Abstract
Purpose
To compare reproductive outcomes following conventional in vitro fertilization (IVF) and intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) in poor responders fulfilling the Bologna criteria, with a single oocyte retrieved.
Methods
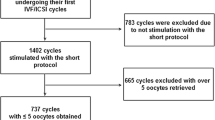
The present retrospective study included 243 Bologna poor responders with a single oocyte retrieved, who were categorized into three groups, depending on the fertilization method and semen quality (IVF non-male factor-IVF/NMF n = 101; ICSI non-male factor ICSI/NMF n = 50; ICSI male factor-ICSI/MF n = 92).
Results
In IVF/NMF, ICSI/NMF and ICSI/MF similar fertilization rates [65.3, 66, 58.7 %, respectively], proportions of embryo formation [63.4, 60, 53.3 %, respectively], proportions of good quality embryos [54.7, 56.7, 57.1 %, respectively], implantation rates [8.9, 10, 8.2 % respectively] and live birth rates per oocyte retrieval [5.0, 4.0, 3.3 %, respectively] were observed. Degeneration rate of oocytes due to mechanical damage was significantly higher after ICSI in the ICSI/NMF and ICSI/MF groups (8 and 6.5 %, respectively) compared to IVF/NMF (0 %) (p = 0.02).
Conclusions
Conventional IVF and ICSI are associated with similar reproductive outcomes in poor responder patients with a single oocyte retrieved. Therefore, the choice of fertilization method should be based primarily on semen quality, in combination with the patient’s previous history. A randomized controlled trial should be performed to confirm this study’s findings that conventional IVF and ICSI have similar reproductive outcomes in poor responders.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Palermo G, Joris H, Devroey P, Van Steirteghem AC. Pregnancies after intracytoplasmic injection of single spermatozoon into an oocyte. Lancet. 1992;340(8810):17–8.
Van Steirteghem AC, Nagy Z, Joris H, Liu J, Staessen C, Smitz J, et al. High fertilization and implantation rates after intracytoplasmic sperm injection. Hum Reprod. 1993;8(7):1061–6.
Fishel S, Aslam I, Lisi F, Rinaldi L, Timson J, Jacobson M, et al. Should ICSI be the treatment of choice for all cases of in-vitro conception? Hum Reprod. 2000;15(6):1278–83.
Oehninger S, Gosden RG. Should ICSI be the treatment of choice for all cases of in-vitro conception? No, not in light of the scientific data. Hum Reprod. 2002;17(9):2237–42.
Nyboe Andersen A, Carlsen E, Loft A. Trends in the use of intracytoplasmatic sperm injection marked variability between countries. Hum Reprod Update. 2008;14(6):593–604.
Sullivan EA, Zegers-Hochschild F, Mansour R, Ishihara O, de Mouzon J, Nygren KG, et al. International Committee for Monitoring Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ICMART) world report: assisted reproductive technology 2004. Hum Reprod. 2013;28(5):1375–90.
Mansour R, Ishihara O, Adamson GD, Dyer S, de Mouzon J, Nygren KG, et al. International committee for monitoring assisted reproductive technologies world report: Assisted Reproductive Technology 2006. Hum Reprod. 2014;29(7):1536–51.
Kupka MS, Ferraretti AP, de Mouzon J, Erb K, D’Hooghe T, Castilla JA, et al. Assisted reproductive technology in Europe, 2010: results generated from European registers by ESHRE. Hum Reprod. 2014;29(10):2099–113.
Hodes-Wertz B, Mullin CM, Adler A, Noyes N, Grifo JA, Berkeley AS. Is intracytoplasmic sperm injection overused? J Urol. 2012;187(2):602–6.
Ferraretti AP, Goossens V, de Mouzon J, Bhattacharya S, Castilla JA, Korsak V, et al. Assisted reproductive technology in Europe, 2008: results generated from European registers by ESHRE. Hum Reprod. 2012;27(9):2571–84.
Khamsi F, Yavas Y, Roberge S, Lacanna IC, Wong JC, Endman M. The status of controlled prospective clinical trials for efficacy of intracytoplasmic sperm injection in in vitro fertilization for non-male factor infertility. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2000;17(9):504–7.
Khamsi F, Yavas Y, Roberge S, Wong JC, Lacanna IC, Endman M. Intracytoplasmic sperm injection increased fertilization and good-quality embryo formation in patients with non-male factor indications for in vitro fertilization: a prospective randomized study. Fertil Steril. 2001;75(2):342–7.
Kim HH, Bundorf MK, Behr B, McCallum SW. Use and outcomes of intracytoplasmic sperm injection for non-male factor infertility. Fertil Steril. 2007;88(3):622–8.
Van der Westerlaken L, Naaktgeboren N, Verburg H, Dieben S, Helmerhorst F. Conventional in vitro fertilization versus intracytoplasmic sperm injection in patients with borderline semen: a randomized study using sibling oocytes. Fertil Steril. 2006;85(2):395–400.
