Abstract
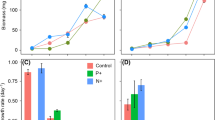
Raphidiopsis raciborskii is the dominant species in several subtropical aquatic ecosystems. This study addressed the influence of nutrient concentration on cyanobacteria growth and saxitoxin synthesis. Therefore, we performed bioassays of interaction between the Chlorophyceae Monoraphidium contortum and R. raciborskii simulating oligotrophic and supereutrophic environments. Experiments were carried out in a climatized room for 15 days in pure cultures of each species (control) and mixed (interaction). The biomass growth (biovolume) and specific growth rates were measured. Saxitoxin was analyzed using the ELISA biochemical method. In the oligotrophic environment, the cell volume of R. raciborskii decreased. This species also showed senescence in interaction with M. contortum. However, there were no statistical differences in the saxitoxin synthesis in both conditions. In the supereutrophic environment, the growth of R. raciborskii and saxitoxin production was similar in both the control and interaction conditions. However, M. contortum growth decreased in interaction with the cyanobacteria. The increase in trophic status from oligo- to supereutrophic contributes to the growth of M. contortum in subtropical aquatic ecosystems, but the decrease in the area/volume ratio of cyanobacteria and the saxitoxin synthesis is an evident survival strategy in oligotrophic environments.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguilera A, Gomez EB, Kastovsky J, Echenique RO, Salerno GL (2018) The polyphasic analysis of two native Raphidiopsis isolates supports the unification of the genera Raphidiopsis and Cylindrospermopsis (Nostocales, Cyanobacteria). Phycologia 57:130–146
Amaral V, Bonilla S, Aubriot L (2014) Growth optimization of the invasive cyanobacterium Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii in response to phosphate fluctuations. Eur J Phycol 49:134–141
American Public Health Association (APHA) (2005) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 19th edn. Byrd Prepess Spingfield, Washington
Andersen RA, Kawachi M (2005) Traditional microalgae isolation techniques. In: Andersen RA (ed) Algal Culturing Techniques. Elsevier Academic Press, San Diego, pp 83–100
Antunes JT, Leão PN, Vasconcelos VM (2015) Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii: review of the distribution, phylogeography, and ecophysiology of a global invasive species. Front Microbiol 6:1–13
Beghelli FGS, Frascareli D, Pompêo MLM, Moschini-Carlos V (2016) Trophic state evolution over 15 years in a tropical reservoir with low nitrogen concentrations and cyanobacteria predominance. Water Air Soil Pollut 227:95
Berry JP, Lind O (2010) First evidence of “paralytic shellfish toxins” and cylindrospermopsin in a Mexican freshwater system, Lago Catemaco, and apparent bioaccumulation of the toxins in “tegogolo” snails (Pomacea patula catemacensis). Toxicon 55:930–938
Bestion E, García-Carreras B, Schaum CE, Pawar S, Yvon-Dorucher G (2018) Metabolic traits predict the effects of warming in phytoplankton competition. Ecol Lett 21:655–664
Bittencourt-Oliveira MC, Piccin-Santos V, Moura AN, Aragão-Tavares NKC, Cordeiro-Araújo MK (2014) Cyanobacteria, microcystins and cylindrospermopsin in public drinking supply reservoirs of Brazil. Ann Acad Brasil Ciênc 86:297–309
Bonilla S, Aubriot L, Soares MCS, González-Piana M, Fabre A, Huszar VLM, Lürling M, Antoniades D, Padisák J, Kruk C (2012) What drives the distribution of the bloom-forming cyanobacteria Planktothrix agardhii and Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii? FEMS Microbiol Ecol 79:594–607
Bouvy M, Falcão D, Marinho M, Pagano M, Moura A (2000) Occurrence of Cylindrospermopsis (Cyanobacteria) in 39 Brazilian tropical reservoirs during the 1998 drought. Aquat Microb Ecol 23:13–27
Briand JF, Robillot C, Quiblier-Llobéras C, Humbert JF, Couté A, Bernard C (2002) Environmental context of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Cyanobacteria) blooms in a shallow pond in France. Water Res 36:3183–3192
Burford MA, Johnson SA, Cook AJ, Packer TV, Taylor BM, Townsley ER (2007) Correlations between watershed and reservoir characteristics and algal blooms in subtropical reservoirs. Water Res 41:4105–4114
Burford MA, Davis TW, Orr PT, Sinha R, Willis A, Neilan BA (2014) Nutrient-related changes in the toxicity of field blooms of the cyanobacterium, Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 89:135–148
