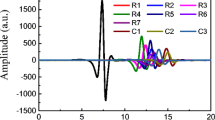
The process of coal mining generates high amounts of coal gangue. Accordingly, coal–gangue separation is a key problem limiting coal production and quality. Terahertz time-domain spectroscopy was combined with multivariate statistical analyses to identify different kinds of coal and gangue. First, the terahertz spectrum and power spectrum of the sample were measured, and the refractive index and absorption coefficient of the sample were calculated from the terahertz time-domain spectrum of the sample. Significant differences in the power spectrum, refractive index, and absorption coefficient were found between different kinds of coal and gangue. After combining multivariate statistical methods — cluster analysis (CA) and principal component analysis (PCA) — a model based on THz parameters and different types of coal and gangue was established. During cluster analysis, the Euclidean distance of two types of samples and the score of the first principal component in the principal component analysis could reflect the similarity and dissimilarity between coal and gangue samples, and consistent results were obtained for CA and PCA. The experimental results showed that the combination of terahertz technology and multivariate statistical methods yielded an accurate approach to distinguishing between coal and gangue.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Y. Ge, Y. Y. Jiang, Z.H. Xu, F. Y. Lian, Y. Zhang, and S. H. Xia, Opt. Express, 22, 12533–12544 (2014).
Y. F. Hua and H. J. Zhang, IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory, 58, 2064–2070 (2010).
C. B. Reid, G. Reese, A. P. Gibson, and V. P. Wallace, IEEE J. Biomed. Health, 17, 774–778 (2013).
Y. B. Ji, C. H. Park, H. Kim, S. H. Kim, G. M. Lee, S. K. Noh, T. I. Jeon, J. H. Son, Y. M. Huh, S. Haam, S. J. Oh, S. K. Lee, and J. S. Suh, Biomed. Opt. Express, 6, 1398–1406 (2015).
A. A. Gowen, C. O’Sullivan, and C. P. O’Donnell, Trends Food Sci. Tech., 25, 40–46 (2012).
H. L. Zhan, J. F. Xi, K. Zhao, R. M. Bao, and L. Z. Xiao, Food Control, 67, 114–118 (2016).
S. Wietzke, C. Jansen, T. Jung, M. Reuter, B. Baudrit, M. Bastian, S. Chatterjee, and M. Koch, Opt. Express, 17, 19006–19014 (2009).
J. Neu and C. A. Schmuttenmaer, J. Appl. Phys., 124, Article ID 231101 (2018).
H. L. Zhan, K. Zhao, and L. Z. Xiao, Energy, 93, 1140–1145 (2015).
M. Mumtaz, M. A. Mahmood, A. Shahzad, S. D. Khan, M. A. Zia, M. Ahmed, and I. Ahmad, J. Infrared, Millim. Te., 41, 1181–1188 (2020).
D. Wang, Y. Zhang, J. Han, X. Li, X. F. Chen, T. Z. Qiu, and H. Chen, Sci. Rep., 11, Article ID 13209 (2021).
T. D. Dorney, R. G. Baraniuk, and D. M. Mittleman, J. Opt. Soc. Am. A, 18, 1562–1571 (2001).
F. Wang, S. Guo, J. F. Zhao, H. Y. Xia, R. M. Bao, H. L. Zhan, and J. N. Wang, Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal., 38, 3638–3644 (2018).
H. L. Zhan, S. X. Wu, R. M. Bao, L. N. Ge, and K. Zhao, Fuel, 143, 189–193 (2015).
H. Park and J. H. Son, Sensors, 21, Article ID 1186 (2021).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Published in Zhurnal Prikladnoi Spektroskopii, Vol. 89, No. 4, pp. 555–561, July–August, 2022.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shao, D., Miao, S., Fan, Q. et al. Classification Method of Coal and Gangue Using Terahertz Time-Domain Spectroscopy, Cluster Analysis and Principal Component Analysis. J Appl Spectrosc 89, 719–725 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10812-022-01416-3
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10812-022-01416-3