Abstract
Purpose
Dysregulated behaviors of trophoblast cells leading to defective placentation are considered the main cause of preeclampsia (PE). Abnormal miRNA expression profiles have been observed in PE placental tissue, indicating the significant role of miRNAs in PE development. This study aimed to investigate the expression of miR-101-5p in PE placental tissue and its biological functions.
Methods
The expression of miR-101-5p in placental tissue was detected by quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR). The localization of miR-101-5p in term placental tissue and decidual tissue was determined by the fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH)-immunofluorescence (IF) double labeling assay. The effect of miR-101-5p on the migration, invasion, proliferation, and apoptosis of the HTR8/SVneo trophoblast cells was investigated. Online databases combined with transcriptomics were used to identify potential target genes and related pathways of miR-101-5p. Finally, the interaction between miR-101-5p and the target gene was verified by qRT-PCT, WB, dual-luciferase reporter assay, and rescue experiments.
Results
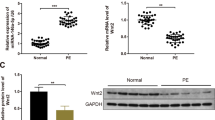
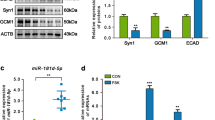
The study found that miR-101-5p was upregulated in PE placental tissue compared to normal controls and was mainly located in various trophoblast cell subtypes in placental and decidual tissues. Overexpression of miR-101-5p impaired the migration and invasion of HTR8/SVneo cells. DUSP6 was identified as a potential downstream target of miR-101-5p. The expression of miR-101-5p was negatively correlated with DUSP6 expression in HTR8/SVneo cells, and miR-101-5p directly bound to the 3′ UTR region of DUSP6. DUSP6 upregulation rescued the migratory and invasive abilities of HTR8/SVneo cells in the presence of miR-101-5p overexpression. Additionally, miR-101-5p downregulated DUSP6, resulting in enhanced ERK1/2 phosphorylation.
Conclusion
This study revealed that miR-101-5p inhibits the migration and invasion of HTR8/SVneo cells by regulating the DUSP6-ERK1/2 axis, providing a new molecular mechanism for the pathogenesis of PE.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding authors upon reasonable request.
References
Chappell LC, Cluver CA, Kingdom J, Tong S. Pre-eclampsia. Lancet. 2021;398:341–54.
Mol BWJ, Roberts CT, Thangaratinam S, Magee LA, de Groot CJM, Hofmeyr GJ. Pre-eclampsia. Lancet. 2016;387:999–1011.
Burton GJ, Redman CW, Roberts JM, Moffett A. Pre-eclampsia: pathophysiology and clinical implications. BMJ. 2019;366:l2381
Ji L, Brkić J, Liu M, Fu G, Peng C, Wang Y-L. Placental trophoblast cell differentiation: physiological regulation and pathological relevance to preeclampsia. Mol Aspects Med. 2013;34:981–1023.
Duan F-M, Fu L-J, Wang Y-H, Adu-Gyamfi EA, Ruan L-L, Xu Z-W, et al. THBS1 regulates trophoblast fusion through a CD36-dependent inhibition of cAMP, and its upregulation participates in preeclampsia. Genes Dis. 2021;8:353–63.
Bartel DP. microRNAs. Cell. 2004;116:281–97.
Mendell JT, Olson EN. microRNAs in stress signaling and human disease. Cell. 2012;148:1172–87.
Lykoudi A, Kolialexi A, Lambrou GI, Braoudaki M, Siristatidis C, Papaioanou GK, et al. Dysregulated placental microRNAs in early and late onset preeclampsia. Placenta. 2018;61:24–32.
Xu P, Zhao Y, Liu M, Wang Y, Wang H, Li Y, et al. Variations of microRNAs in human placentas and plasma from preeclamptic pregnancy. Hypertension. 2014;63:1276–84.
Zhu X, Han T, Sargent IL, Yin G, Yao Y. Differential expression profile of microRNAs in human placentas from preeclamptic pregnancies vs normal pregnancies. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2009;200:661.e1–7.
Toda H, Seki N, Kurozumi S, Shinden Y, Yamada Y, Nohata N, et al. RNA-sequence-based microRNA expression signature in breast cancer: tumor-suppressive miR-101-5p regulates molecular pathogenesis. Mol Oncol. 2020;14:426–46.
Shen W, Xie X-Y, Liu M-R, Wang L-L. microRNA-101-5p inhibits the growth and metastasis of cervical cancer cell by inhibiting CXCL6. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23:1957–68.
Ferretti C, Bruni L, Dangles-Marie V, Pecking AP, Bellet D. Molecular circuits shared by placental and cancer cells, and their implications in the proliferative, invasive and migratory capacities of trophoblasts. Hum Reprod Update. 2006;13:121–41.
Caunt CJ, Keyse SM. Dual-specificity MAP kinase phosphatases (MKPs): shaping the outcome of MAP kinase signalling. FEBS J. 2013;280:489–504.
Wu G, Tan J, Li J, Sun X, Du L, Tao S. miRNA-145-5p induces apoptosis after ischemia-reperfusion by targeting dual specificity phosphatase 6. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234:16281–9.
