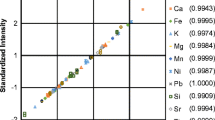
In energy dispersive X-ray fluorescence (EDXRF) analytical studies of samples, the absorption and enhancement of analyte X-rays, collectively called matrix effects, complicate the relation between intensity of analyte X-rays and its concentration. Earlier, the absorption and enhancement relative terms have been derived from the builtup experimental relations of analyte X-ray counts with XRF fundamental parameters and the parameters of the experimental setup for each selective and enhanced X-rays. Now, the terms are implemented on the determined amounts of potassium and calcium nutrients in plants and pot soils from an experiment performed in the lab by growing fenugreek plants on the soils with variable contamination levels and applied fertilizers. The variation pattern of the terms with respective nutrient contents is found to be affected by the basic nature of soils. The pattern shows the high sensitivity of the terms to the plant's behaviour in soil and reflects the picture of supressed benefits of applied fertilizers to the heavy-metals contaminated soils.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
E. P. Bertin, Principles and Practice of X-Ray Spectrometric Analysis, 2nd ed., Plenum Press, New York, London (1975).
R. Jenkins, R. W. Gould, and D. Gedcke, Quantitative X-ray Spectrometry, 2nd ed., Marcel Dekker Inc., New York (1995).
B. Beckhoff, B. Kanngieber, N. Langhoff, R. Wedell, and H. Wolff, Handbook of Practical X-Ray Fluorescence Analysis, Springer-Verlag Berlin, Heidelberg, Germany (2006).
M. Bansal and R. Mittal, DAE-BRNS Symposium on Atomic Molecular and Optical Physics (NCAMP-XVII), IUAC, New Delhi, p. 138 (2009).
M. Bansal and R. Mittal, Asian J. Chem., 21b, 264–270 (2009).
M. Bansal, K. Deep, and R. Mittal, Appl. Radiat. Isot., 70, 2525–2533 (2012).
T. Crommentuijn, M. D. Polder, and E. J. van de Plassche, RIVM Report no. 601501 001, Maximum Permissible Concentrations and Negligible Concentrations for metals, taking background concentrations into account (1997).
H. Shayler, M. McBride, and E. Harrison, Cornell Waste Management Institute 2009, pp. 1–6 (2009).
G. S. Dheri, M. S. Brar, and S. S. Malhi, Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal., 38, 1655–1672 (2007).
S. Singh, M. Zacharias, S. Kalpana, and S. Mishra, J. Environ. Chem. Ecotoxicol., 4, 75–81 (2012).
K. Grodzinvska, Int. J. Environ. Pollut., 9, 83–97 (1978).
R. Kostka-Rick and W. J. Manning, Environ. Pollut., 82, 107–138 (1993).
R. Mittal, K. L. Allawadhi, B. S. Sood, N. Singh, Anita, and P. Kumar, X-ray Spectrom., 22, 413–417 (1993).
I. Cakmak, J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci., 168, 521–530 (2005).
Q. R. Wang, Y. S. Cui, X. M. Liu, Y. T. Dong, and P. Christie, J. Environ. Sci. Health, A, 38, 823–838 (2011).
S. Chen, L. Sun, T. Sun, L. Chao, and G. Guo, Environ. Geochem. Health, 29, 435–446 (2007).
P. K. Hepler, Plant Cell, 17, 2142–2155 (2005).
S. T. Jakobsen, Acta Agric. Scand. B: Soil Plant Sci., 43, 6–10 (2009).
M. N. Cordones, F. Aleman, and V. M. F. Rubio, J. Plant Physiol., 171, 688–695 (2014).
N. Tuteja and S. Mahajan, Plant Signal. Behav., 2, 79–85 (2007).
C. Johansen, D. G. Edwards., and J. F. Loneragan, Plant Physiol., 43, 1717–1721 (1968).
U. R. Malvi and Karnataka, J. Agric. Sci., 24, 106–109 (2011).
Vandana and R. Mittal, Appl. Radiat. Isot., 54, 377–382 (2001).
D. B. Metcalfe, M. Williams, L. E. Aragao, A. C. da Costa, S. S. de Almeida, A. P. Braga, P. H. Goncalves, J. de Athaydes, S. Junior, Y. Malhi, and P. A. Meir, New Phytol., 174, 697–703 (2007).
R. Mittal, K. L. Allawadhi, and B. S. Sood, X-Ray Spectrom., 16, 37–39 (1987).
M. Bansal, Studies of X-ray Fluorescence for Its Analytical Applications, Ph.D. Thesis, Punjabi University, Patiala, India (2008).
S. Gupta, K. Deep, L. Jain, M. A. Ansari, V. K. Mittal, and R. Mittal, Appl. Radiat. Isot., 68, 1922–1927 (2010).
Z. Rengel, In: Heavy Metal Stress in Plants, Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg (1999).
G. U. Chibuike and S. C. Obiora, Appl. Environ. Soil Sci., 1–12 (2014).
D. Cataldo and R. Wildung, Environ. Health Perspect., 27, 149–159 (1978).
A. Siedlecka, Acta Soc. Bot. Pol., 64, 265–272 (1995).
M. Pesarrakli, Handbook of Plant and Crop Stress, 2nd ed., Marcel Decker Inc., New York (1999).
K. L. Sahrawat, J. Indian Soc. Soil Sci., 51, 409–417 (2003).
M. Becker and F. Asch, J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci., 168, 558–573 (2005).
J. D. Bewley and M. Black, Seeds: Physiology of Development and Germination, Springer, US, pp. 1–27 (1985).
R. S. Mehta, B. S. Patel, and S. S. Meena, Indian J. Agric. Sci., 80, 970–974 (2010).
R. E. D. Snowden (nee Cook) and B. D. Wheeler, J. Ecol., 81, 35–46 (1993).
J. B. Wilson, Evolution, 42, 408–413 (1988).
H. Li, X. Yang, and A. C. Luo, J. Plant Nutr., 24, 1849–1860 (2001).
B. K. Parida, I. M. Chhibba, and V. K. Nayyar, Scientia Hort., 98, 113–119 (2003).
L. Kaur, J. Agric. Ecol., 1, 22–34 (2016).
T. Tandano, J. Sci. Soil Manure, 41, 498–501 (1970).
M. Yamauchi, Plant Soil, 117, 275–286 (1989).
B. P. Singh, M. Das, M. Ram, B. S. Dwevedi, and R. N. Prasad, J. Indian Soil Sci., 40, 326–328 (1992).
K. K. Baruah and B. Nath, Indian J. Plant Physiol., 1, 114–118 (1996).
W. F. Lorehwing, Plant Physiol., 3, 261–275 (1928).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Abstract of article is published in Zhurnal Prikladnoi Spektroskopii, Vol. 87, No. 6, p. 1023, November–December, 2020.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rao, P., Mittal, R. Energy Dispersive X-Ray Fluorescence Matrix Analysis for Nutrients in Fenugreek Plant–Soil Setup Influenced by both Fertilization and Soil Texture. J Appl Spectrosc 87, 1185–1195 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10812-021-01128-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10812-021-01128-0