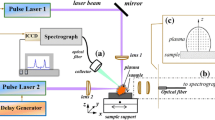
The destruction of concrete is often associated with local chloride corrosion. The ability to determine by laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) the level of chlorine in concrete below that resulting in destructive material changes was demonstrated. The intensity of the analytical line Cl I 837.60 nm increased significantly with the use of double-pulse LIBS. The effects of the interpulse delay and the plasma observation time after the second pulse were studied in order to combine the second harmonics of Q-switched Nd:YAG and Nd:YALO lasers (532 nm + 540 nm). The optimal temporal parameters of double-pulse LIBS determination of chlorine were 4.0 and 0.5 μs, respectively. Under these conditions, the detection limit of chlorine was 50 ppm.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
B. Sallé, P. Mauchien, and S. Maurice, Spectrochim. Acta, Part B, 62, 739–768 (2007).
D. W. Hahn and N. Omenetto, Appl. Spectrosc., 66, 347–419 (2012).
D. A. Cremers and L. J. Radziemski, Handbook of Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy [Russian translation], Tekhnosfera, Moscow (2009), pp. 10–45.
G. Wilsch, F. Weritz, D. Schaurich, and H. Wiggenhauser, Construct. Build. Mater., 19, 724–730 (2005).
M. A. Gondal, Z. H. Yamani, T. Hussain, and O. S. B. Al-Amoudi, Spectrosc. Lett., 42, 171–177 (2009).
F. Weritz, D. Schaurich, and G. Wilsch, Spectrochim. Acta, Part B, 62, 1404–1511 (2007).
C. D. Gehlen, E. Wiens, R. Noll, G. Wilsch, and K. Reichling, Spectrochim. Acta, Part B, 64, 1135–1140 (2009).
M. A. Gondal, A. Dastageer, M. Maslehuddin, A. J. Alnehmi, and O. S. B. Al-Amoudi, J. Environ. Sci. Health, Part A: Toxic/Hazard. Subst. Environ. Eng., 46, 198–203 (2011).
K. Sugiyama, T. Fujii, T. Matsumura, Y. Shiogama, M. Yamaguchi, and K. Nemoto, Appl. Opt., 49, 181–190 (2010).
V. S. Burakov, V. V. Kiris, and S. N. Raikov, Zh. Prikl. Spektrosk., 74, No. 3, 289–295 (2007).
V. I. Babushok, F. C. De Lucia, Jr., J. L. Gottfried, C. A. Munson, and A. W. Miziolek, Spectrochim. Acta, Part B, 61, 999–1014 (2006).
NIST Atomic Spectra Database; http://www.nist.gov/pml/data/asd.cfm.
N. B. Zorov, A. A. Gorbatenko, T. A. Labutin, and A. M. Popov, Spectrochim. Acta, Part B, 65, 642–657 (2010).
F. Weritz, D. Schaurich, A. Taffe, and G. Wilsch, Anal. Bioanal. Chem., 385, 248–255 (2006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Zhurnal Prikladnoi Spektroskopii, Vol. 80, No. 3, pp. 325–329, May–June, 2013.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Labutin, T.A., Popov, A.M., Raikov, S.N. et al. Determination of chlorine in concrete by laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy in air. J Appl Spectrosc 80, 315–318 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10812-013-9766-8
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10812-013-9766-8