Sharma N, Kubaczka C, Kaiser S, Nettersheim D, Mughal SS, Riesenberg S, et al. Tpbpa-Cre-mediated deletion of TFAP2C leads to deregulation of Cdkn1a, Akt1 and the ERK pathway, causing placental growth arrest. Development. 2016;143(5):787–98.
Burton GJ, Sebire NJ, Myatt L, Tannetta D, Wang Y-L, Sadovsky Y, et al. Optimising sample collection for placental research. Placenta. 2014;35:9–22.
ACOG Practice Bulletin No 203. Chronic hypertension in pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol. 2019;133:e26–50.
Staff AC. The two-stage placental model of preeclampsia: an update. J Reprod Immunol. 2019;134–135:1–10.
Anton L, Olarerin-George AO, Schwartz N, Srinivas S, Bastek J, Hogenesch JB, et al. miR-210 inhibits trophoblast invasion and is a serum biomarker for preeclampsia. Am J Pathol. 2013;183:1437–45.
Taga S, Hayashi M, Nunode M, Nakamura N, Ohmichi M. miR-486-5p inhibits invasion and migration of HTR8/SVneo trophoblast cells by down-regulating ARHGAP5. Placenta. 2022;123:5–11.
Wang N, Feng Y, Xu J, Zou J, Chen M, He Y, et al. miR-362-3p regulates cell proliferation, migration and invasion of trophoblastic cells under hypoxia through targeting Pax3. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;99:462–8.
Lv Y, Lu X, Li C, Fan Y, Ji X, Long W, et al. miR-145–5p promotes trophoblast cell growth and invasion by targeting FLT1. Life Sci. 2019;239:117008.
Yang Y, Li H, Ma Y, Zhu X, Zhang S, Li J. miR-221-3p is down-regulated in preeclampsia and affects trophoblast growth, invasion and migration partly via targeting thrombospondin 2. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;109:127–34.
Xu P, Li Z, Wang Y, Yu X, Shao X, Li Y, et al. miR-18a contributes to preeclampsia by downregulating Smad2 (full length) and reducing TGF-β signaling. Mol Ther - Nucleic Acids. 2020;22:542–56.
Hemmatzadeh M, Shomali N, Yousefzadeh Y, Mohammadi H, Ghasemzadeh A, Yousefi M. microRNAs: small molecules with a large impact on pre-eclampsia. J Cell Physiol. 2020;235:3235–48.
Chen Q, Liu D, Hu Z, Luo C, Zheng SL. miRNA-101-5p inhibits the growth and aggressiveness of NSCLC cells through targeting CXCL6. OncoTargets Ther. 2019;12:835–48.
Yamada Y, Nohata N, Uchida A, Kato M, Arai T, Moriya S, et al. Replisome genes regulation by antitumor miR-101-5p in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2020;111:1392–406.
Kidger AM, Keyse SM. The regulation of oncogenic Ras/ERK signalling by dual-specificity mitogen activated protein kinase phosphatases (MKPs). Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2016;50:125–32.
Wu Q-N, Liao Y-F, Lu Y-X, Wang Y, Lu J-H, Zeng Z-L, et al. Pharmacological inhibition of DUSP6 suppresses gastric cancer growth and metastasis and overcomes cisplatin resistance. Cancer Lett. 2018;412:243–55.
Kato M, Onoyama I, Yoshida S, Cui L, Kawamura K, Kodama K, et al. Dual-specificity phosphatase 6 plays a critical role in the maintenance of a cancer stem-like cell phenotype in human endometrial cancer. Int J Cancer. 2020;147:1987–99.
Fan M, Li X, Gao X, Dong L, Xin G, Chen L, et al. LPS induces preeclampsia-like phenotype in rats and HTR8/SVneo cells dysfunction through TLR4/p38 MAPK pathway. Front Physiol. 2019;10:1030.
Szabo S, Mody M, Romero R, Xu Y, Karaszi K, Mihalik N, et al. Activation of villous trophoblastic p38 and ERK1/2 signaling pathways in preterm preeclampsia and HELLP syndrome. Pathol Oncol Res. 2015;21:659–68.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82171668, No. 81771614, No. 82171662, No. 81901506, No. 82001581) and Joint Funds of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. U21A20346).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: Jiacheng Xu; methodology: Jiacheng Xu; investigation: Jiacheng Xu, Jie Wang, Miaomiao Chen; software: Bingdi Chao, Jie He; writing-original draft: Jiacheng Xu; writing-review and editing: Jie Wang; Xin Luo; funding acquisition: Yuxiang Bai, Xiaofang Luo, Xin Luo; formal analysis: Hongli Liu, Lumei Xie; validation: Yuelan Tao; supervision: Hongbo Qi, Xin Luo.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, J., Wang, J., Chen, M. et al. miR-101-5p suppresses trophoblast cell migration and invasion via modulating the DUSP6-ERK1/2 axis in preeclampsia. J Assist Reprod Genet 40, 1597–1610 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-023-02846-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-023-02846-4