Abstract
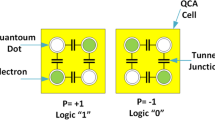
One of the most promising solutions for replacing present technologies is Quantum Cellular Automata (QCA) technology. Considering its nature, this technology has very low energy losses. On the other hand, designing circuits that are without waste of information or reversible can be useful for decreasing energy losses. The arithmetic logic unit (ALU) is recognized as the basis of processor systems. In this paper, a reversible ALU is proposed along with its implementation and simulation QCA cells that benefit from a new reversible gate that we call NHG (Naghibzadeh–Hoshmand Gate). The proposed NHG gate has better performance in terms of cost and delay when compared with similar gates. Thus, the ALU shows acceptable improvement in measures used to evaluate reversible circuits and circuits implemented with QCA cells when compared with previous works.

























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Moore, G.E.: Cramming more components onto integrated circuits. Electronics, Volume 38, Number 8, April 19, (1965), Electronics. Retrieved (2011). doi:10.1109/N-SSC.2006.4785860
Kunalan, D., Cheong, L.C., Chau, C.F., Ghazali, A.B.: Design of a 4-bit adder using reversible logic in quantum-dot cellular automata (QCA). Semicond. Electron. (ICSE) (2014). doi:10.1109/SMELEC.2014.6920795
Devoret, H.M., Glattli, C.: Single-electron transistors. Phys. World (1998). doi:10.1088/2058-7058/11/9/26
Heij, C.P., Hadley, P., Mooij, J.E.: Single electron inverter. Phys. Lett. (2000). doi:10.1063/1.1345822
Oya, T., Asai, T., Fukui, T., Amemiya, Y.: A majority-logic device using an irreversible single-electron box. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. (2003). doi:10.1109/TNANO.2003.808507
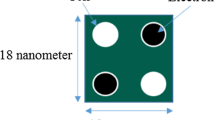
Lent, C.S., Tougaw, P.D., Porod, W.: Bistable saturation in coupled quantum dots for quantum cellular automata. Appl. Phys. Lett. 62, 714 (1993). doi:10.1063/1.108848
Landauer, R.: Irreversibility and heat generation in the computing processes. IBM J. Res. Develop. (1961). doi:10.1147/rd.53.0183
Morris Mano, M.: Computer System Architecture, 3rd edn. Prentice-Hall Inc, Upper Saddle River, NJ (1993)
Gupta, A., Malviya, U., Kapse, V.: Design of speed, energy and power efficient reversible logic based vedic ALU for digital processors. Engineering (NUiCONE). In: Nirma University International Conference (2012). doi:10.1109/NUICONE.2012.6493259
Roohi, A., Khademolhosseini, H., Sayedsalehi, S., Navi, K.: Implementation of reversible logic design in nanoelectronics on basis of majority gates. In: Computer Architecture and Digital Systems. (CADS) CSI International Symposium (2012). doi:10.1109/CADS.2012.6316410
Maity, M., Ghosal, P., Das, B.: Universal reversible logic gate design for low power computation at nano-scale. In: Asia Pacific Conference on Postgraduate Research in Microelectronics and Electronics Hyderabad, IEEE (2012). doi:10.1109/PrimeAsia.2012.6458648
Sen, B., Saran, D., Saha, M., Sikdar, B.K.: Synthesis of Reversible Universal Logic around QCA with Online Testability. In: International Symposium on Electronic System Design (ISED), IEEE (2011). doi:10.1109/ISED.2011.53
Sen, B., Nag, A., De, A., Sikdar, B.K.: Multilayer design of QCA multiplexer. Ann. IEEE India Conf. (2013). doi:10.1109/INDCON.2013.6725909
“QCADesigner Software”, Walus Group at the University of British Columbia, Web Address \(<\) http://www.mina.ubc.ca/qcadesigner_downloads \(>\), (2011)
