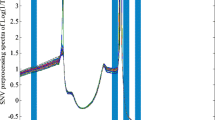
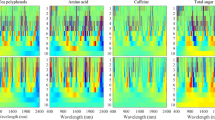
Near infrared spectroscopy and the back propagation artificial neural network model in conjunction with backward interval partial least squares algorithm were used to estimate the purchasing price of Enshi yulu young tea shoots. The near-infrared spectra regions most relevant to the tea shoots price model (5700.5–5935.8, 7613.6–7848.9, 8091.8–8327.1, 8331–8566.2, 9287.5–9522.5, and 9526.6–9761.9 cm–1) were selected using backward interval partial least squares algorithm. The first five principal components that explained 99.96% of the variability in those selected spectral data were then used to calibrate the back propagation artificial neural tea shoots purchasing price model. The performance of this model (coefficient of determination for prediction 0.9724; root-mean-square error of prediction 4.727) was superior to those of the back propagation artificial neural model (coefficient of determination for prediction 0.8653, root-mean-square error of prediction 5.125) and the backward interval partial least squares model (coefficient of determination for prediction 0.5932, root-mean-square error of prediction 25.125). The acquisition price model with the combined backward interval partial least squares–back propagation artificial neural network algorithms can evaluate the price of Enshi yulu tea shoots accurately, quickly and objectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. Bahorun, A. Luximon-Ramma, T. Gunness, D. Sookar, S. Bhoyroo, R. Jugessur, D. Reebye, K. Googoolye, A. Crozier, and O. Aruoma, Toxicology, 278, 68–74 (2010).
X. F. Zhou, Z. L. Yang, S. A. Haughey, P. Galvin-King, L. J. Han, and C. T. Elliott, Food Chem., 189, 13–18 (2015).
X. M. Liu, J. S. Liu, Spectrosc. Lett., 47, 729–739 (2014).
C. F. Wu, Z. G. Wu, R. A. Hashmonay, S. Y. Chang, Y. S. Wu, C. P. Chao, M. J. Chase, and R. H. Kagann, Atm. Environ., 82, 335–342 (2014).
M. A. Tavanaie, N. Esmaeilian, and M. R. M. Mojtahedi, Dyes Pigments, 114, 267–272 (2015).
M. Blanco and A. Peguero, TrAC Trend. Anal. Chem., 29, 1127–1136 (2010).
M. J. Lee, D. Y. Seo, H. E. Lee, W. S. Kim, M. Y. Jeong, and G. J. Choi, Int. J. Pharm., 403, 66–72 (2011).
M. S. Lee, Y. S. Hwang, J. W. Lee, and M. G. Choung, Food Chem., 158, 351–357 (2014).
Y. Huang, G. R. Du, Y. J. Ma, and J. Zhou, Optik, 126, 2030–2034 (2015).
W. He, J. Zhou, H. Cheng, L. Y. Wang, K. Wei, W. F. Wang, and X. H. Li, Spectrochim. Acta, A: Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc., 86, 399–404 (2012).
J. Y. Shi, X. B. Zou, J. W. Zhao, and H. P. Mao, J. Infrared Millim. Waves, 30, 458–452 (2011).
Q. S. Chen, D. L. Zhang, W. X. Pan, H. H. Li, K. Urmila, and J. W. Zhao, Trend. Food Sci. Technol., 43, 63–82 (2015).
D. Ren, F. F. Qu, K. Lv, Z. Zhang, H. L. Xu, and X. Y. Wang, Neurocomputing, 162, 101–111 (2015).
Z. Z. Zhang, S. P. Wang, X. C. Wan, and S. H. Yan, Spectrosc. Eur., 23, 17–21 (2011).
J. Y. Shi, X. B. Zou, H. Mel, K. L. Wang, X. Wang, and H. Chen, Spectrochim. Acta, A: Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc., 94, 271–276 (2012).
D. Wu, Y. P. He, C. Nie, F. Cao, and Y. D. Bao, Anal. Chim. Acta, 659, 229–237 (2010).
A. E. Ghaziri and E. M. Qannari, Chemometr. Intel. Lab. Syst., 148, 95–105 (2015).
Y. L. Yan, B. Chen, and D. Z. Zhu, Near Infrared Spectroscopy Principles, Technologies and Applications, China Light Industry Press, Beijing (2013), pp. 112–114.
Y. D. Liu, X. D. Sun, and A. G. Ouyang, LWT-Food Sci. Technol., 43, 602–607 (2010).
J. Wu, W. Luo, X. K. Wang, Q. Cheng, C. G. Sun, and H. Li, J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal., 80, 186–191 (2013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Abstract of article is published in Zhurnal Prikladnoi Spektroskopii, Vol. 84, No. 4, p. 670, July–August, 2017.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, SP., Gong, ZM., Su, XZ. et al. Estimating the Acquisition Price of Enshi Yulu Young Tea Shoots Using Near-Infrared Spectroscopy by the Back Propagation Artificial Neural Network Model in Conjunction with Backward Interval Partial Least Squares Algorithm. J Appl Spectrosc 84, 704–709 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10812-017-0533-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10812-017-0533-0