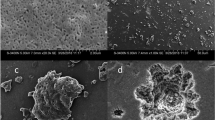
Chelating resins have been widely used in sewage treatment, and the functional mechanism of chelating resins is related to the pH value of the environment, so it is significant to explore the effect of pH on chelating resins. In this work, the laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) was used to analyze how the pH value changes the adsorption state of the chelating resin for Cu2+ and Mn2+ ions. The optimal pH values for the chelating resin adsorption of Cu2+ and Mn2+ through the signal-to-back ratio were obtained and the spectrogram of resin adsorbing heavy metal was compared with the metal mass map to determine the static-specific adsorption saturation capacities of the amino phosphoric acid chelating resin for Cu2+ and Mn2+ at different pH values. Then the calibration curve was compared with the results showing that different pH values would result in different limits of detection (LODs) for water. The higher the static-specific adsorption saturation capacity, the lower the LOD. As for the detection limit of the amino phosphoric acid chelating resin itself, the pH value has no effect on it. This work proved that the influence of the pH value on the adsorption of heavy metals by the chelated resin can be explored by LIBS, while the content of heavy metals in the chelated resin can be obtained by the calibration curve.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Erler, D. Riebe, T. Beitz, et al., Sensors, 20, No. 1, 418 (2020).
O. Gazeli, D. Stefas, and S. Couris, Materials, 14, No. 1, 541 (2021).
M. Akhtar, A. Jabbar, N. Ahmed, et al., Appl. Phys. B, 125, No. 5 (2019).
L. Liu, M. Al-Salihi, R. Yi, et al., Opt. Express, 29, No. 11 (2020).
A. K. Pathak, A. Singh, R. Kumar, et al., Nat. Acad. Sci. Lett., 42, No. 9 (2018).
Z. Hao, Appl. Opt., 58, No. 1, 461–465 (2019).
K. Rifai, L. Özcan, F. R. Doucet, and F. Vidal, Spectrochim. Acta B: At. Spectrosc., 165, No. 9, Article ID 105766 (2020).
Zhi Wang, Yan Wu, et al., Appl. Opt., 58, No. 9, 5615–5620 (2019).
F. M. Fortunato, T. A. Catelani, M. S. Pomares-Alfonso, et al., Analyt. Sci., 35, No. 9 (2018).
C. Zhu, J. Lv, K. Liu, et al., Microchem. J., 168, No. 9, Article ID 106408 (2020)
H. T. Salloom, T. K. Hamad, and A. H. Mohammed, J. Phys. Conf. Ser., 1818, No. 3, Article ID 012178 (2021).
N. Gyftokostas, E. Nanou, D. Stefas, et al., Molecules, 26, No. 5, 1241 (2021).
A. Velásquez-Ferrín, D. V. Babos, C. Marina-Montes, et al., Appl. Spectrosc. Rev., 56, No. 9, 492–512 (2020).
A. A. Carvalho, D. M. Silvestre, F. O. Leme, J. Naozuka, et al., Microchem. J., 144, No. 1, 33–38 (2019).
F. J. Ruizespinar, L. Ripollseguer, M. Hidalgo, et al., Talanta, 191, No. 1, 162–170 (2019).
A. Matsumoto, Y. Shimazu, H. Nakano, et al., Spectrochim. Acta B: At. Spectrosc., 178, No. 2, Article ID 106143 (2021).
X. Liu, Q. Lin, Y. Tian, et al., J. Analyt. At. Spectrom., 35, No. 11 (2020).
A. D. Saleh, M. M. Sirhan, and A. S. Ismail, Energy Rep., 6, No. 2, 243–249 (2020).
L. Ulloa, M. Martinez-Minchero, E. Bringas, et al., Sep. Purif. Technol., 253, No. 8, Article ID 117516 (2020).
M. Martínez-Minchero, L. Ulloa, A. Cobo, et al., Spectrochim. Acta B: At. Spectrosc., 180, No. 3, Article ID 106170 (2021).
H. Tian, L. Jiao, and D. Dong, Sci. Rep., 9, No. 7, 1 (2019).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Abstract of article is published in Zhurnal Prikladnoi Spektroskopii, Vol. 89, No. 6, p. 901, November–December, 2022.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, X., Yang, Y., Lin, J. et al. Effect of pH Value on Chelating Resin Removal of Heavy Metals in Sewage Using Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopic Detection. J Appl Spectrosc 89, 1185–1192 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10812-023-01485-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10812-023-01485-y