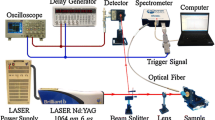
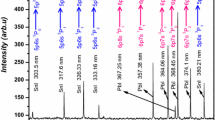
A procedure for matrix effect reduction is proposed to enhance the precision of quantitative analysis of metal alloys using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS). This procedure is based on a number of successive steps in order to correct the signal fluctuations caused by plasma interaction and the matrix effect. The first step is the selection of optimum parameter settings of the detection system, such as laser power, delay time, and focal distance. The second step is the estimation of the absolute or relative values of impurities on the basis of the internal standard calibration. The third step is the analysis of the metal basis of the alloy used as an internal standard, which requires spectrum averaging, whole integral spectrum normalization, and self-absorption correction. Three sets of metal-based alloys (aluminum, steel, and copper) are used in this investigation as reference standards for calibration and validation. Successive improvements of the quality of calibration curves are observed during the proposed procedure.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. A. Cremers and L. J. Radziemski, Handbook of Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy, Copyright, John Wiley & Sons Ltd. (2006).
D. Hahn and Nicollo’ Omenetto, J. Appl. Spectrosc., 64, 335–366A (2010).
D. A. Cremers and R. C. Chinni, Appl. Spectrosc. Rev., 44, 457–506 (2009).
A. P. M. Michel, Spectrochim. Acta, B, 65, 185–191 (2010).
F. Anabitarte, A. Cobo, and J. M. Lopez-Higuera, Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy: Fundamentals, Applications, and Challenges, Int. Scholarly Res. Network, ISRN Spectroscopy (2012); ID 285240; doi: https://doi.org/10.5402/2012/285240.
R. Gaudiuso, M. Dell’Aglio, O. Pascale, G. S. Senesi, and A. D. Giacomo, Sensors, 10, 7434–7468 (2010); doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/s100807434.
K. X. Li, W. D. Zhou, Q. M. Shen, J. Shao, and H. G. Qian, Spectrochim. Acta, B, 65, 420–424 (2010).
A. Koujelev and S. L. Lui, Artifi cial Neural Networks for Material Identifi cation, Mineralogy and Analytical Geochemistry Based on Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy, Canadian Space Agency (2011), ISBN: 978-953-307-220-3, InTech.
B. Salle, D. A. Cremers, S. Maurice, and R. C. Wiens, Spectrochim. Acta, B, 60, 479–490 (2005).
I. Osticioli, N.F.C. Mendes, S. Porcinai, A. Cagnini, and E. Castellucci, Bioanal. Chem., 394, 1033–1041 (2009); doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-009-2653-8.
A. Jurado-López and M. D. Luque de Castro, Talanta, 59, No. 2, 409–415 (2003); doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0039-9140(02)00527-1.
S. Y. Oh, F. Y. Yueh, J. P. Singh, C. C. Herman, and K. Zeigler, Spectrochim. Acta, B, 64, 113–118 (2009).
T. Ctvrtnickova, L. Cabalin, J. Laserna, V. Kanicky, and G. Nicolas, Appl. Surf. Sci., 255, 5329–5333 (2009).
S. Pandhija and A. K. Rai, J. Phys., 70, 553–563 (2008).
V. Lazic, F. Colao, R. Fantoni, V. Spizzichino, and S. Jovicevic, Spectrochim. Acta, B, 62, 30–39 (2007).
J. Hermann, L. Mercadier, E. Mothe, G. Socol, and P. Alloncle, Spectrochim. Acta, B, 65, 636–641 (2010).
B. C. Windom and D.W. Hahn, J. Anal. At. Spectrom., 24, 1665–1675 (2009).
C. Aragon and J. A. Aguilera, Spectrochim. Acta, B, 63, 893–916 (2008).
D. Hahn and Nicollo’ Omenetto, Appl. Spectrosc., 66, 337–419 (2012).
J. A. Aguilera, C. Arago’n, V. Madurga, and J. Manrique, Spectrochim. Acta, B, 64, 993 (2009).
N. B. Zorov, A. A. Gorbatenko, T. A. Labutinand, and A. M. Popov, Spectrochim. Acta, B, 65, 642–657 (2010).
J. Feng, Z. Wang, Z. Li, and W. Ni, Spectrochim. Acta, B, 65, 549–556 (2010).
A. Hrdlicka, L. Zaorálková, M. Galiová, T. Ctvrtnícková, V. Kanický, V. Otruba, K. Novotný, P. Krásenský, J. Kaiser, R. Malina, and K. Páleníková, Spectrochim. Acta, B, 64, 74–78 (2009).
Z. Wang, J. Feng, L. Li, and W. Ni, Z. Li, J. Anal. At. Spectrom. , 26 (11), 2175–2182 (2011).
A. Kadachiand and M. El-Eshaikh, Spectrosc. Lett., 48, 403–410 (2015).
L. Fornarini, F. Colao, R. Fantoni, V. Lazic, and V. Spizzicchino, Spectrochim. Acta, B, 60, 1186–1201 (2005).
Spectrochim. Acta, B, 74-75, 38–45 (2012).
N. B. Zorov, A. A. Gorbatenko, T. A. Labutin, and A. M. Popov, Spectrochim. Acta, B, 65, 642–657 (2010).
David Harvey, Standardizing Analytical Methods; http://www.saylor.org/site/wp-content/uploads/2012/07/Chapter511.pdf.
Ashraf Mohmoud El Sherbini and Abdulaziz Saad Al Aamer, J. Signal Inform. Process, 3, 502–515 (2012).
J. W. Robinson, E. S. Frame, and G. M. Frame, II, Undergraduate Instrumental Analysis, Textbook-1264, 7th ed., CRC Press (2014).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Abstract of article is published in Zhurnal Prikladnoi Spektroskopii, Vol. 84, No. 4, p. 673, July–August, 2017.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Al-Eshaikh, M.A. Procedure for Matrix Effect Reduction in Metal Analysis Using Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy. J Appl Spectrosc 84, 725–730 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10812-017-0536-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10812-017-0536-x