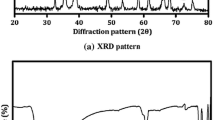
Nowadays zinc nanoparticles (NPs) have attracted many applications in display technology. Due to the dispersion of nanoparticles in liquid crystals (LCs), the display properties are enhanced. The present work focuses on the significant changes in the properties of LC displays with the dispersion of ZnO NPs. Schiff-based LC compounds like p–n-decyloxybenzaldehyde and corresponding p–n-alkoxy anilines (10O.Om, with m = 3, 6) are prepared with the dispersion of ZnO NPs (1 wt.%). The tools used to characterize the nanoparticles in LCs are X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), polarizing optical microscopy (POM), and modified spectrometer. With XRD studies, the size of ZnO NPs is determined. By using SEM and EDS, the homogeneous dispersion and elemental analysis is estimated. With the data of POM, the textural analysis is examined. With DSC, the phase transition temperature of different phases is noted. With the modified spectrometer, the values of refractive indices and birefringence are determined. Furthermore, with these values, the molecular orientational order parameter S is measured by the Kuczynski and Haller extrapolation methods. It is observed that the birefringence and order parameter values are decreased with the dispersion of 1 wt.% ZnO NPs in Schiff-based LC compounds.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. K. Bisoyi and S. Kumar, Chem. Soc. Rev., 40, 306–319 (2011).
G. W. Gray, In: Handbook of Liquid Crystals, Eds. D. Demus, J. Goodby, G. W. Gray, H. W. Spiess, and V. Vill, Vol. 1, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 1–16 (1998).
S. Gauza, C. H. Wen, S. T. Wu, N. Janarthanan, and C. S. Hsu, J. Appl. Phys., 43, 7634–7638 (2004).
S. T. Wu, Q. T. Zhang, and S. Marder, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys., 37, L1254–L1256 (1998).
S. K. Prasad, M. V. Kumar, and C. V. Yelamaggad, Carbon, 59, 512–517 (2013).
J. Branch, R. Thompson, J. W. Taylor, L. Salamanca-Riba, and L. J. Martínez-Miranda, J. Appl. Phys., 115, Article ID 164313 (2014).
L. Marino, S. Marino, D. Wang, E. Bruno, and N. Scaramuzza, Soft Matter, 10, 3842–3849 (2014).
A. Chandran, J. Prakash, K. K. Naik, A. K. Srivastava, R. Dąbrowski, M. Czerwiński, and A. J. Biradar, J. Mater. Chem., C2, 1844–1853 (2014).
P. Goel, M. Arora, and A.M. Biradar, J. Appl. Phys., 115, Article ID 124905 (2014).
L. Wang, W. L. He, X. Xiao, M. Wang, P. Y. Yang, Z. J. Zhou, and H. Yang, H. F. Yu, and Y. F. Lu, Mater. Chem., 22, 19629–19633(2012).
X. W. Zhang, D. Luo, Y. Li, M. Zhao, B. Han, M. T. Zhao, and H. T. Dai, Liq. Cryst., 42, 1257–1263 (2015).
U. Manzoor, M. Islam, L. Tabassam, and S. U. Rahman, Physica E, 41, 1669–1672 (2015).
J. C. Nie, J. Y. Yang, Y. Piao, H. Li, Y. Sun, Q. M. Xue, C. M. Xiong, R. F. Dou, and Q. Y. Tu, Appl. Phys. Lett., 93, Article ID 173104 (2008).
A. V. Kabashin, A. Trudeau, and W. Marine, Appl. Phys. Lett., 91, Article ID 201101 (2007).
S. D. Haranath, A. G. Sahai, and B. K. Joshi Gupta, Nanotech., 20, Article ID 42570 (2009).
X. D. Li, T. P. Chen, P. Liu, Y. Liu, and K. C. Leong, Opt. Express, 21, 14131–14138 (2013).
A. L. Schoenhalz, J. T. Arantes, A. Fazzio, and G. M. Dalpian, J. Phys. Chem. C, 114, 18293–18297 (2010).
P. Khushboo Sharma, P. Malik, and K. K. Raina, Liq. Cryst., 44, 1717–1726 (2017).
K. Pal, S. Thomas, and M. L. N. M. Mohan, J. Nanosci. Nanotech., 17, 2401–2412 (2017).
W. Lee, C.-Y. Wang, and Y.-C. Shih, Appl. Phys. Lett., 85, 513–515 (2004).
W. T. Chen, P. S. Chen, and C. Y. Chao, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys., 48, Article ID 015006 (2009).
N. Kapernaum and F. Giesselmann, Phys. Rev. E, 78, Article ID 062701 (2008).
I. Haller, Prog. Solid State Chem., 10, 103–118 (1975).
H. J. Kim, Y. G. Kang, H. G. Park, K. M. Lee, H. Y. Jung, and D. S. Seo, Liq. Cryst., 38, 871–875 (2011).
G. Pathak, R. Katiyar, K. Agrahari, A. Srivastava, R. Dabrowski, K. Garbat, and R. Manohar, Opto-Electron. Rev., 26, 11–18 (2018).
H. Eskalen Özgan, O. Alver, and S. Kerli, Acta Phys. Polonica A, 127, 756–760 (2015).
L. J. Martínez-Miranda, K. M. Traister, and I. Meléndez-Rodríguez, Appl. Phys. Lett., 97, Article ID 223301 (2010).
P. V. Raja Shekar, D. Madhavi Latha, and V. G. K. M. Pisipati, Opt. Mater., 64, 564–568 (2017).
S.-T. Wu, Phys. Rev. A, 33, No. 2, 1270–1274 (1986).
H. Mada and , S. Kobayashi, Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst., 33, Nos. 1–2, 47–53 (1976).
J. Li and S.-T. Wu, J. Appl. Phys., 96, No. 1, 170–174 (2004).
L. M. Blinov, Electro-Optical and Magneto-Optical Properties of Liquid Crystals, Wiley, New York (1983).
S. T. Wu, J. Appl. Phys., 69, 2080–2087 (1991).
S. T. Wu, C. S. Wu, M. Warenghem, and M. Ismaili, Opt. Eng., 32, 1775–1780 (1993).
E. M. Averyanov, J. Opt. Technol., 64, 417 (1997).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Abstract of article is published in Zhurnal Prikladnoi Spektroskopii, Vol. 90, No. 4, p. 652, July–August, 2023.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jayaprada, P., Manepalli, R.K.N.R., Madhav, B.T.P. et al. Spectral, Optical, and Birefringence Studies of ZnO Dispersed Schiff-Based Liquid Crystal Compounds for Display Device Application. J Appl Spectrosc 90, 847–859 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10812-023-01606-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10812-023-01606-7