Abstract
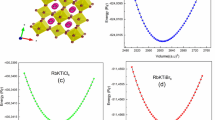
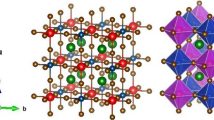
Using first-principles density functional theory, we investigated the geometrical structure and magnetic, electronic, and transport properties of blue phosphorene doped with a multitude of substitutional impurities, including both metallic and semiconducting elements. Substitutional dopants modified the properties of blue phosphorene. B, Al, Ga, Sb, Bi, and Sc substitutional dopants led to an indirect- to direct-gap transition. Blue phosphorene with C, Si, Ge, Sn, O, S, Se, and Fe substitutional dopant atoms showed dilute magnetic semiconducting properties. Furthermore, the effective mass as well as zero-bias transmission spectrum of this material support the fact that the transport properties of blue phosphorene are modified by the above-mentioned impurity atoms. The effective mass of holes for the Bi- and Sb-doped systems was about \(0.138m_{0}\), implying that these systems have high hole mobility. Meanwhile, the Sb-doped system exhibited the smallest effective mass for electrons of \(0.244m_{0}\). The results of this study illustrate that doped blue phosphorene exhibits different electronic, magnetic, transport, and optical properties from pristine blue phosphorene, which may enable many useful applications in nanoelectronics, gas sensing, optoelectronics, and spintronics.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Novoselov, K.S., Geim, A.K., Morozov, S.V., Jiang, D., Katsnelson, M.I., Grigorieva, I.V., Dubonos, S.V., Firsov, A.A.: Two-dimensional gas of massless Dirac fermions in graphene. Nature 438(7065), 197–200 (2005)
Geim, A.K., Novoselov, K.S.: The rise of graphene. Nat. Mater. 6(3), 183–191 (2007)
Jin, C., Lin, F., Suenaga, K., Iijima, S.: Fabrication of a freestanding boron nitride single layer and its defect assignments. Phys. Rev. Lett. 102(19), 195505 (2009)
Radisavljevic, B., Radenovic, A., Brivio, J., Giacometti, V., Kis, A.: Single-layer MoS\(_{2}\) transistors. Nat. Nanotechnol. 6(3), 147–150 (2011)
Wang, Q.H., Kalantar-Zadeh, K., Kis, A., Coleman, J.N., Strano, M.S.: Electronics and optoelectronics of two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenides. Nat. Nanotechnol. 7(11), 699–712 (2012)
Vogt, P., De Padova, P., Quaresima, C., Avila, J., Frantzeskakis, E., Asensio, M.C., Resta, A., Ealet, B., Le Lay, G.: Silicene: compelling experimental evidence for graphenelike two-dimensional silicon. Phys. Rev. Lett. 108(15), 155501 (2012)
Qi, J., Qian, X., Qi, L., Feng, J., Shi, D., Li, J.: Strain-engineering of band gaps in piezoelectric boron nitride nanoribbons. Nano Lett. 12(3), 1224–1228 (2012)
Bianco, E., Butler, S., Jiang, S., Restrepo, O.D., Windl, W., Goldberger, J.E.: Stability and Exfoliation of germanane: a germanium graphane analogue. ACS Nano 7(5), 4414–4421 (2013)
Koppens, F.H.L., Mueller, T., Avouris, P., Ferrari, C., Vitiello, M.S., Polini, M.: Photodetectors based on graphene, other two-dimensional materials and hybrid systems. Nat. Nanotechnol. 9(10), 780–793 (2014)
Tao, L., Cinquanta, E., Chiappe, D., Grazianetti, C., Fanciulli, M., Dubey, M., Molle, A., Akinwande, D.: Silicene field-effect transistors operating at room temperature. Nat. Nanotechnol. 10(3), 227–231 (2015)
Lu, G., Wu, T., Yuan, Q., Wang, H., Wang, H., Ding, F., Xie, X., Jiang, M.: Synthesis of large single-crystal hexagonal boron nitride grains on Cu–Ni alloy. Nat. Commun. 6, 6160 (2015)
Liu, H., Neal, A.T., Zhu, Z., Xu, X., Tomanek, D., Ye, P.D., Luo, Z.: Phosphorene: an unexplored 2D semiconductor with a high hole mobility. ACS Nano 8(4), 4033–4041 (2014)
Du, Y., Liu, H., Deng, Y., Ye, P.D.: Device perspective for black phosphorus field-effect transistors: contact resistance, ambipolar behavior, and scaling. ACS Nano 8(10), 10035–10042 (2014)
Li, L., Yu, Y., Ye, G.J., Ge, Q., Ou, X., Wu, H., Feng, D., Chen, X.H., Zhang, Y.: Black phosphorus field-effect transistors. Nat. Nanotechnol. 9(5), 372–377 (2014)
