Abstract
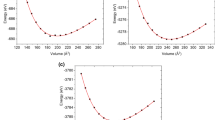
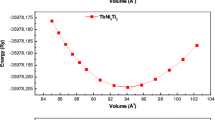
First-principles electronic, thermoelectric, thermodynamic, and optical calculations of an alkali pnictide compound, Li3Bi, are implemented by WIEN2k, BoltzTraP and Gibbs2 using density functional theory in the presence of spin–orbit coupling. The generalized gradient approximation and modified Becke and Janson functionals with the generalized gradient approximation are utilized for the treatment of exchange and correlation potential. The Li3Bi electronic band structure indicates that this compound is a semiconductor at zero pressure. The energy band gap of this compound closes at a pressure of 6.0 GPa. In contrast, low pressures enhance the energy band gap and reduce the band width of the valence and conduction bands. The pressure and temperature effects on the thermoelectric and thermodynamic performance of this compound are investigated. This results reveal (1) an increase in the power factor values under high temperatures and low pressures, (2) a reduction in the thermal expansion and the specific heat capacity at constant volume and an increase in the Debye temperature under high pressures at constant temperature. Also, the evaluation of optical properties under various hydrostatic pressures shows an increase in the static real part of the dielectric function and the static reflectivity of Li3Bi at a pressure of 6 GPa.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beister, H.J., Klein, J., Schewe, J., Syassen, K.: Structural phase transitions of alkali metal pnictides and chalcogenides under pressure. High Pressure Res. 7(1), 91–95 (1991)
Brauer, G., Zintl, E.: Konstitution von Phosphiden, Arsemiden, Antimoniden und Wismutiden des Lithiums, Natriums und Kaliums. Z. Phys. Chem. 37B(5/6), 323–352 (2017)
Spicer, W.E.: Photoemissive, photoconductive, and optical absorption studies of alkali-antimony compounds. Phys. Rev. 112, 114 (1958)
Gnutzmann, V.G., Dorn, F.W., Klemm, W.: Uber einige A3B- und AB2-Verbindungen der schweren Alkalimetalle mit Elementen der V Gruppe. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 309(3/4), 210–225 (1961)
Hafner, P., Range, K.-J.: Na3As revised: high-pressure synthesis of single crystals and structure refinement. J. Alloys Compd. 216(1), 7 (1994)
Taft, E.A., Philipp, H.R.: Structure in the energy distribution of photoelectrons from K3Sb and Cs3Sb. Phys. Rev. 115, 1583 (1959)
Kalarasse, L., Bennecer, B., Kalarasse, F.: Elastic and electronic properties of the alkali pnictide compounds Li3Sb, Li3Bi, Li2NaSb and Li2NaBi. Comput. Mat. Sci 50, 2880–2885 (2011)
Leonova, M.E., Bdikin, I.K., Kulinich, S.A., Gulish, O.K., Sevast’yanova, L.G., Burdina, K.P.: High-pressure phase transition of hexagonal alkali pnictides. Inorg. Mater. 39(3), 266–270 (2003)
Gulebaglan, S.E., Dogan, E.K.: Structural electronic and dynamic properties of Li3Bi and Li2NaBi. Mater. Res. Exp. 7, 015913 (2020)
Weppner, W., Huggins, R.A.: Electrochemical investigation of the chemical diffusion, partial ionic conductivities, and other kinetic parameters in Li3Sb and Li3Bi. J. Solid State Chem. 22, 297–308 (1977)
Kalarasse, L., Bennecer, B., Kalarasse, F.: Optical properties of the alkali antimonide semiconductors Cs3Sb, Cs2KSb, CsK2Sb and K3Sb. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 71, 314 (2010)
Zhou, G.T., Palchik, O., Pol, V.G., Sominski, E., Koltypin, Y., Gedanken, A.: Microwave-assisted solid-state synthesis and characterization of intermetallic compounds of Li3Bi and Li3Sb. J. Mater. Chem. 13, 2607 (2003)
Peng, K., Zhou, Z., Wang, H., Wu, H., Ying, J., Han, G., Lu, X.: Thermoelectric performance of binary lithium-based compounds: Li3Sb and Li3Bi. Appl. Phys. Lett. 119(3), 033901 (2021)
Yang, X., Dai, Z., Zhao, Y., Liu, J., Meng, S.: Low lattice thermal conductivity and excellent thermoelectric behavior in Li3Sb and Li3Bi. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 30, 425401 (2018)
Perdew, J.P., Burke, K., Ernzerhof, M.: Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 77, 3865–3868 (1996)
Tran, F., Blaha, P.: Accurate band gaps of semiconductors and insulators with a semilocal exchange–correlation potential. Phys. Rev. Lett. 102, 226401 (2009)
Engel, E., Dreizler, R.M.: Density Functional Theory: An Advanced Course. Springer, Berlin (2011)
Blaha, P., Schwarz, K., Tran, F., Laskowski, R., Madsen, G.K.H., Marks, L.D.: WIEN2k: an APW+lo program for calculating the properties of solids. J. Chem. Phys. 152, 074101 (2020)
Madsen, G.K.H., Singh, D.J.: BoltzTraP. A code for calculating band-structure dependent quantities. Comput. Phys. Commun. 175, 67–71 (2006)
Blanco, M.A., Francisco, E., Luana, V.: GIBBS: isothermal-isobaric thermodynamics of solids from energy curves using a quasi-harmonic Debye model. Comput. Phys. Commun. 158, 57–72 (2004)