Burford MA, Beardall J, Willis A, Orr PT, Magalhaes VF, Rangel LM, Azevedo SMFOE, Neilan BA (2016) Understanding the winning strategies used by the bloom-forming cyanobacterium Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii. Harmful Algae 54:44–53
Callegari-Jacques SM (2003) Bioestatística – Princípios e Aplicações, 1st edn. Artmed, Porto Alegre
Carlson RE (1977) A trophic state index for lakes. Limnol Oceanogr 22:361–380
Carmichael WW (1994) An overview of toxic cyanobacterial research in the United States. In: Proc. Of Toxic Cyanobacteria – A Global Perspective. Adelaide, South Australia Centre for Water Quality Research
Casali SP, Dos Santos ACA, Falco PB, Calijuri MC (2017) Influence of environmental variables on saxitoxin yields by Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii in a mesotrophic subtropical reservoir. J Water Health 15:509–518
Chellappa NT, Borba JM, Rocha O (2008) Phytoplankton community and physical-chemical characteristics of water in the public reservoir of Cruzeta, RN, Brazil. Braz J Biol 68:477–494
Cirés S, Ballot A (2016) A review of the phylogeny, ecology and toxin production of bloom-forming Aphanizomenon spp. and related species within the Nostocales (cyanobacteria). Harmful Algae 54:21–43
Cunha DGF, Bottino F, Calijuri MC (2012) Can free-floating and emerged macrophytes influence the density and diversity of phytoplankton in subtropical reservoirs? Lake Reserv Manag 28:255–264
Cunha DGF, Calijuri MC, Lamparelli MC (2013) A trophic state index for tropical/subtropical reservoirs (TSItsr). Ecol Eng 60:126–134
Dodds WK, Bouska WW, Eitzmann JL, Pilger TJ, Pitts KL, Riley AJ, Schloesser JT, Thornbrugh DJ (2009) Eutrophication of U.S. freshwaters: analysis of potential economic damages. Environ Sci Technol 43:12–19
Glober CJ, Burkholder JM, Davis TW, Harke MJ, Johengen T, Stow CA, Van de Waal DB (2016) The dual role of nitrogen supply in controlling the growth and toxicity of cyanobacterial blooms. Harmful Algae 54:87–97
Gorham PR, McLachlan J, Hammer UT (1964) Isolation and culture of toxic strains of Anabaena flos-aquae (Lyngb.) de Bréb. Verh Internat Verein Limnol 15:796–804
Harke MJ, Steffen MM, Glober CJ, Otten TG, Wilhelm SW, Wood SA, Paerl HW (2016) A review of the global ecology, genomics, and biogeography of the toxic cyanobacterium, Microcystis spp. Harmful Algae 54:04–20
Hillebrand H, Dürselen CD, Kirschtel D (1999) Biovolume calculations for pelagic and benthic microalgae. J Phycol 35:403–424
Holland A, Kinnear S (2013) Interpreting the possible ecological role(s) of cyanotoxins: compounds for competitive advantage and/or physiological aide? Mar Drugs 11:2239–2258
Hoshaw RW, Rosowski JR (1973) Isolation and purification – methods for microscopic algae. In: Stein JR (ed) Handbook of phycological methods: culture methods and growth measurements. Cambridge University, Cambridge, pp 53–67
Hyenstrand P, Burkert U, Pettersson A, Blomqvist P (2000) Competition between the green alga Scenedesmus and the cyanobacterium Synechococcus under different modes of inorganic nitrogen supply. Hydrobiologia 435:91–98
INMET - Brazilian Institute of Meteorology. 2009. Data on climatic variables: air temperature, rainfall and Wind. [cited 7 Dec 2018]. Available from http://www.inmet.gov.br
INMET - Brazilian Institute of Meteorology. 2010. Data on climatic variables: air temperature, rainfall and wind. [cited 7 Dec 2018]. Available from: http://www.inmet.gov.br
Kearns KD, Hunter MD (2000) Green algal extracellular products regulate antialgal toxin production in a cyanobacterium. Environ Microbiol 2:291–297
Kim HS, Hwang SJ, Shin JK, An KG, Yoon CG (2007) Effects of limiting nutrients and N:P ratios on the phytoplankton growth in a shallow hypertrophic reservoir. Hydrobiologia 581:255–267
Lamparelli MC (2004) Grau de trofia em corpos d’água do estado de São Paulo: Avaliação dos métodos de monitoramento. Dissertation, Instituto de Biociências da Universidade de São Paulo
Lee GF, Jones-Lee A (1998) Determination of nutrient limiting maximum algal biomass in waterbodies. Report of G. Fred Lee & Associates, El Macero, CA. http://www.gfredlee.com/Nutrients/nut_limit.pdf Accessed 30 August 2017
Nuch EA (1980) Comparison of different methods for chlorophyll and phaeopigment. Arch Hydrobiol Beih Ergebn Limnol 14:14–36
