Abstract
Purpose
Expression of the Na,K-ATPase α4 isoform is required for sperm motility and fertility and is controlled by the Atp1a4 promoter. Here, we have investigated the specific tissue, cell type and developmental regulation of expression mediated by the Atp1a4 promoter.
Methods
We have inserted the green fluorescent protein (GFP), downstream of the endogenous Atp1a4 promoter, in place of the Na,K-ATPase α4 gene, and used it as a marker for α4 expression in mice (Atp1a4 null(GFP) mice).
Results
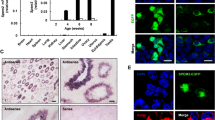
Replacement of α4 by GFP completely disrupted α4 expression and activity, produced sperm morphological and functional abnormalities, and caused infertility of Atp1a4 null(GFP) male mice. Immunoblot analysis of Atp1a4 null(GFP) mouse tissues showed GFP expression in testis. This particular expression pattern was found in adult, but not in mouse embryos or in 7, 18 day old mice. In agreement with expression of GFP, adult Atp1a4 null(GFP) mouse testis displayed the typical fluorescence of GFP. Immunocytochemistry of testis identified GFP in more differentiated male germ cells, but not in spermatogonia, Leydig or Sertoli cells. Further analysis, using immunoblot of fluorescently sorted testis cells with cell specific markers, detected GFP only in spermatocytes, spermatids and spermatozoa. While epididymis showed GFP expression, this was confined to the spermatozoa within the epididymal tubules.
Conclusions
Our results show that the Atp1a4 promoter drives GFP expression exclusively in male germ cells of the testis, where it restricts it to post-meiotic stages of spermatogenesis. These findings highlight the exquisite spatial and temporal control of expression exerted by the Atp1a4 promoter on Na,K-ATPase α4, which is particularly well suited to fulfill the special functions of spermatozoa.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kaplan JH. Biochemistry of Na, K-ATPase. Annu Rev Biochem. 2002;71:511–35.
Martin DW. Structure-function relationships in the NA+, K + −pump. Semin Nephrol. 2005;25(5):282–91.
Blanco G. Na, K-ATPase subunit heterogeneity as a mechanism for tissue-specific ion regulation. Semin Nephrol. 2005;25(5):292–303.
Blanco G, Mercer RW. Isozymes of the Na-K-ATPase: heterogeneity in structure, diversity in function. Am J Physiol. 1998;275(5 Pt 2):F633–50.
Mobasheri A, Avila J, Cozar-Castellano I, Brownleader MD, Trevan M, Francis MJ, Lamb JF, Martin-Vasallo P. Na+, K + −ATPase isozyme diversity; comparative biochemistry and physiological implications of novel functional interactions. Biosci Rep. 2000;20(2):51–91.
Lingrel J, Moseley A, Dostanic I, Cougnon M, He S, James P, Woo A, O'Connor K, Neumann J. Functional roles of the alpha isoforms of the Na, K-ATPase. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2003;986:354–9.
Jewell EA, Shamraj OI, Lingrel JB. Isoforms of the alpha subunit of Na, K-ATPase and their significance. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1992;607:161–9.
Woo AL, James PF, Lingrel JB. Sperm motility is dependent on a unique isoform of the Na, K-ATPase. J Biol Chem. 2000;275(27):20693–9.
Wagoner K, Sanchez G, Nguyen AN, Enders GC, Blanco G. Different expression and activity of the alpha1 and alpha4 isoforms of the Na, K-ATPase during rat male germ cell ontogeny. Reproduction. 2005;130(5):627–41.
Woo AL, James PF, Lingrel JB. Characterization of the fourth alpha isoform of the Na, K-ATPase. J Membr Biol. 1999;169(1):39–44.
Blanco G, Melton RJ, Sanchez G, Mercer RW. Functional characterization of a testes-specific alpha-subunit isoform of the sodium/potassium adenosinetriphosphatase. Biochemistry. 1999;38(41):13661–9.
Jimenez T, Sanchez G, Wertheimer E, Blanco G. Activity of the Na, K-ATPase alpha4 isoform is important for membrane potential, intracellular Ca2+, and pH to maintain motility in rat spermatozoa. Reproduction. 2010;139(5):835–45.
Woo AL, James PF, Lingrel JB. Roles of the Na, K-ATPase alpha4 isoform and the Na+/H + exchanger in sperm motility. Mol Reprod Dev. 2002;62(3):348–56.
Sanchez G, Nguyen AN, Timmerberg B, Tash JS, Blanco G. The Na, K-ATPase alpha4 isoform from humans has distinct enzymatic properties and is important for sperm motility. Mol Hum Reprod. 2006;12(9):565–76.