Buscema, M., Groenendijk, D.J., Blanter, S.I., Steele, G.A., Van Der Zant, H.S.J., Castellanos-Gomez, A.: Fast and broadband photoresponse of few-layer black phosphorus field-effect transistors. Nano Lett. 14(6), 3347–3352 (2014)
Na, J., Lee, Y.T., Lim, J.A., Hwang, D.K., Kim, G.-T., Choi, W.K., Song, Y.-W.: Few-layer black phosphorus field-effect transistors with reduced current fluctuation. ACS Nano 8(11), 11753–11762 (2014)
Xia, F., Wang, H., Jia, Y.: Rediscovering black phosphorus as an anisotropic layered material for optoelectronics and electronics. Nat. Commun. 5, 4458 (2014)
Qiao, J., Kong, X., Hu, Z.-X., Yang, F., Ji, W.: High-mobility transport anisotropy and linear dichroism in few-layer black phosphorus. Nat. Commun. 5, 4475 (2014)
Kou, L., Chen, C., Smith, S.C.: Phosphorene: fabrication, properties, and applications. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 6(14), 2794–2805 (2015)
Kim, J., Baik, S.S., Ryu, S.H., Sohn, Y., Park, S., Park, B.-G., Denlinger, J., Yi, Y., Choi, H.J., Kim, K.S.: Observation of tunable band gap and anisotropic Dirac semimetal state in black phosphorus. Science 349(6249), 723–726 (2015)
Zhu, Z., Tománek, D.: Semiconducting layered blue phosphorus: a computational study. Phys. Rev. Lett. 112(17), 176802 (2014)
Cheng, Y.C., Zhu, Z.Y., Mi, W.B., Guo, Z.B., Schwingenschlögl, U.: Prediction of two-dimensional diluted magnetic semiconductors: doped monolayer MoS\(_{2}\) systems. Phys. Rev. B 87(10), 100401 (2013)
Ramasubramaniam, A., Naveh, D.: Mn-doped monolayer MoS\(_{2}\): an atomically thin dilute magnetic semiconductor. Phys. Rev. B 87(19), 195201 (2013)
Sun, M., Ren, Q., Zhao, Y., Wang, S., Yu, J., Tang, W.: Magnetism in transition metal-substituted germanane: a search for room temperature spintronic devices. J. Appl. Phys. 119(14), 143904 (2016)
Sun, M., Wang, S., Du, Y., Yu, J., Tang, W.: Transition metal doped arsenene: a first-principles study. Appl. Surf. Sci. 389, 594–600 (2016)
Sun, M., Ren, Q., Wang, S., Zhang, Y., Du, Y., Yu, J., Tang, W.: Magnetism in transition-metal-doped germanene: a first-principles study. Comput. Mater. Sci. 118, 112–116 (2016)
Sun, M., Ren, Q., Zhao, Y., Chou, J.P., Yu, J., Tang, W.: Electronic and magnetic properties of 4\(d\) series transition metal substituted graphene: a first-principles study. Carbon 120, 265–273 (2017)
Sun, M., Tang, W., Ren, Q., Zhao, Y., Wang, S., Yu, J., Du, Y., Hao, Y.: Electronic and magnetic behaviors of graphene with 5d series transition metal atom substitutions: a firstprinciples study. Phys. E Low Dimens. Syst. Nanostruct. 80, 142–148 (2016)
Robertson, A.W., Montanari, B., He, K., Kim, J., Allen, C.S., Wu, Y.A., Olivier, J., Neethling, J., Harrison, N., Kirkland, A.I., Warner, J.H.: Dynamics of single Fe atoms in graphene vacancies. Nano Lett. 13(4), 1468–1475 (2013)
Wang, H., Wang, Q., Cheng, Y., Li, K., Yao, Y., Zhang, Q., Dong, C., Wang, P., Schwingenschlögl, U., Yang, W., Zhang, X.X.: Doping monolayer graphene with single atom substitutions. Nano Lett. 12(1), 141–144 (2012)
Rodríguez-Manzo, J.A., Cretu, O., Banhart, F.: Trapping of metal atoms in vacancies of carbon nanotubes and graphene. ACS Nano 4(6), 3422–3428 (2010)
Guan, J., Zhu, Z., Tománek, D.: Phase coexistence and metal-insulator transition in few-layer phosphorene: a computational study. Phys. Rev. Lett. 113(4), 46804 (2014)
Xie, J., Si, M.S., Yang, D.Z., Zhang, Z.Y., Xue, D.S.: A theoretical study of blue phosphorene nanoribbons based on firstprinciples calculations. J. Appl. Phys. 116(7), 73704 (2014)
Ding, Y., Wang, Y.: Structural, electronic, and magnetic properties of adatom adsorptions on black and blue phosphorene: a first-principles study. J. Phys. Chem. C 119(19), 10610–10622 (2015)
Sun, M., Tang, W., Ren, Q., Wang, S., Yu, J., Du, Y.: A first-principles study of light non-metallic atom substituted blue phosphorene. Appl. Surf. Sci. 356, 110–114 (2015)