O’Neil JM, Davis TW, Burford MA, Gobler CJ (2012) The rise of harmful cyanobacteria blooms: the potential roles of eutrophication and climate change. Harmful Algae 14:313–334
Orr PT, Willis A, Burford MA (2018) Application of first order rate kinetics to explain changes in bloom toxicity—the importance of understanding cell toxin quotas. J Oceanol Limnol 36:1063–1074
Padisák J (1997) Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Woloszynska) Seenayya et Subba Raju, an expanding, highly adaptative cyanobacterium: worldwide distribution and review of its ecology. Arch Hydrobiol 107:563–593
Padisák J, Crossetti LO, Naselli-Flores L (2009) Use and misuse in the application of the phytoplankton functional classification: a critical review with updates. Hydrobiologia 621:1–19
Piccini C, Aubriot L, Fabre A, Amaral V, Piana MG, Giani A, Figueredo CC, Vidal L, Kruk C, Bonilla S (2011) Genetic and eco-physiological differences of South American Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii isolates support the hypothesis of multiple ecotypes. Harmful Algae 10:644–653
Reynolds CS (1988) Functional morphology and the adaptive strategies of freshwater phytoplankton. In: Sandgren CD (ed) Growth and reproductive strategies of freshwater phytoplankton. Cambridge University Press, New York, pp 388–433
Reynolds CS (2006) The ecology of phytoplankton: ecology, biodiversity, and conservation. Cambridge University Press, New York
Rocha O, Duncan A (1985) The relationship between cell carbon and cell volume in freshwater algal species used in zooplanktonic studies. J Plankton Res 7:279–294
Rodrigo MA, Rojo C, Segura M, Larrosa J (2009) Mechanisms of microalgae selection during the assembly of a planktonic community. Aquat Ecol 43:61–72
Smith VH (1983) Low nitrogen to phosphorus ratios favor dominance by blue-green algae in lake phytoplankton. Science 221:669–671
Stal LJ, Albertano P, Bergman B, Bröckel K, Gallon JR, Hayes PK, Sivonen K, Walsby AE (2003) BASIC: Baltic Sea cyanobacteria. An investigation of the structure and dynamics of water blooms of cyanobacteria in the Baltic Sea—responses to a changing environment. Cont Shelf Res 23:1695–1714
Stein JR (2003) Handbook of phycological methods: culture methods and growth measurements. Cambridge University Press, New York
Törökne A, Asztalos M, Bánkiné M, Bickel H, Borbély G, Carmeli S, Codd GA, Fastner J, Huang Q, Humpage A, Metcalf JS, Rábai E, Sukenik A, Surányi G, Vasas G, Weiszfeiler V (2004) Interlaboratory comparison trial on cylindrospermopsin measurement. Anal Biochem 332:280–284
Wetzel RG (1993) Limnologia. Editora Fundação Calouste Gulbenkian, Lisboa
Wu Z, Shi J, Li R (2009) Comparative studies on photosynthesis and phosphate metabolism of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii with Microcystis aeruginosa and Aphanizomenon flos-aquae. Harmful Algae 8:910–915
Yilmaz M, Phlips EJ, Szabo NJ, Badylak S (2008) A comparative study of Florida strains of Cylindrospermopsis and Aphanizomenon for cylindrospermopsin production. Toxicon 51:130–139
Zhou Q, Zhang Y, Lin D, Shan K, Luo Y, Zhao L, Tan Z, Song L (2016) The relationships of meteorological factors and nutrient levels with phytoplankton biomass in a shallow eutrophic lake dominated by cyanobacteria, Lake Dianchi from 1991 to 2013. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:15616–15626
Zhu W, Wan L, Zhao L (2010) Effect of nutrient level on phytoplankton community structure in different water bodies. J Environ Sci 22:32–39
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the thematic project team from Escola de Engenharia de São Carlos da Universidade de São Paulo (EESC-USP), Universidade Federal de São Carlos-Campus Sorocaba (UFSCar Sorocaba), Universidade Federal do ABC (UFABC), and Universidade Paulista Campus Sorocaba (Unesp Sorocaba).
Funding
We would like to thank the Conselho de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES) and Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (FAPESP) (process 2008/55636-9) for the financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vargas, S.R., dos Santos, P.V., Bottino, F. et al. Effect of nutrient concentration on growth and saxitoxin production of Raphidiopsis raciborskii (Cyanophyta) interacting with Monoraphidium contortum (Chlorophyceae). J Appl Phycol 32, 421–430 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-019-01972-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-019-01972-w