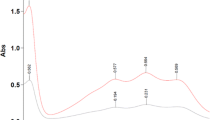
The antioxidant activities of flavonoid mixtures can be used to investigate the synergistic antioxidant mechanism of flavonoids. The antioxidant capacities of three flavonoids (quercetin, baicalein, and daidzein) and β-carotene in binary and ternary mixtures with kaempferol were analyzed using a 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) inhibition assay by means of absorption spectroscopy. The results showed that the number of hydroxyl groups and o-hydroxyl groups had a significant effect on the antioxidant activity of the flavonoids, and the mixture of kaempferol, quercetin, and baicalein showed optimal synergistic antioxidant activity. Compared with quercetin and baicalein, kaempferol had the fastest inhibition rate, and multiple prolonged kinetic processes associated with the scavenging of DPPH radicals occurred in mixtures of kaempferol with the other flavonoids and β-carotene. Kaempferol has a potential synergistic antioxidant effect when mixed with daidzein and β-carotene, and the results suggested that this may be due to the regeneration of kaempferol after antioxidation. By means of classic UV-Vis spectroscopy, reaction details of the synergistic antioxidant process of DPPH radical scavenging by flavonoids can be obtained.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. Galati and P. J. O'Brien, Free Rad. Biol. Med., 37, 287–3 03 (2004).
Q. Wang, Y. T. Wang, S. P. Pu, and Y. T. Zheng, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 324, 605–6 10 (2004).
M. Hidalgo, C. Sanchez-Moreno, and S. de Pascual-Teresa, Food Chem., 121, 691–6 96 (2010).
A. S. Meyer, M. Heinonen, and E. N. Frankel, Food Chem., 61, 71– 75 (1998).
S. S. Pekkarinen, I. M. Heinonen, and A. I. Hopia, J. Sci. Food Agric., 79, 499–5 06 (1999).
H. Matsufuji, R. Sasa, Y. Honma, H. Miyajima, M. Chino, T. Yamazaki, T. Shimamura, H. Ukeda, T. Matsui, K. Matsumoto, and K. Yamagata, J. Jpn. Soc. Food Sci. Technol. — Nippon Shokuhin Kagaku Kogaku Kaishi, 56, 129–1 36 (2009).
M. Fattore, D. Montesano, E. Pagano, R. Teta, F. Borrelli, A. Mangoni, S. Seccia, and S. Albrizio, J. Food Compos. Anal., 53, 61– 68 (2016).
D. Skroza, I. G. Mekinic, S. Svilovic, V. Simat, and V. Katalinic, J. Food Compos. Anal., 38, 13– 18 (2015).
J. P. A. Freitas, F. R. M. Franca, M. S. Silva, R. J. Toms, and G. F. da Silva, Korean J. Chem. Eng., 36, 1298–13 04 (2019).
X. Li, Chemistry Select, 3, 13081–130 86 (2018).
X. Li, X. Ouyang, R. Cai, and D. Chen, Molecules (Basel, Switzerland), 24, 1– 10 (2019).
E. Hvattum, Y. Stenstrom, and D. Ekeberg, J. Mass Spectrom., 39, 1570–15 81 (2004).
D. I. Tsimogiannis and V. Oreopoulou, Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol., 7, 140–1 46 (2006).
N. Aftab and A. Vieira, Phytother. Res., 24, 500–5 02 (2010).
S. S. Wang, D. M. Wang, and Z. H. Liu, Ind. Crop. Prod., 67, 227–2 38 (2015).
G. Mercado-Mercado, L. A. de la Rosa, and E. Alvarez-Parrilla, J. Mol. Struct., 1199, 1 –8 (2020).
R. Liang, C. H. Chen, X. C. Ai, and J. P. Zhang, Chin. J. Mag. Res., 27, 132–1 40 (2010).
C. L. Tian, X. Liu, Y. Chang, R. X. Wang, T. M. Lv, C. C. Cui, and M. C. Liu, S. Afr. J. Bot., 137, 257–2 64 (2021).
Y. J. Hua, X. C. Li, W. H. Zhang, B. Chen, Y. M. Liu, X. J. Zhao, H. Xie, and D. F. Chen, J. Saudi Chem. Soc., 25, 1– 10 (2021).