Sun, M., Hao, Y., Ren, Q., Zhao, Y., Du, Y., Tang, W.: Tuning electronic and magnetic properties of blue phosphorene by doping Al, Si, As and Sb atom: a DFT calculation. Solid State Commun. 242, 36–40 (2016)
Bai, R., Chen, Z., Gou, M., Zhang, Y.: A first-principles study of group IV and VI atoms doped blue phosphorene. Solid State Commun. 270, 76–81 (2018)
Yu, W., Zhu, Z., Niu, C.-Y., Li, C., Cho, J.-H., Jia, Y.: Dilute magnetic semiconductor and half-metal behaviors in 3\(d\) transition-metal doped black and blue phosphorenes: a first-principles study. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 11(1), 77 (2016)
Sun, M., Chou, J.-P., Yu, J., Tang, W.: Electronic properties of blue phosphorene/graphene and blue phosphorene/graphenelike gallium nitride heterostructures. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 19(26), 17324–17330 (2017)
Sun, M., Wang, S., Yu, J., Tang, W.: Hydrogenated and halogenated blue phosphorene as Dirac materials: a first principles study. Appl. Surf. Sci. 392, 46–50 (2017)
Banerjee, L., Mukhopadhyay, A., Sengupta, A., Rahaman, H.: Performance analysis of uniaxially strained monolayer black phosphorus and blue phosphorus n-MOSFET and p-MOSFET. J. Comput. Electron. 15(3), 919–930 (2016)
Luo, H.C., Meng, R.S., Gao, H., Sun, X., Xiao, J., Ye, H.Y., Zhang, G.Q., Chen, X.P.: First-principles study of nitric oxide sensor based on blue phosphorus monolayer. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 38(8), 1139–1142 (2017)
Liu, N., Zhou, S.: Gas adsorption on monolayer blue phosphorus: implications for environmental stability and gas sensors. Nanotechnology 28(17), 175708 (2017)
Soler, J.M., Artacho, E., Gale, J.D., García, A., Junquera, J., Ordejón, P., Portal, D.S.: The SIESTA method for ab initio order-N materials simulation. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 14(11), 2745–2779 (2002)
Perdew, J.P., Burke, K., Ernzerhof, M.: Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 77(18), 3865–3868 (1996)
Troullier, N., Martins, J.L.: Efficient pseudopotentials for plane-wave calculations. II. Operators for fast iterative diagonalization. Phys. Rev. B 43(11), 8861–8869 (1991)
Monkhorst, H.J., Pack, J.D.: Special points for Brillouin-zon integrations. Phys. Rev. B 13(12), 5188–5192 (1976)
Zheng, H., Yang, H., Wang, H., Du, X., Yan, Y.: Electronic and magnetic properties of nonmetal atoms doped blue phosphorene: first-principles study. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 408, 121–126 (2016)
Sui, X., Si, C., Shao, B., Zou, X., Wu, J., Gu, B.-L., Duan, W.: Tunable magnetism in transition-metal-decorated phosphorene. J. Phys. Chem. C 119(18), 10059–10063 (2015)
Xu, L.-C., Song, X.-J., Yang, Z., Cao, L., Liu, R.-P., Li, X.-Y.: Phosphorene nanoribbons: passivation effect on bandgap and effective mass. Appl. Surf. Sci. 324, 640–644 (2015)
Ghosh, B., Nahas, S., Bhowmick, S., Agarwal, A.: Electric field induced gap modification in ultrathin blue phosphorus. Phys. Rev. B 91(11), 115433 (2015)
Peng, X., Wei, Q., Copple, A.: Strain-engineered direct-indirect band gap transition and its mechanism in two-dimensional phosphorene. Phys. Rev. B 90(8), 85402 (2014)
Suvansinpan, N., Hussain, F., Zhang, G., Chiu, C.H., Cai, Y., Zhang, Y.-W.: Substitutionally doped phosphorene: electronic properties and gas sensing. Nanotechnology 27(6), 65708 (2016)
He, Y., Xia, F., Shao, Z., Zhao, J., Jie, J.: Surface charge transfer doping of monolayer phosphorene via molecular adsorption. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 6(23), 4701–4710 (2015)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Safari, F., Fathipour, M. & Yazdanpanah Goharrizi, A. Tuning electronic, magnetic, and transport properties of blue phosphorene by substitutional doping: a first-principles study. J Comput Electron 17, 499–513 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10825-018-1159-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10825-018-1159-z