Lewandowski, M., Ranganathan, N., Morrison, M.: Behavioral model of integrated qubit gates for quantum reversible logic design. In: VLSI (ISVLSI), IEEE Computer Society Annual Symposium (2013). doi:10.1109/ISVLSI.2013.6654658
Mohammadi, M., Eshghi, M.: On figures of merit in reversible and quantum logic designs. Q. Inf. Process. (2009). doi:10.1007/s11128-009-0106-0
Syamala, Y., Tilak, A.V.N.: Reversible arithmetic logic unit. In: Electronics Computer Technology (ICECT), International Conference (2011). doi:10.1109/ICECTECH.2011.5941987
Guan, Z., Li, W., Ding, W., Hang, Y., Ni, L.: An Arithmetic Logic Unit design based on reversible logic gates. In: IEEE Pacific Rim Conference on Communications, Computers and Signal Processing (2011). doi:10.1109/PACRIM.2011.6033020
Gopal, L., Mahayadin, N. S. M., Chowdhury, A.K., Gopalai, A.A., Singh, A. K.: Design and synthesis of reversible arithmetic and Logic Unit (ALU). In: Computer, Communications, and Control Technology (I4CT), International Conference (2014). doi:10.1109/I4CT.2014.6914191
Haghparast, N., Navi, K.: A Novel reversible BCD adder for nanotechnology based systems. Am. J. Appl. Sci. (2008). doi:10.3844/ajassp.2008.282.288
Ranganthan, N., Morrison, M.: Design of a reversible ALU based on novel programmable reversible logic gate structures. In: IEEE Computer Society Annual Symposium (2011). doi:10.1109/ISVLSI.2011.30
Rakshith, T.R., Saligram, R.: Parity preserving logic based fault tolerant reversible ALU. In: Information & Communication Technologies (ICT) IEEE Conference (2013). doi:10.1109/CICT.2013.6558144
Kaur, T., Singh, N.: Design of fault tolerant arithmetic & logical unit using reversible logic. In: International Conference on Machine Intelligence Research and Advancement (2013). doi:10.1109/CICT.2013.6558144
Morrison, M., Lewandowski, M., Meana, R., Ranganathan, N.: Design of a novel reversible ALU using an enhanced carry look- ahead adder. In: IEEE Nanotechnology Conference (2011). doi:10.1109/NANO.2011.6144406
Sen, B., Dutta, M., Singh, D. K., Saran, D., Sidkar, B. K.: QCA multiplexer based design of reversible ALU. In: IEEE International Conference on Circuits and Systems (ICCAS) (2012). doi:10.1109/ICCircuitsAndSystems.2012.6408309
Sen, B., Dutta, M., Goswami, M., Sidkar, B.K.: Modular Design of testable reversible ALU by QCA multiplexer with increase in programmability. Microelectron. J. (2014). doi:10.1016/j.mejo.2014.08.012
Sen, B., Dutta, M., Banik, D., Singh, D.K., Sidkar, B.K.: Design of fault tolerant reversible arithmetic logic unit in QCA. In: International Symposium on Electronic System Design (ISED) (2012). doi:10.1109/ISED.2012.50
Chaves, J.F., Silva, D.S., Camargos, V.V., Neto, O.P.V.: Towards reversible QCA computers: Reversible gates and ALU.” In: IEEE 6th Latin American Symposium on Circuits & Systems (LASCAS) (2015). doi:10.1109/LASCAS.2015.7250458
Gupta P, Agrawal A, Jha N (2006) An algorithm for synthesis of reversible logic circuits. IEEE Trans. Comput. Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. doi:10.1109/TCAD.2006.871622
Miller, D.M., Dueck,G.W., Maslov, D.:Atransformation based algorithm for reversible logic synthesis. In: Proceedings of the 40th Design Automation Conference, Anaheim, CA, pp. 318–323 (2003)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Naghibzadeh, A., Houshmand, M. Design and simulation of a reversible ALU by using QCA cells with the aim of improving evaluation parameters. J Comput Electron 16, 883–895 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10825-017-1004-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10825-017-1004-9