Check JH, Bollendorf A, Summers-Chase D, Horwath D, Hourani W. Conventional oocyte insemination may result in a better pregnancy outcome than intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) for unexplained infertility. Clin Exp Obstet Gynecol. 2009;36(3):150–1.
Hershlag A, Paine T, Kvapil G, Feng H, Napolitano B. In vitro fertilization-intracytoplasmic sperm injection split: an insemination method to prevent fertilization failure. Fertil Steril. 2002;77(2):229–32.
Johnson LNC, Sasson IE, Sammel MD, Dokras A. Does intracytoplasmic sperm injection improve the fertilization rate and decrease the total fertilization failure rate in couples with well-defined unexplained infertility? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Fertil Steril. 2013;100(3):704–11.
Aboulghar MA, Mansour RT, Serour GI, Amin YM, Kamal A. Prospective controlled randomized study of in vitro fertilization versus intracytoplasmic sperm injection in the treatment of tubal factor infertility with normal semen parameters. Fertil Steril. 1996;66(5):753–6.
Staessen C, Camus M, Clasen K, De Vos A, Van Steirteghem A. Conventional in-vitro fertilization versus intracytoplasmic sperm injection in sibling oocytes from couples with tubal infertility and normozoospermic semen. Hum Reprod. 1999;14(10):2474–9.
Hwang JL, Seow KM, Lin YH, Hsieh BC, Huang LW, Chen HJ, et al. IVF versus ICSI in sibling oocytes from patients with polycystic ovarian syndrome: a randomized controlled trial. Hum Reprod. 2005;20(5):1261–5.
Moreno C, Ruiz A, Simon C, Pellicer A, Remohi J. Intracytoplasmic sperm injection as a routine indication in low responder patients. Hum Reprod. 1998;13(8):2126–9.
Vicdan K, Isik AZ. Intracytoplasmic sperm injection is not associated with poor outcome in couples with normal semen parameters and previous idiopathic fertilization failure in conventional in vitro fertilization. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 1999;87(1):87–90.
Omland A, Bjercke S, Ertzeid G, Fedorcsak P, Oldereid N, Storeng R, et al. Intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) in unexplained and stage I endometriosis-associated infertility after fertilization failure with in vitro fertilization (IVF). J Assist Reprod Genet. 2006;23(2):351–7.
Taylor TH, Wright G, Jones-Colon S, Mitchell-Leef D, Kort HI, Nagy ZP. Comparison of ICSI and conventional IVF in patients with increased oocyte immaturity. Reprod BioMed Online. 2008;17(1):46–52.
Orief Y, Dafopoulos K, Al-Hassani S. Should ICSI be used in non-male factor infertility? Reprod BioMed Online. 2004;9(3):348–56.
Bhattacharya S, Hamilton MP, Shaaban M, Khalaf Y, Seddler M, Ghobara T, et al. Conventional in-vitro fertilisation versus intracytoplasmic sperm injection for the treatment of non-male-factor infertility: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2001;357(9274):2075–9.
Kim JY, Kim JH, Jee BC, Lee JR, Suh CS, Kim SH. Can intracytoplasmic sperm injection prevent total fertilization failure and enhance embryo quality in patients with non-male factor infertility? Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2014;178:188–91.
van Rumste MME, Evers JLH, Farquhar CM. ICSI versus conventional techniques for oocyte insemination during IVF in patients with non-male factor subfertility: a Cochrane review. Hum Reprod. 2004;19(2):223–7.
Practice Committees of the American Society for Reproductive M, Society for Assisted Reproductive T. Intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) for non-male factor infertility: a committee opinion. Fertil Steril. 2012;98(6):1395–9.
Borini A, Gambardella A, Bonu MA, Dal Prato L, Sciajno R, Bianchi L, et al. Comparison of IVF and ICSI when only few oocytes are available for insemination. Reprod BioMed Online. 2009;19(2):270–5.
Luna M, Bigelow C, Duke M, Ruman J, Sandler B, Grunfeld L, et al. Should ICSI be recommended routinely in patients with four or fewer oocytes retrieved? J Assist Reprod Genet. 2011;28(10):911–5. doi:10.1007/s10815-011-9614-9. LA - English.
Ou YC, Lan KC, Huang FJ, Kung FT, Lan TH, Chang SY. Comparison of in vitro fertilization versus intracytoplasmic sperm injection in extremely low oocyte retrieval cycles. Fertil Steril. 2010;93(1):96–100.
Gozlan I, Dor A, Farber B, Meirow D, Feinstein S, Levron J. Comparing intracytoplasmic sperm injection and in vitro fertilization in patients with single oocyte retrieval. Fertil Steril. 2007;87(3):515–8.
Ferraretti AP, La Marca A, Fauser BCJM, Tarlatzis B, Nargund G, Gianaroli L, et al. ESHRE consensus on the definition of ‘poor response’ to ovarian stimulation for in vitro fertilization: the Bologna criteria. Hum Reprod. 2011;26(7):1616–24.
