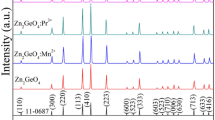
Nitrogen-doped Zn2GeO4 (ZGO:N) phosphors were synthesized using a chemical hydrothermal approach. The influence of nitrogen doping on the structural and optical properties of ZGO phosphors was investigated. Results indicated that N ions substituted for O ions successfully and N doping expanded throughout the unit cell of the crystal host lattice. We observed a slight blue-shift in bandgap energy, which signified the weak quantum confinement of the prepared ZGO nanoparticles. At a 260-nm excitation wavelength, compared with the photoluminescence (PL) spectrum of the ZGO phosphors, the peak position of emission of the N-doped ZGO phosphors blue shifted. In the vibrational modes of ZGO owing to N incorporation, H substituted at the O site, subsequently causing passivation in ZGO:N nanoparticles. The concentration of N ions in ZGO:N played important roles in the evolution of PL intensity and quality of nanocrystals. This result contributed to the optimization of nitrogen-doped phosphors with 5 mol% content. The possible luminescence mechanism of ZGO:N phosphors was also discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. I. Bo, S. Shu-yan, S. U. N. Xiu-juan, P. Jing, W. Bo, and X. Yan, Chem. Res. Chin., 28, 764–767 (2012).
Z. Liu and X. Jing L. Wang, J. Electrochem. Soc., 154, H500 (2007).
Y. Li, K. Ding, B. Cheng, Y. Zhang, and Y. Lu, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 17, 5613–5623 (2015).
N. M. C. H. P. Lan, C. X. Thang, V.-H. Pham, P. T. Kien, V. T. N. Minh, and T. T. H. Tam, Optik (Stuttg.), 199, Article ID 163310 (2019).
J. Sato, H. Kobayashi, K. Ikarashi, N. Saito, and H. Nishiyama, J. Phys. Chem. B, 108, 4369–4375 (2004).
S. Takeshita, J. Honda, T. Isobe, T. Sawayama, and S. Niikura, Cryst. Growth Des., 10, 4494–4500 (2010).
Z. Gu, F. Liu, X. Li, and Z. W. Pan, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 15, 7488–7493 (2013).
Q. Liu, Y. Zhou, J. Kou, X. Chen, Z. Tian, J. Gao, S. Yan, and Z. Zou, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 132, 14385–14387 (2010).
M. Shang, G. Li, D. Yang, X. Kang, C. Peng, and J. Lin, Dalton Trans., 41, 8861–8868 (2012).
Y. Li, A. Zhao, C. Chen, C. Zhang, J. Zhang, and G. Jia, Dyes Pig., 150, 267–274 (2018).
Q. Bai, P. Li, Z. Wang, S. Xu, T. Li, Z. Yang, and Z. Xu, Spectrochim. Acta A: Mol. Biomol. Spectr., 199, 179–188 (2018).
Q. Bai, Z. Wang, P. Li, S. Xu, T. Li, and Z. Yang, RSC Adv., 6, 102183–102192 (2016).
G. Gao and L. Wondraczek, J. Mater. Chem. C, 1, 1952–1958 (2013).
R. Kumari, A. Sahai, and N. Goswami, Progress Nat. Sci. Mater. Int., 25, 300–309 (2015).
M. Cohen, Elements of Diffraction, Addison-Wesley Co. Inc., pp. 459–460 (1956).
N. Goswami and D. K. Sharma, Physica E, 42, 1675–1682 (2010).
O. Yamaguchi, J. Hidaka, and K. Hirota, J. Mater. Sci. Lett., 10, 1471 (1991).
S. Limpijumnong, X. Li, S. H. Wei, and S. Zhang, Physica B, 376, 686–689 (2006).
Z. J. Gu, F. Liu, X. F. Li, and Z. W. Pan, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 15, 7488 (2013).
G. J. Gao and L. Wondraczek, J. Mater. Chem. C Mater. Opt. Electron. Dev., 1, 1952 (2013).
J. I. Pankove, Optical Processes in Semiconductors, New York, Courier Corporation (2012).
A. Boonchun and W. R. Lambrecht, Phys. Status Solidi b, 250, 2091–2101 (2013).
S. Lautenschlaeger, M. Hofmann, S. Eisermann, G. Haas, M. Pinnisch, A. Laufer, and B. Meyer, Phys. Status Solidi b, 248, 1217–1221 (2011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Published in Zhurnal Prikladnoi Spektroskopii, Vol. 89, No. 4, pp. 485–490, July–August, 2022.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lan, N.M.C.H.P., Tuan, D.V., Tuan, T.Q. et al. Effect of Nitrogen Doping on the Structural and Optical Properties of Zn2GeO4 Phosphors. J Appl Spectrosc 89, 652–657 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10812-022-01406-5
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10812-022-01406-5