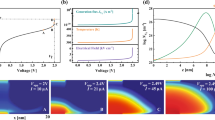
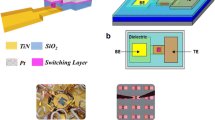
Abstract
The ultimate challenge of filamentary oxide-based ReRAM devices for storage-class memory application is the control of oxygen vacancies. As a result of the specifications dictated by the performance–cost dependency, oxygen vacancies in the conductive filament are predominantly isolated. This paper tries to shed light on the properties and implications of isolated vacancies in conductive filaments of oxide-based ReRAM devices. The isolated defects are a consequence of the low power requirements and result in very unstable resistance states. To find viable engineering solutions, the physical origins of these unstable states need to be investigated. Some of the possible origins like isolated vacancies and the effect of excess charge in the switching layer are outlined in this paper.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fleck, K., Aslam, N., Hoffmann-Eifert, S., Longo, V., Roozeboom, F., Kessels, W. M. M., Böttger, U., Waser, R., Menzel, S.: The influence of non-stoichiometry on the switching kinetics of strontium-titanate ReRAM devices. TED-2016-05-0784-R to IEEE-TED, no. (2016)
Baeumer, C., Schmitz, C., Ramadan, A.H.H., Du, H., Skaja, K., Feyer, V., Müller, P., Arndt, B., Jia, C.-L., Mayer, J., De Souza, R.A., Schneider, C.M., Waser, R., Dittmann, R.: Spectromicroscopic insights for rational design of redox-based memristive devices. Nat. Commun. 6, 8610 (2015)
Baeumer, C., Schmitz, C., Marchewka, A., Mueller, D.N., Valenta, R., Hackl, J., Raab, N., Rogers, S.P., Khan, M.I., Nemsak, S., Shim, M., Menzel, S., Schneider, C.M., Waser, R., Dittmann, R.: Quantifying redox-induced Schottky barrier variations in memristive devices via in operando spectromicroscopy with graphene electrodes. Nat. Commun. 7, 12398 (2016)
Smyth, D.M.: Defect Chemistry of Metal Oxides. Oxford University Press, Oxford (2000)
Maier, J.: Physical Chemistry of Ionic Materials: Ions and Electrons in Solids. Wiley, Hoboken (2004)
Yang, M.Y., Kamiya, K., Magyari-Köpe, B., Niwa, M., Nishi, Y., Shiraishi, K.: Charge-dependent oxygen vacancy diffusion in Al2O3-based resistive-random-access-memories. Appl. Phys. Lett. 103(9), 93504 (2013)
Magyari-Köpe, B., Park, S.G., Lee, H.D., Nishi, Y.: First principles calculations of oxygen vacancy-ordering effects in resistance change memory materials incorporating binary transition metal oxides. J. Mater. Sci. 47(21), 7498–7514 (2012)
Duncan, D., Magyari-Köpe, B., Nishi, Y.: Filament-induced anisotropic oxygen vacancy diffusion and charge trapping effects in hafnium oxide RRAM. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 37(4), 400–403 (2016)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wicklein, S. General considerations and implications of isolated oxygen vacancies in oxide-based filamentary ReRAM devices. J Comput Electron 16, 1038–1044 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10825-017-1046-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10825-017-1046-z