Q. Zhang, W. B. Yang, J. C. Liu, H. Liu, Z. Z. Lv, C. L. Zhang, D. L. Chen, and Z. G. Jiao, Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev., 1– 12 (2020).
K. L. Khanduja and A. Bhardwaj, Indian J. Biochem. Biophys., 40, 416–4 22 (2003).
K. P. Suja, A. Jayalekshmy, and C. Arumughan, J. Agric. Food Chem., 52, 912–9 15 (2004).
Z. H. Gao, K. X. Huang, X. L. Yang, and H. B. Xu, Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Gen. Subj., 1472, 643–6 50 (1999).
S. S. Qiu, C. C. Jiang, R. J. Zhou, and C. H. Li, Chin. J. Struct. Chem., 39, 57– 65 (2020).
A. G. Veiko, E. A. Lapshina, and I. B. Zavodnik, Mol. Cell. Biochem., 476, 4287–42 99 (2021).
M. K. Johnson and G. Loo, Mutat. Res.-DNA Repair, 459, 211–2 18 (2000).
E. A. Gonzalez and M. A. Nazareno, LWT-Food Sci. Technol., 44, 558–5 64 (2011).
J. Valerga, M. Reta, and M. C. Lanari, LWT-Food Sci. Technol., 45, 28– 35 (2012).
M. Colon and C. Nerin, Eur. Food Res. Technol., 242, 211–2 20 (2016).
D. Tsimogiannis, A. Bimpilas, and V. Oreopoulou, Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol., 119, 1 –9 (2017).
B. J. F. Hudson, Food Antioxidants, Elsevier Applied Science, Lond on (1990).
H. Y. Zhang, Y. M. Sung, and X. L. Wang, Chem.-Eur. J., 9, 502–5 08 (2003).
M. N. Peyrat-Maillard, M. E. Cuvelier, and C. Berset, J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc., 80, 1007–10 12 (2003).
L. Bateman, H. Hughes, and A. L. Morris, Discuss. Faraday Soc., 14, 190–1 99 (1953).
H. J. Wang, R. Liang, L. M. Fu, R. M. Han, J. P. Zhang, and L. H. Skibsted, Food Funct., 5, 1573–15 78 (2014).
T. Zhang, S. Deng, Y. H. Chen, and X. P. Du, Food and Fermentation Industries, 47, 8– 15 (2021).
J. Liang, Y. X. Tian, F. Yang, J. P. Zhang, L. H. Skibsted, Food Chem., 115, 1437–14 42 (2009).
R. M. Han, Y. X. Tian, E. M. Becker, M. L. Andersen, J. P. Zhang, and L. H. Skibsted, J. Agric. Food Chem., 55, 2384–23 91 (2007).
B. Zhou, Z. Chen, Y. Chen, Z. Jia, Y. Jia, L. Zeng, L. Wu, L. Yang, and Z. L. Liu, Appl. Magn. Res., 18, 397–4 06 (2000).
M. T. Schroeder, E. M. Becker, and L. H. Skibsted, J. Agric. Food Chem., 54, 3445–34 53 (2006).
L. Muller, K. Frohlich, and V. Bohm, Food Chem., 129, 139–1 48 (2011).
M. C. Foti, J. Agric. Food Chem., 63, 8765–87 76 (2015).
S. B. Kedare and R. P. Singh, J. Food Sci. Technol., 48, 412–4 22 (2011).
M. C. Foti, C. Daquino, and C. Geraci, J. Org. Chem., 69, 2309–23 14 (2004).
V. Thavasi, R. P. A. Bettens, and L. P. Leong, J. Phys. Chem. A, 113, 3068–30 77 (2009).
K. Sak, Mini-Rev. Med. Chem., 14, 494–5 04 (2014).
L. M. Magalhães, M. A. Segundo, S. Reis, and J. Lima, Anal. Chim. Acta, 558, 310–318 (2006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Abstract of article is published in Zhurnal Prikladnoi Spektroskopii, Vol. 90, No. 4, p. 656, July–August, 2023.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, Y., Guo, YD., Mi, YD. et al. Potential of UV-Vis Spectroscopy for Determining the Mechanism of the Synergistic Antioxidant Process of Kaempferol with Three Other Flavonoids and β-Carotene. J Appl Spectrosc 90, 883–892 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10812-023-01610-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10812-023-01610-x