. Comput-Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 40(3), 521–532 (2021)
Halawani, Y., Mohammad, B., Al-Qutayri, M., Al-Sarawi, S.F.: Memristor-based hardware accelerator for image compression. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. Syst. 26(12), 2749–2758 (2018)
Yesil, A., Babacan, Y., Kaçar, F.: A new DDCC based memristor emulator circuit and its applications. Microelectron. J. 45(3), 282–287 (2014)
Abuelma’atti, M.T., Khalifa, Z.J.: A continuous-level memristor emulator and its application in a multivibrator circuit. AEU-Int J Electron. Commun. 69(4), 771–775 (2015)
Sánchez-López, C., Carrasco-Aguilar, M.A., Muñiz-Montero, C.: A 16Hz–160kHz memristor emulator circuit. AEU-Int. J. Electron. C. 69(9), 1208–1219 (2015)
Vista, J., Ranjan, A.: A simple floating MOS-memristor for high-frequency applications. IEEE Trans.Very Large Scale Integr. Syst. 27(5), 1186–1195 (2019)
Sözen, H., Çam, U.: Electronically tunable memristor emulator circuit. Analog Integr. Circ. Sig. Process 89, 655–663 (2016)
Kumar N., Kumar M. & Pandey N.: Single DXCCTA based Charge Controlled Floating Incremental/Decremental Memristor Emulator. 2022 8th International Conference on Signal Processing and Communication (ICSC), Noida, India, 663–668(2022).
Gupta, S., Rai, S.K.: New grounded and floating decremental/incremental memristor emulators based on CDTA and its application. Wireless Pers. Commun. 113(2), 773–798 (2020)
Petrovic, P.: A universal electronically controllable memelement emulator based on VDCC with variable configuration. Electronics 11, 3657 (2022)
Ghosh, M., Mondal, P., Borah, S.S., Kumar, S.: Resistorless memristor emulators: floating, grounded using OTA and VDBA for high frequency applications. IEEE Trans. Comput.-Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 42, 978–986 (2022)
Raj, N., Ranjan, R.K., Khateb, F.: Flux-controlled memristor emulator and its experimental results. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst. 28(4), 1050–1061 (2020)
Shankar, C., Singh, S.V., Imam, R.: SIFO–VM/TIM universal biquad filter using single DVCCTA with fully CMOS realization. Analog Integr. Circ. Sig. Process 109, 33–46 (2021)
Memristive model of amoeba learning. Phys. Rev. E, Stat. Phys. Plasmas Fluids Relat. Interdiscip. Top.80, 2009, Art. no. 021926.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge Swati Verma for her valuable insights and suggestions.
Funding
This research was conducted without receiving any funding from public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors would like to assert that there are no conflicts of interest regarding this research study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bhuwal, N., Majumder, M.K. & Gupta, D. Floating/grounded charged controlled memristor emulator using DVCCTA. J Comput Electron (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10825-024-02176-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10825-024-02176-3