Otero-de-la-Roza, A., Abbasi-Pérez, D., Luaña, V.: Gibbs2: a new version of the quasiharmonic model code. II. Models for solid-state thermodynamics, features and implementation. Comput. Phys. Commun. 182, 2232–2248 (2011)
Narimani, M., Yalameha, S., Nourbakhsh, Z.: High thermoelectric efficiency of LaX (X = Sb, Bi) two dimensional topological insulators. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 32, 255501 (2020)
Narimani, M., Yalameha, S., Nourbakhsh, Z.: Quantum spin Hall effect, thermoelectric performance, and optical properties of XBi (X = Sc, Y) monolayers. Physica E 122, 114199 (2020)
Guo, S.-D.: Spin–orbit and strain effect on power factor in monolayer MoS2. Comput. Mater. Sci. 123, 8–13 (2016)
Guo, S.-D., Wang, J.L.: Pressure enhanced thermoelectric properties in Mg2Sn. RSC Adv. 6(37), 31272–31276 (2016)
Hicks, L.D., Harman, T.C., Sun, X., Dresselhaus, M.S.: Experimental study of the effect of quantum-well structures on the thermoelectric figure of merit. Phys. Rev. B 53, R10493 (1996)
Onoue, M., Ishii, F., Oguchi, T.J.: Electronic and thermoelectric properties of the intermetallic compounds MNiSn (M = Ti, Zr, and Hf). Phys. Soc. Jpn. 77, 054706 (2008)
Dresselhaus, M., Chen, G., Ren, Z., Fleurial, J.P., Gogna, P., Tang, M.Y.: Nanocomposites to enhance ZT in thermoelectric. In: MRS Online Proceedings Library Archive, p. 1044 (2007)
Satyala, N., Norouzzadeh, P.: Nano Bulk Thermoelectric: Concepts, Techniques, and Modeling in Nanoscale Thermoelectric, pp. 141–183. Springer, Berlin (2014)
Zamanipour, Z., Shi, X., Mozafari, M., Krasinski, J.S., Tayebi, L.: Synthesis characterization, and thermoelectric properties of nanostructured bulk p-type MnSi1.73, MnSi1.75, and MnSi1.77. Ceram. Int. 39, 2353–2358 (2013)
Satyala, N., Vashaee, D.: Modeling of thermoelectric properties of magnesium silicide (Mg2Si). J. Electron. Mater. 41, 1785–1791 (2012)
Satyala, N., Vashaee, D.: Detrimental influence of nanostructuring on the thermoelectric properties of magnesium silicide. J. Appl. Phys. 112, 093716 (2012)
Norouzzadeh, P., Zamanipour, Z., Krasinski, J.S.: The effect of nanostructuring on thermoelectric transport properties of p-type higher manganese silicide MnSi1.73. J. Appl. Phys. 112, 124308 (2012)
Zamanipour, Z., Krasinski, J.S.: Comparison of boron precipitation in p-type bulk nanostructured and polycrystalline silicon germanium alloy. J. Appl. Phys. 113, 143715 (2013)
Toher, C., Plata, J.J., Levy, O., Jong, M., Asta, M., Nardelli, M.B., Curtarolo, S.: High-throughput computational screening of thermal conductivity, Debye temperature, and Grüneisen parameter using a quasiharmonic Debye model. Phys. Rev. B 90, 174107 (2014)
Narimani, M., Nourbakhsh, Z.: Topological phase, structural, electronic, thermodynamic and optical properties of XPtSb (X = Lu, Sc) compounds. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 102, 121–129 (2017)
Yalameha, S., Vaez, A.: Structural, electronic, elastic and thermodynamic properties of Al1−xZxNi (Z = Cr, V and x = 0, 0.125, 0.25) alloys: first principles calculations. Comput. Condens. Matter 21, e00415 (2019)
Yalameha, S., Vaez, A.: Ab-inito thermodynamic and elastic properties of AlNi and AlNi3 intermetallic compounds. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 32(11), 1850129 (2018)
Saeidi, P., Yalameha, S., Nourbakhsh, Z.: The investigation of structural, electronic, elastic and thermodynamic properties of Gd1−xYxAuPb alloys: a first principle study. Phys. Lett. A 383(2–3), 221–230 (2019)
Liu, L., Du, J., Zhao, J., Liu, H., Wu, D., Zhao, F.: Study of high-pressure and high-temperature behaviors and α-to-β phase transition of forsterite by first-principles and quasi-harmonic Debye model. Comput. Phys. Commun. 179, 417–423 (2008)
Ambrosch-Draxl, C., Sofo, J.O.: Linear optical properties of solids within the full potential linearized augmented plane wave method. Comput. Phys. Commun. 175, 1–14 (2006)
Narimani, M., Nourbakhsh, Z.: Topological phase and optical properties of LuNiBi bulk and nano-layer. Thin Solid Films 634, 112–120 (2017)
Narimani, M., Nourbakhsh, Z.: Topological phase, electronic, magnetic and optical properties of ScPdBi compound with Gd, Np and Cm impurities. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 434, 62–67 (2017)
Narimani, M., Nourbakhsh, Z.: Electronic, topological phase and optical properties of XPdBi (X = Lu, Sc) nano-layers. Thin Solid Films 616, 287–296 (2016)
Penn, D.R.: Wave-number-dependent dielectric function of semiconductors. Phys. Rev. 128, 2093–2097 (1962)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Narimani, M., Yalameha, S. & Nourbakhsh, Z. The pressure effects on electronic, thermoelectric, thermodynamic, and optical features of Li3Bi. J Comput Electron 20, 2300–2307 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10825-021-01811-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10825-021-01811-7