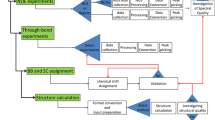
Abstract
Protein domains that can fold in isolation are significant targets in diverse area of proteomics research as they are often readily analyzed by high-throughput methods. Here, we report IS-Dom, a dataset of Independent Structural Domains (ISDs) that are most likely to fold in isolation. IS-Dom was constructed by filtering domains from SCOP, CATH, and DomainParser using quantitative structural measures, which were calculated by estimating inter-domain hydrophobic clusters and hydrogen bonds from the full length protein’s atomic coordinates. The ISD detection protocol is fully automated, and all of the computed interactions are stored in the server which enables rapid update of IS-Dom. We also prepared a standard IS-Dom using parameters optimized by maximizing the Youden’s index. The standard IS-Dom, contained 54,860 ISDs, of which 25.5 % had high sequence identity and termini overlap with a Protein Data Bank (PDB) cataloged sequence and are thus experimentally shown to fold in isolation [coined autonomously folded domain (AFDs)]. Furthermore, our ISD detection protocol missed less than 10 % of the AFDs, which corroborated our protocol’s ability to define structural domains that are able to fold independently. IS-Dom is available through the web server (http://domserv.lab.tuat.ac.jp/IS-Dom.html), and users can either, download the standard IS-Dom dataset, construct their own IS-Dom by interactively varying the parameters, or assess the structural independence of newly defined putative domains.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ISD:
-
Independent Structural Domain: Domains that fulfill the inter-domain interaction criteria calculated from the atomic coordinates of the full length protein, and are therefore likely to fold in isolation (or independently)
- AFD:
-
Autonomously folded domain: Domains that fulfill the sequence identity and termini overlap criteria with sequences listed in the PDB, and are therefore experimentally or "nearly" experimentally demonstrated to fold in isolation
- CATH:
-
Class, Architecture, Topology and Homologous superfamily
- MC:
-
Main-chain
- SC:
-
Side-chain
- PDB:
-
Protein Data Bank
- SCOP:
-
Structural Classification of Proteins
- SEM:
-
Standard Error of the Mean
References
Brenner SE (2000) Nat Struct Biol 7(Suppl):967
Jacobs SA, Podell ER, Cech TR (2006) Nat Struct Mol Biol 13(3):218
Hondoh T, Kato A, Yokoyama S, Kuroda Y (2006) Protein Sci 15(4):871
Vastermark A, Almen MS, Simmen MW, Fredriksson R, Schioth HB (2011) BMC Evol Biol 11:123
Chikayama E, Kurotani A, Tanaka T, Yabuki T, Miyazaki S, Yokoyama S, Kuroda Y (2010) BMC Bioinformatics 11:113
Andreeva A, Howorth D, Chandonia JM, Brenner SE, Hubbard TJ, Chothia C, Murzin AG (2008) Nucleic Acids Res 36(Database issue):D419
Greene LH, Lewis TE, Addou S, Cuff A, Dallman T, Dibley M, Redfern O, Pearl F, Nambudiry R, Reid A, et al (2007) Nucleic Acids Res 35(Database issue):D291
Punta M, Coggill PC, Eberhardt RY, Mistry J, Tate J, Boursnell C, Pang N, Forslund K, Ceric G, Clements J, et al (2012) Nucleic Acids Res 40(Database issue):D290
Miyazaki S, Kuroda Y, Yokoyama S (2002) J Struct Funct Genomics 2(1):37
Miyazaki S, Kuroda Y, Yokoyama S (2006) BMC Bioinformatics 7:323
Taylor WR (1999) Protein Eng 12(3):203
Swindells MB (1995) Protein Sci 4(1):103
Xu Y, Xu D, Gabow HN (2000) Bioinformatics 16(12):1091
Zhou H, Xue B, Zhou Y (2007) Protein Sci 16(5):947
Guo JT, Xu D, Kim D, Xu Y (2003) Nucleic Acids Res 31(3):944
Dumontier M, Yao R, Feldman HJ, Hogue CW (2005) J Mol Biol 350(5):1061
Siddiqui AS, Barton GJ (1995) Protein Sci 4(5):872
Rost B (1999) Protein Eng 12(2):85
Kuroda Y, Tani K, Matsuo Y, Yokoyama S (2000) Protein Sci 9(12):2313
Ebina T, Toh H, Kuroda Y (2011) Bioinformatics 27(4):487
McDonald IK, Thornton JM (1994) J Mol Biol 238(5):777
Youden WJ (1950) Cancer 3(1):32
Tanaka T, Yokoyama S, Kuroda Y (2006) Biopolymers 84(2):161
Ebina T, Toh H, Kuroda Y (2009) Biopolymers 92(1):1
Kabsch W, Sander C (1983) Biopolymers 22(12):2577
Goncalves-Almeida VM, Pires DE, de Melo-Minardi RC, da Silveira CH, Meira W, Santoro MM (2012) Bioinformatics 28(3):342
Acknowledgments
We thank Mr. Yuta Kumagai, Takao Arai, Tomohiro Furuyama, Shun Iwasaki and Ryotaro Tsuji (TUAT, Kuroda Lab) for their help with dataset construction. This work was funded by a Grant-in-aid from the Japanese Society for the Promotion of Science to Y.K. (JSPS-18500225).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Teppei Ebina and Yuki Umezawa contributed equally to this work.
Availability: IS-Dom is available at http://domserv.lab.tuat.ac.jp/IS-Dom.html and http://domserv.lab.tuat.ac.jp/
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ebina, T., Umezawa, Y. & Kuroda, Y. IS-Dom: a dataset of independent structural domains automatically delineated from protein structures. J Comput Aided Mol Des 27, 419–426 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10822-013-9654-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10822-013-9654-6