Jimenez T, McDermott JP, Sanchez G, Blanco G. Na, K-ATPase alpha4 isoform is essential for sperm fertility. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108(2):644–9.
Konrad L, Dietze R, Kirch U, Kirch H, Eva A, Scheiner-Bobis G. Cardiotonic steroids trigger non-classical testosterone signaling in Sertoli cells via the alpha4 isoform of the sodium pump. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011;1813(12):2118–24.
Rodova M, Nguyen AN, Blanco G. The transcription factor CREMtau and cAMP regulate promoter activity of the Na, K-ATPase alpha4 isoform. Mol Reprod Dev. 2006;73(11):1435–47.
Keryanov S, Gardner KL. Physical mapping and characterization of the human Na, K-ATPase isoform, ATP1A4. Gene. 2002;292(1–2):151–66.
Lee EC, Yu D, MartinezdeVelasco J, Tessarollo L, Swing DA, Court DL, Jenkins NA, Copeland NG. A highly efficient Escherichia coli-based chromosome engineering system adapted for recombinogenic targeting and subcloning of BAC DNA. Genomics. 2001;73(1):56–65.
Jimenez T, Sanchez G, McDermott JP, Nguyen AN, Kumar TR, Blanco G. Increased expression of the Na, K-ATPase alpha4 isoform enhances sperm motility in transgenic mice. Biol Reprod. 2011;84(1):153–61.
Blanco G, Sanchez G, Melton RJ, Tourtellotte WG, Mercer RW. The alpha4 isoform of the Na, K-ATPase is expressed in the germ cells of the testes. J Histochem Cytochem. 2000;48(8):1023–32.
Marty MS, Chapin RE, Parks LG, Thorsrud BA. Development and maturation of the male reproductive system. Birth Defects Res B Dev Reprod Toxicol. 2003;68(2):125–36.
Matson CK, Zarkower D. Sex and the singular DM domain: insights into sexual regulation, evolution and plasticity. Nat Rev Genet. 2012;13(3):163–74.
Buaas FW, Kirsh AL, Sharma M, McLean DJ, Morris JL, Griswold MD, de Rooij DG, Braun RE. Plzf is required in adult male germ cells for stem cell self-renewal. Nat Genet. 2004;36(6):647–52.
Fujiwara Y, Komiya T, Kawabata H, Sato M, Fujimoto H, Furusawa M, Noce T. Isolation of a DEAD-family protein gene that encodes a murine homolog of Drosophila vasa and its specific expression in germ cell lineage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994;91(25):12258–62.
Chennathukuzhi V, Morales CR, El-Alfy M, Hecht NB. The kinesin KIF17b and RNA-binding protein TB-RBP transport specific cAMP-responsive element modulator-regulated mRNAs in male germ cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100(26):15566–71.
Shamraj OI, Lingrel JB. A putative fourth Na+, K(+)-ATPase alpha-subunit gene is expressed in testis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994;91(26):12952–6.
Hlivko JT, Chakraborty S, Hlivko TJ, Sengupta A, James PF. The human Na, K-ATPase alpha 4 isoform is a ouabain-sensitive alpha isoform that is expressed in sperm. Mol Reprod Dev. 2006;73(1):101–15.
Underhill DA, Canfield VA, Dahl JP, Gros P, Levenson R. The Na, K-ATPase alpha4 gene (Atp1a4) encodes a ouabain-resistant alpha subunit and is tightly linked to the alpha2 gene (Atp1a2) on mouse chromosome 1. Biochemistry. 1999;38(45):14746–51.
Kosir R, Juvan P, Perse M, Budefeld T, Majdic G, Fink M, Sassone-Corsi P, Rozman D. Novel insights into the downstream pathways and targets controlled by transcription factors CREM in the testis. PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e31798.
Acknowledgements
We thank Renate Lewis and The Transgenic Vectors Core at Washington University in St. Louis for generating the constructs used to engineer the mice used in this study, Leslie Heckert at University of Kansas Medical Center (KUMC) for providing the Dmrt1 antibody and Stan Fernald (KUMC) for his help with the microscopy images presented. Work was supported by NIH grants HD043044 and HD055763.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Capsule
The Na,K-ATPase a4 promoter drives protein expression specifically in testis male germ cells after meiosis.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McDermott, J.P., Sánchez, G., Chennathukuzhi, V. et al. Green fluorescence protein driven by the Na,K-ATPase α4 isoform promoter is expressed only in male germ cells of mouse testis. J Assist Reprod Genet 29, 1313–1325 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-012-9876-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-012-9876-x