World Health Organization. Laboratory manual for the examination and processing of human semen. 5th ed. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 2010.
World Health Organization. WHO laboratory manual for the examination of human semen and sperm-cervical mucus interaction. 4th ed. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 1999. 128 p.
Lainas TG, Sfontouris IA, Papanikolaou EG, Zorzovilis JZ, Petsas GK, Lainas GT, et al. Flexible GnRH antagonist versus flare-up GnRH agonist protocol in poor responders treated by IVF: a randomized controlled trial. Hum Reprod. 2008;23(6):1355–8.
Kolibianakis E, Zikopoulos K, Camus M, Tournaye H, Van Steirteghem A, Devroey P. Modified natural cycle for IVF does not offer a realistic chance of parenthood in poor responders with high day 3 FSH levels, as a last resort prior to oocyte donation. Hum Reprod. 2004;19(11):2545–9.
Kedem A, Tsur A, Haas J, Yerushalmi GM, Hourvitz A, Machtinger R, et al. Is the modified natural in vitro fertilization cycle justified in patients with “genuine” poor response to controlled ovarian hyperstimulation? Fertil Steril. 2014;101(6):1624–8.
Busnelli A, Papaleo E, Del Prato D, La Vecchia I, Iachini E, Paffoni A, et al. A retrospective evaluation of prognosis and cost-effectiveness of IVF in poor responders according to the Bologna criteria. Hum Reprod. 2015;30(2):315–22.
Polyzos NP, Blockeel C, Verpoest W, De Vos M, Stoop D, Vloeberghs V, et al. Live birth rates following natural cycle IVF in women with poor ovarian response according to the Bologna criteria. Hum Reprod. 2012;27(12):3481–6.
Polyzos NP, Nwoye M, Corona R, Blockeel C, Stoop D, Haentjens P, et al. Live birth rates in Bologna poor responders treated with ovarian stimulation for IVF/ICSI. Reprod BioMed Online. 2014;28(4):469–74.
Geraedts J, Montag M, Magli MC, Repping S, Handyside A, Staessen C, et al. Polar body array CGH for prediction of the status of the corresponding oocyte. Part I: clinical results. Hum Reprod. 2011;26(11):3173–80.
Gutierrez-Mateo C, Colls P, Sanchez-Garcia J, Escudero T, Prates R, Ketterson K, et al. Validation of microarray comparative genomic hybridization for comprehensive chromosome analysis of embryos. Fertil Steril. 2011;95(3):953–8.
Horcajadas JA, Pellicer A, Simon C. Wide genomic analysis of human endometrial receptivity: new times, new opportunities. Hum Reprod Update. 2007;13(1):77–86.
Yoeli R, Orvieto R, Ashkenazi J, Shelef M, Ben-Rafael Z, Bar-Hava I. Comparison of embryo quality between intracytoplasmic sperm injection and in vitro fertilization in sibling oocytes. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2008;25(1):23–8.
Devroey P, Van Steirteghem A. A review of ten years experience of ICSI. Hum Reprod Update. 2004;10(1):19–28.
Bonduelle M, Liebaers I, Deketelaere V, Derde M-P, Camus M, Devroey P, et al. Neonatal data on a cohort of 2889 infants born after ICSI (1991-1999) and of 2995 infants born after IVF (1983–1999). Hum Reprod. 2002;17(3):671–94.
Bonduelle M, Ponjaert I, Steirteghem AV, Derde MP, Devroey P, Liebaers I. Developmental outcome at 2 years of age for children born after ICSI compared with children born after IVF. Hum Reprod. 2003;18(2):342–50.
Davies MJ, Moore VM, Willson KJ, Van Essen P, Priest K, Scott H, et al. Reproductive technologies and the risk of birth defects. N Engl J Med. 2012;366(19):1803–13.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Dr George Petsas and Dr Ioannis Zorzovilis for clinical work, Mrs K. Anagnostara for embryology work, and Mrs G. Stavropoulou for patient coordination.
Funding/competing interests
The study was self-funded. No external funding was obtained. The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ contributions
IAS conceived the study, performed acquisition, analysis and interpretation of data, writing and revision of the manuscript, and embryology work. EMK and GTL participated in the analysis and interpretation of data, writing and revision of the manuscript. BCT and RN participated in the interpretation of data and revision of the manuscript. TGL had the general supervision of the study, participated in study design, analysis and interpretation of data, writing and revision of the manuscript, and performed clinical work. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Capsule Conventional IVF and ICSI are associated with similar single oocyte retrieved and normal semen parameters.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sfontouris, I.A., Kolibianakis, E.M., Lainas, G.T. et al. Live birth rates using conventional in vitro fertilization compared to intracytoplasmic sperm injection in Bologna poor responders with a single oocyte retrieved. J Assist Reprod Genet 32, 691–697 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-015-0459-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-015-0459-5